
Got an application in .deb file format and wondering how to install it in Ubuntu?
You can think of .deb files as .exe files in Windows. You double-click on the .exe file and it starts the installation procedure in Windows. Deb packages are pretty much the same.
You can find these deb packages in the download section of a software provider’s website. For example, to install Google Chrome on Ubuntu, you download the Chrome deb package from its website, double-click on it and it is installed.
That's one way of doing things. There are other ways, too.
In this tutorial, I'll share how to install .deb files in Ubuntu and how to remove the applications installed this way.
Installing .deb files on Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux Distributions
You can choose a GUI or command-line tool for installing a deb package. The choice is yours. Let’s go on and see how to install deb files.
Method 1: Use the default Software Center
The simplest method is to use the default software center in Ubuntu. Here's how you achieve that.
Step 1:
Go to the folder where you have downloaded the Deb file. It is usually the Downloads folder.
Right click on the deb file and select Open With...
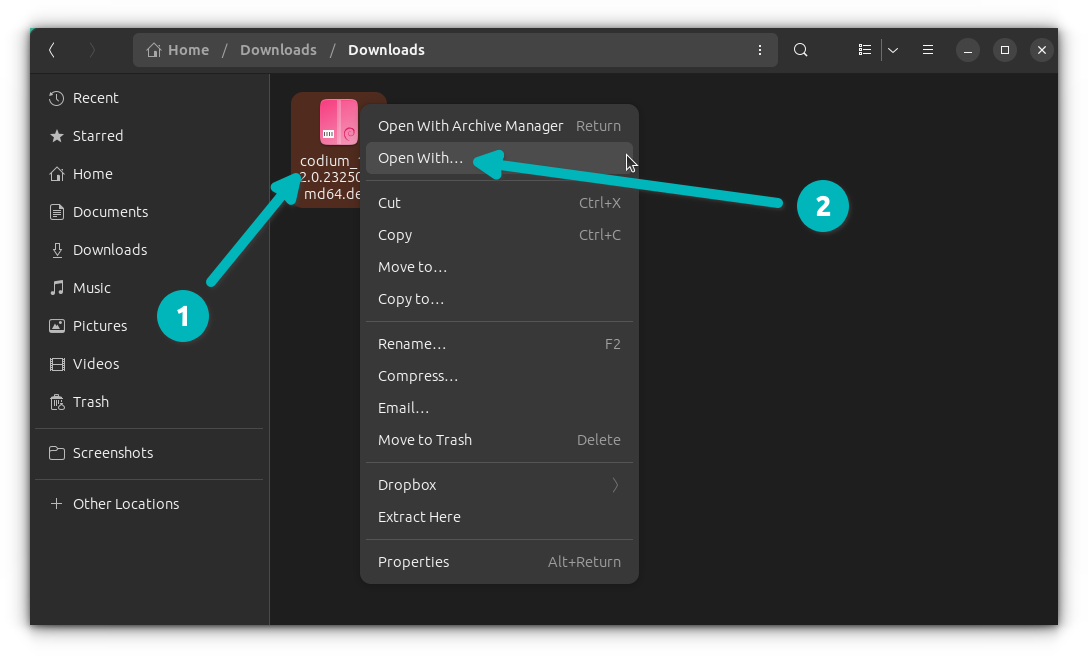
Step 2
In the window that pops up now, Select 'Software Install', check the 'Always use for this file type' option at the bottom and then click the 'Open' button.
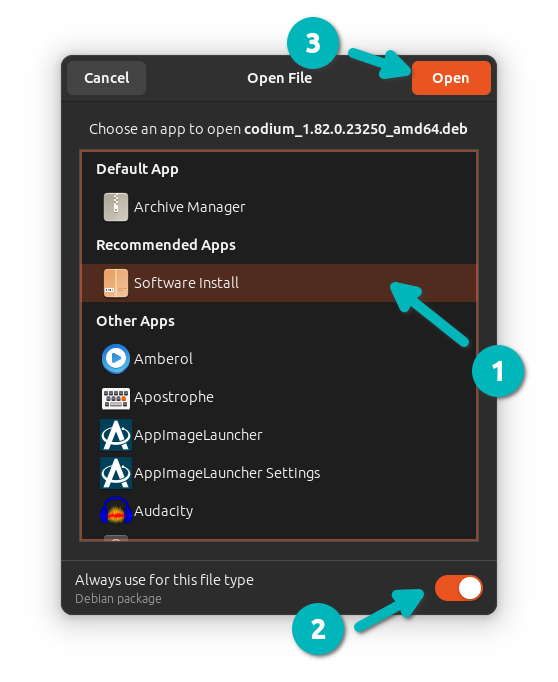
Step 3
It will open the software center, where you should see the option to install the software. All you have to do is hit the install button.
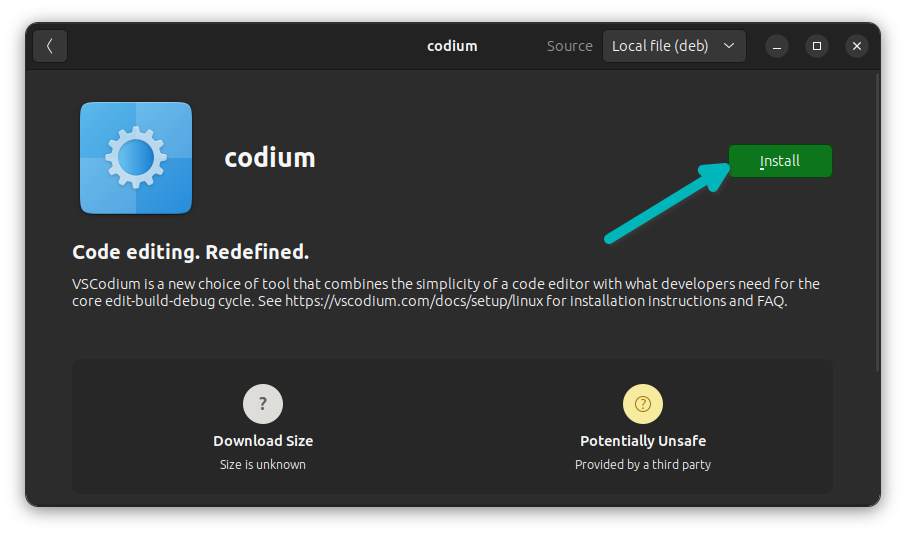
It will ask for your account password. It's the same password you used to login to the system.
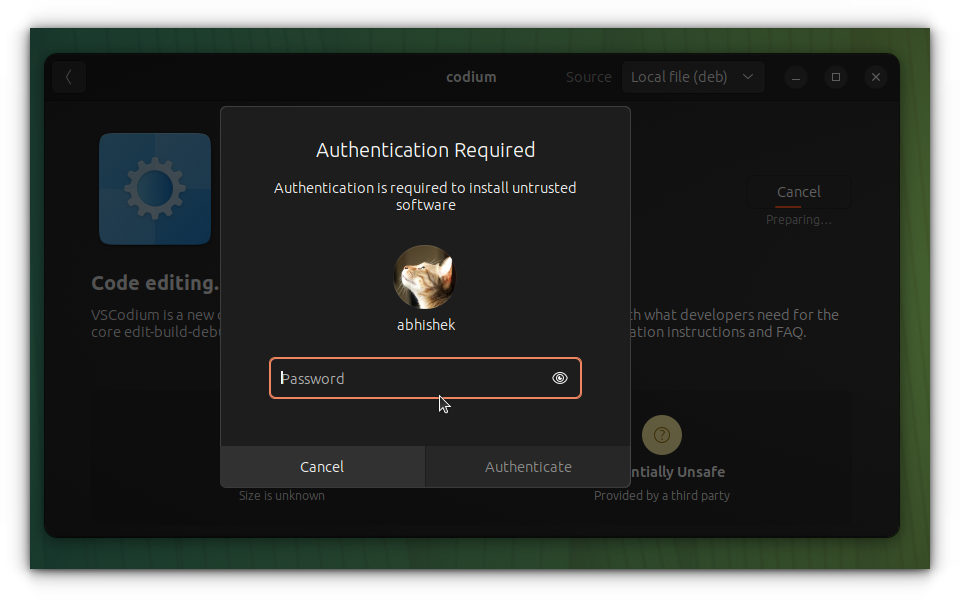
Once you enter the password, you'll see that the deb package is now being installed.
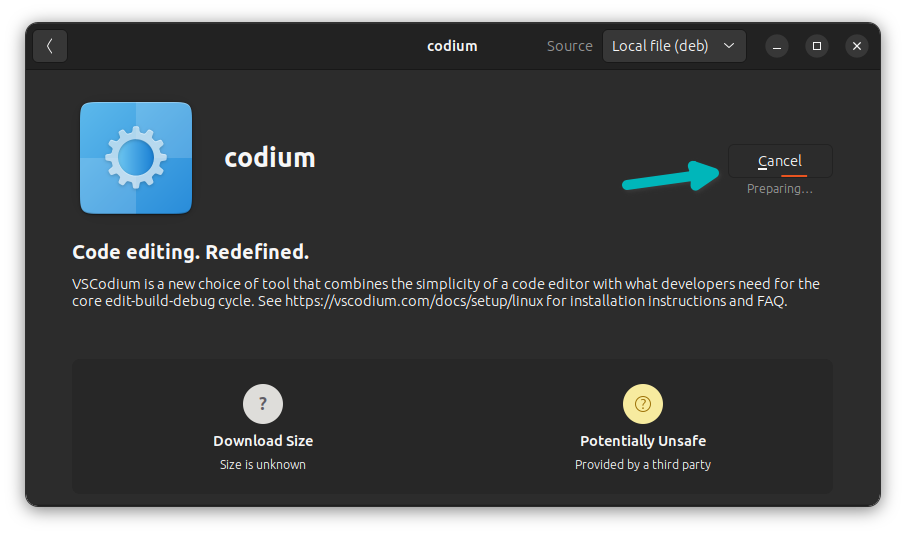
A few seconds later, the software would have been installed as it starts showing the uninstall option now.
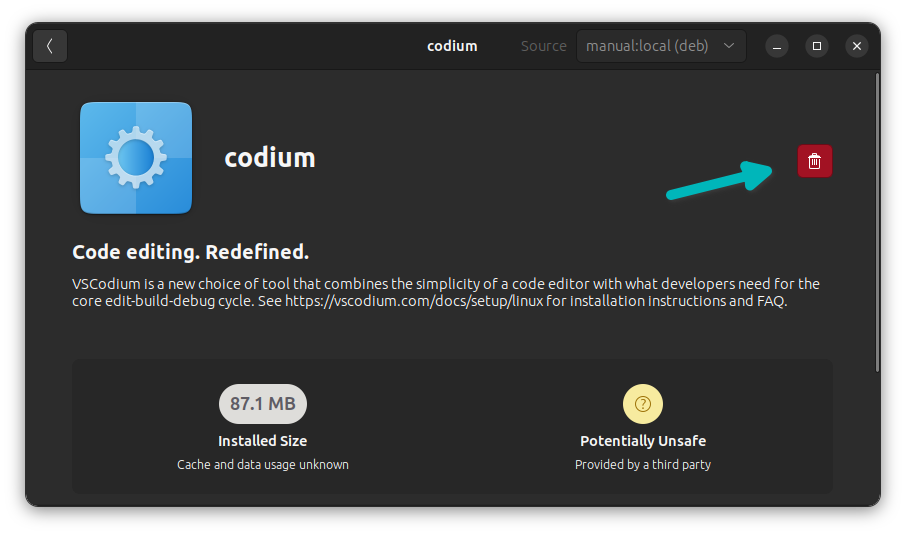
Congratulations! You have successfully installed an application from the Deb file. That was not too hard, right?
Method 2: Use GDebi for installing deb packages
There is a legacy but lightweight tool Gdebi that allows you to install the deb files in Debian-based distributions. It is also slightly better equipped to handle dependency issues.
You can install GDebi deb package installer from the software center or using the command below:
sudo apt install gdebiYou can use it in a similar fashion that you saw with Software Center.
Right-click on the deb file and select the 'Open with GDebi Package Installer' option.
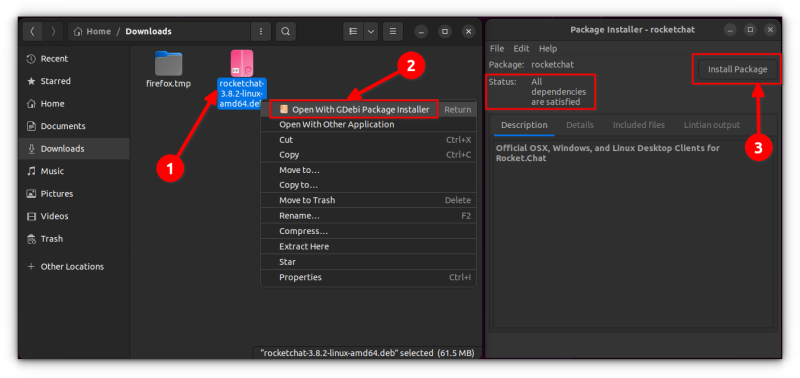
It is a lightweight application, so the installation seems quicker. You can read in detail about using gDebi and making it the default for installing DEB packages.

Method 3: Install .deb files in the command line
If you want to install deb packages in the command line, you can use either the apt command or the dpkg command. The apt command uses the dpkg command underneath it, but apt is more popular and easier to use.
If you want to use the apt command for deb files, use it like this:
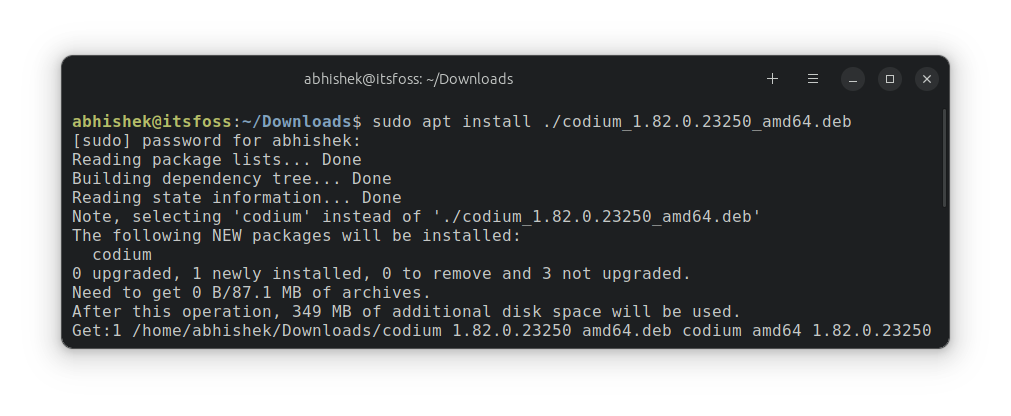
sudo apt install path_to_deb_fileIf you are in the same directory where the deb file is located, use it like this:
sudo apt install ./deb_fileFor example, for the , deb file I had downloaded, here's how the command line installation looks like:
Alternatively, you can use the dpkg command for installing deb packages, here’s how to do it:
sudo dpkg -i path_to_deb_fileIn both commands, you should replace path_to_deb_file with the path and name of the deb file you’ve downloaded.
How to remove deb packages
Removing a deb package isn’t a big deal, either. And no, you don’t need the original deb file you used to install the program.
All you need is the name of the program you’ve installed and then you can use the apt remove command with it.
sudo apt remove program_nameHow do you find the exact program name you need to use in the remove command? The apt command has a solution for that as well.
You can find the list of all installed files with the apt command, but manually going through this will be a pain. So you can use the grep command to search for your package.
For example, I installed the RocketChat application in the previous section but if I want to find out the exact program name, I can use something like this:
sudo apt list --installed | grep chatThis will give me all the packages that have ‘chat’ in their name, and I can get the exact program name from there.
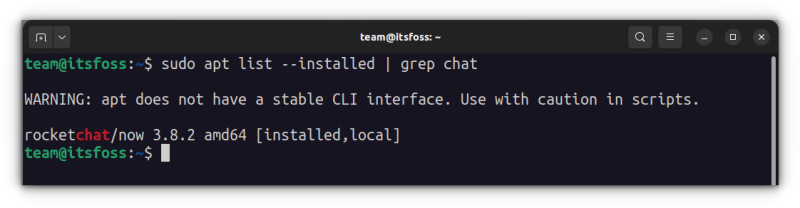
As you can see, a program called ‘rocketchat’ is installed. Now you can use this program name with the apt remove command.

What about updating the applications installed from deb files?
That depends on how the deb file was packaged.
Some deb packages (like Chrome) add theslves to the sources.list so that they can provide newer versions of software through system updates.
But for most other software, you’ll have to remove the existing program and install the newer version.
For example, when you install Discord on Ubuntu from the deb file, every time there is a new version available, you download the new deb file, remove the existing one and install the new deb file.
More ways of installing software in Ubuntu
Deb packages are just one of the several ways of installing new applications in Ubuntu. Here's a detailed guide for Ubuntu desktop users.

Like Deb, there are AppImage packages, too. Unlike Deb, they are not installed on the system.

Fedora's Flatpak packaging system cannot be ignored as well.

I hope this beginner’s guide helped you install deb packages on Ubuntu. I added the removal part so that you can have better control over your installed programs.


