
You’re using an Ubuntu-based system and you just can’t seem to connect to your network? You’d be surprised how many problems a simple restart can fix.
In this article, I’ll go over multiple ways to restart the network in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions, so you can use whatever suits your needs.
The methods are basically divided into two parts:
- Restart Network in Command Line
- Restart Network via GUI
Restart the network in Ubuntu via the command line
If you are using the Ubuntu server edition, you are already in the terminal. If you are using the desktop edition, you can access the terminal using Ctrl+Alt+T keyboard shortcut in Ubuntu.
1. Restarting the Network Manager Service
This is the easiest way to restart your network using the command line. It’s equivalent to the graphical way of doing it (restarts the Network-Manager service).
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.serviceThe network icon should disappear for a moment and then reappear.
2. nmcli
This is yet another tool for handling networks on a Linux machine. It is a pretty powerful tool that I find very practical. Many sysadmins prefer it since it is easy to use. This tool is a part of the NetworkManager package.
There are two steps to this method: turning the network off and then turning it back on.
sudo nmcli networking offThe network will shut down and the icon will disappear. To turn it back on:
sudo nmcli networking onYou can check out the man page of nmcli for more options.
3. nmtui
This is another method often used by system administrators. It is a text menu (in a Terminal User Interface) for managing networks right in your terminal. It is also a part of the Network Manager tool.
nmtuiThis should open up the following menu:
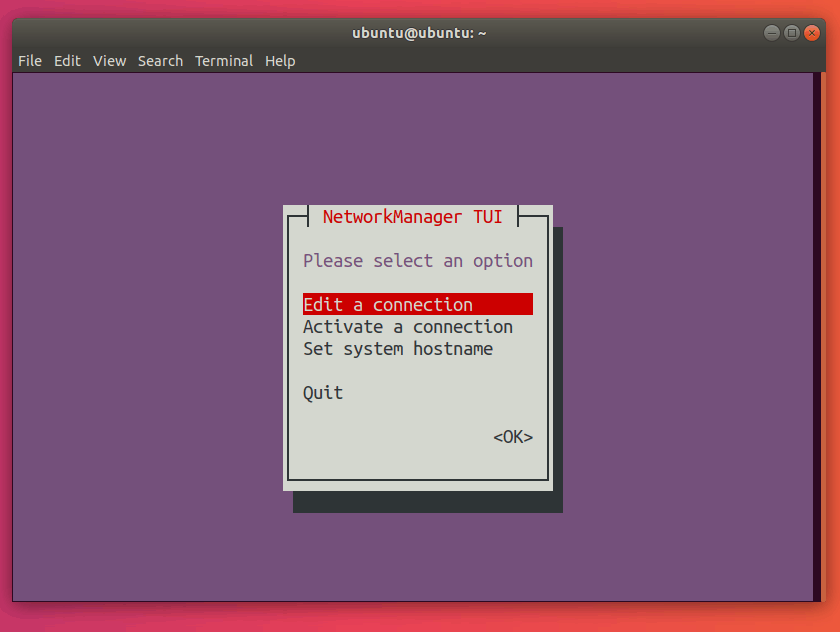
Note that in nmtui, you can select another option by using the up and down arrow keys.
Select Activate a connection:
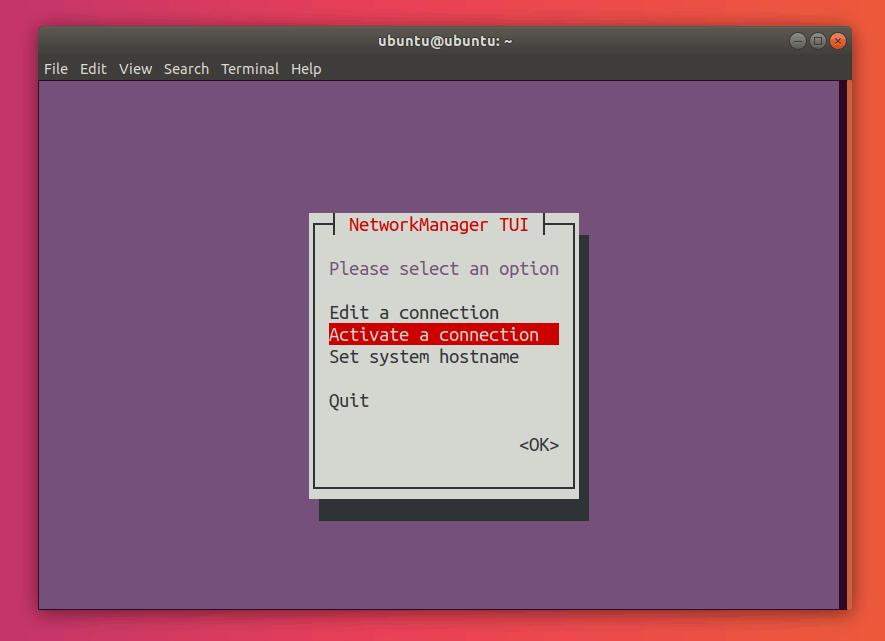
Press Enter. This should now open the connections menu.
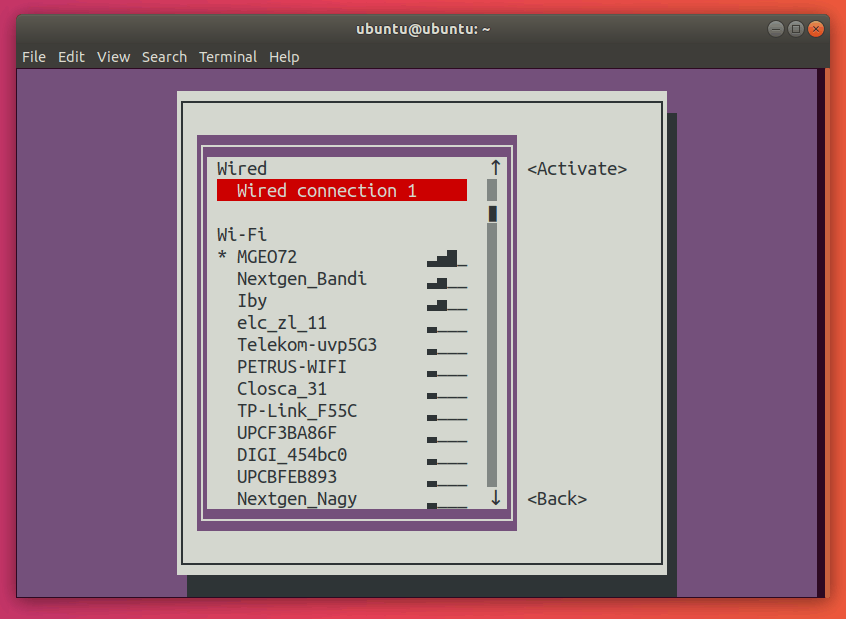
Here, go ahead and select the network with a star (*) next to it. In my case, it’s MGEO72.
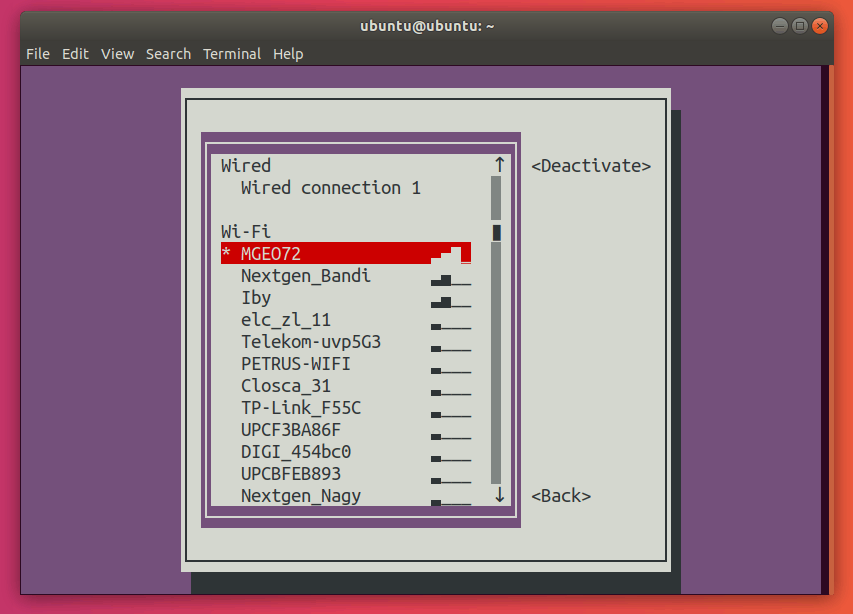
Press Enter. This should deactivate your connection.
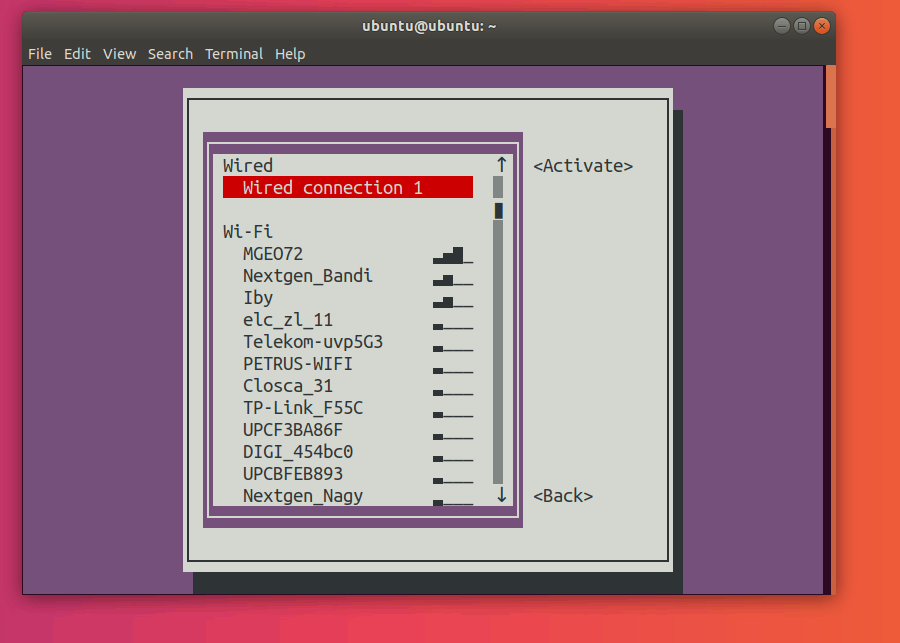
Select the connection you want to activate and press Enter. This should activate the desired connection.
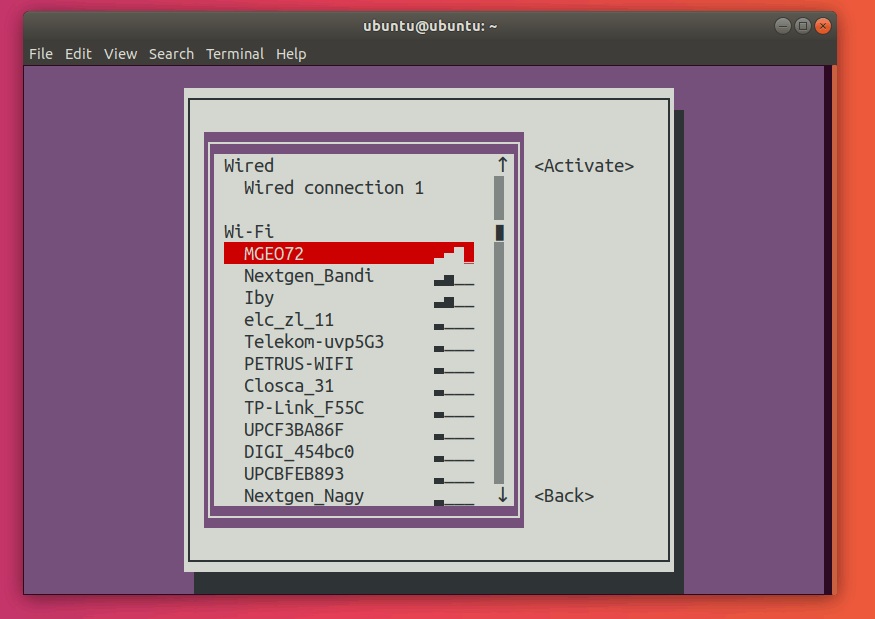
Press Tab twice to select the <Back> button, and exit from the main menu. This is how you can restart a connection with nmtui.
4. ifup & ifdown
These commands handle a network interface directly, changing its state to one in which it either can or can not transmit and receive data. It’s one of the must-know networking commands in Linux.
To shut down all network interfaces, use ifdown and then use ifup to turn all network interfaces back on.
A good practice would be to combine both of these commands:
sudo ifdown -a && sudo ifup -aThat’s it! You have successfully restarted your network.
Restart the network in Ubuntu graphically
This is, of course, the easiest way of restarting the network for Ubuntu desktop users. If this one doesn’t work, you can of course check the command line options mentioned in the previous section.
NM-applet is the system tray applet indicator for NetworkManager. That’s what we’re going to use to restart our network.
First of all, check out your top panel. You should find a network icon in your system tray (in my case, it is a Wi-Fi icon, since that’s what I use).
Go ahead and click on that icon (or the sound or battery icon). This will open up the menu. Select “Turn Off” here.
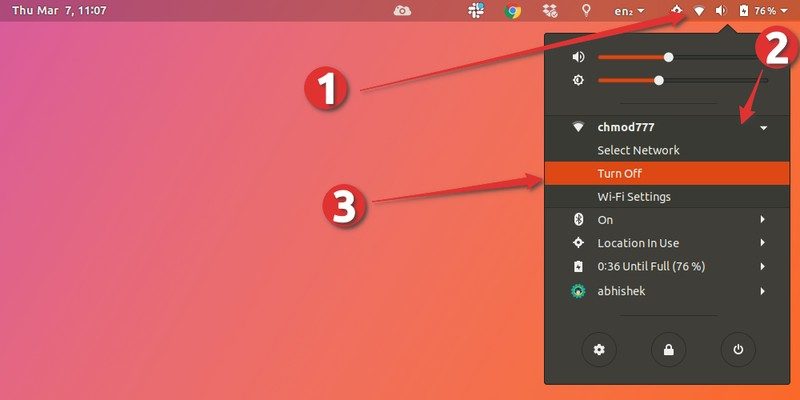
The network icon should now disappear from the top panel. This means the network has been successfully turned off.
Click again on your systray to reopen the menu. Select “Turn On”.
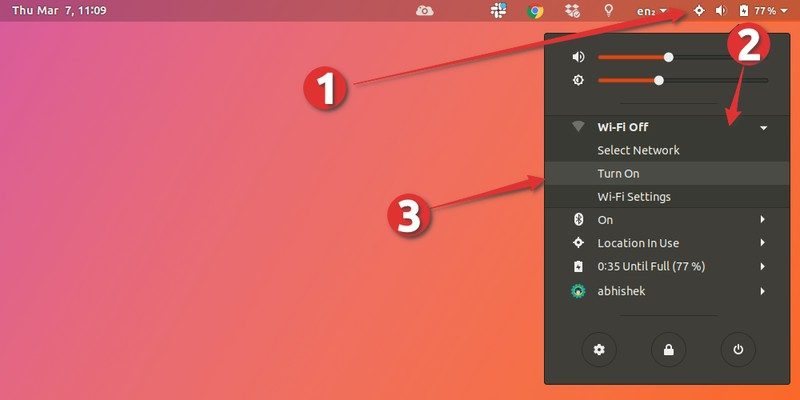
Congratulations! You have now restarted your network.
Bonus Tip: Refresh the available network list
Suppose you are connected to a network already but you want to connect to another network. How do you refresh the WiFi to see what other networks are available? Let me show you that.
Ubuntu doesn’t have a ‘refresh wifi networks’ option directly. It’s sort of hidden.
You’ll have to open the setting menu again and this time, click on “Select Network”.
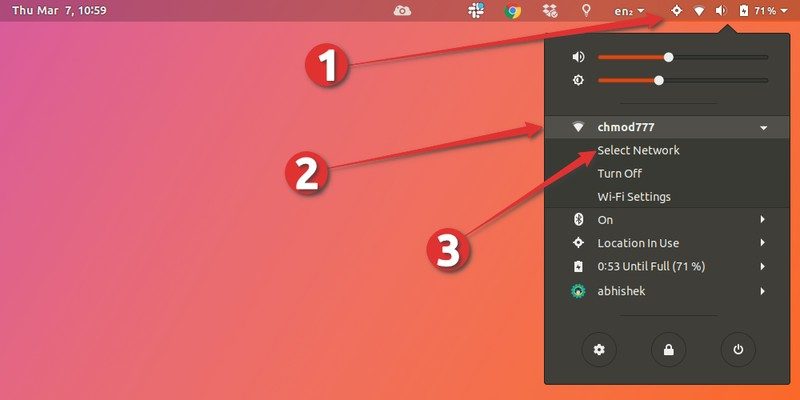
Now, you won’t see the list of available wireless networks immediately. When you open the networks list, it takes around 5 seconds to refresh and show up other available wireless networks.
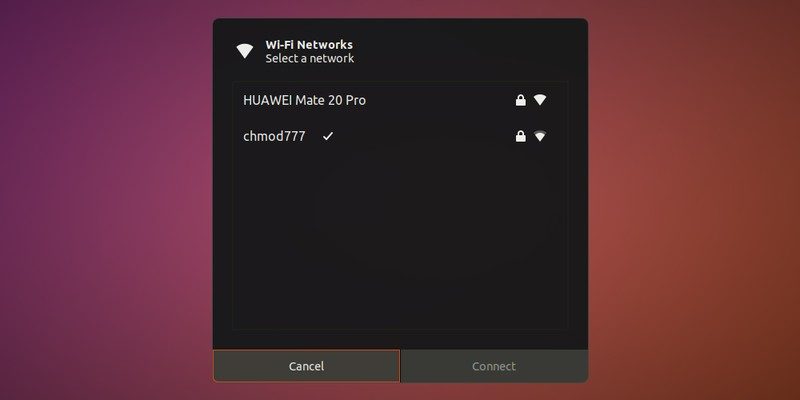
And here, you can select the network of your choice and click "Connect". That’s it.
Wrapping Up
Restarting your network or connection is something that every Linux user has to go through at some point in their experience. These tools can come in handy for doing the same.
But, if you're stranded with not finding any wireless interface to connect with (no Wi-fi hardware detected), you can refer to this article.
You can also check out some of the most important networking commands in Linux:

We hope that we have helped you with plenty of methods for handling such issues!
What do you use to restart/handle your network? Is there something we missed? Leave us a comment below.


