Windows users often look for CCleaner alternatives for Linux. CCleaner is a popular Windows application that lets you easily free up space by removing unnecessary files and completely uninstalling software.
Stacer is a new application for Ubuntu that functions similar to CCleaner, i.e., to optimize your system.
The entire app is written in C++. This ensures that the applications perform fast and helps you optimize the system without getting in your way.
Stacer: System Optimizer for Linux
The features of Stacer can be broken down into five sections:
1. Dashboard: For a quick glance at your system resources
The dashboard shows various information about your system (like Memory, CPU etc.) and a visual overview of resource usage, similar to what you see in Ubuntu task manager.
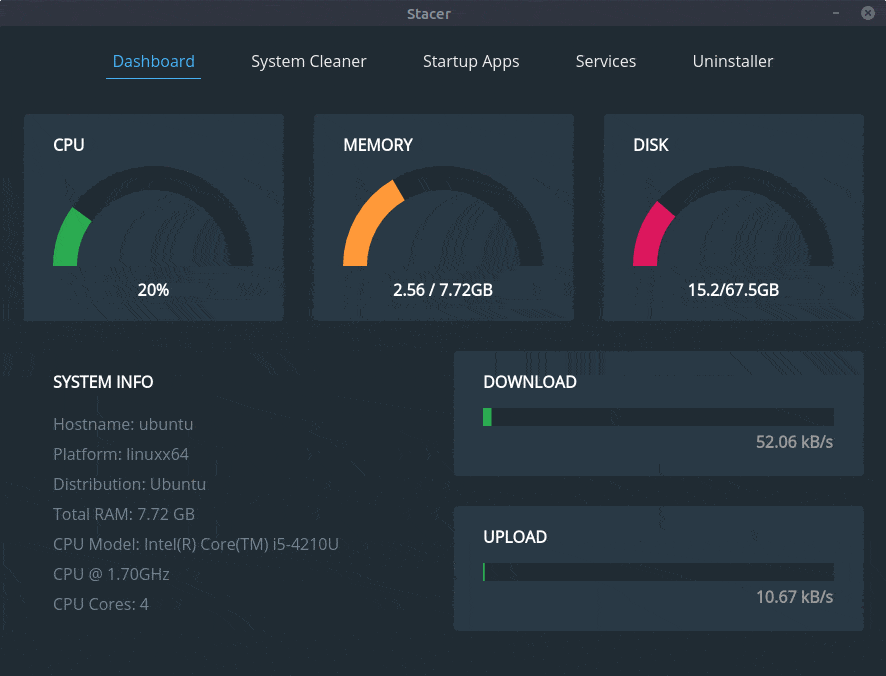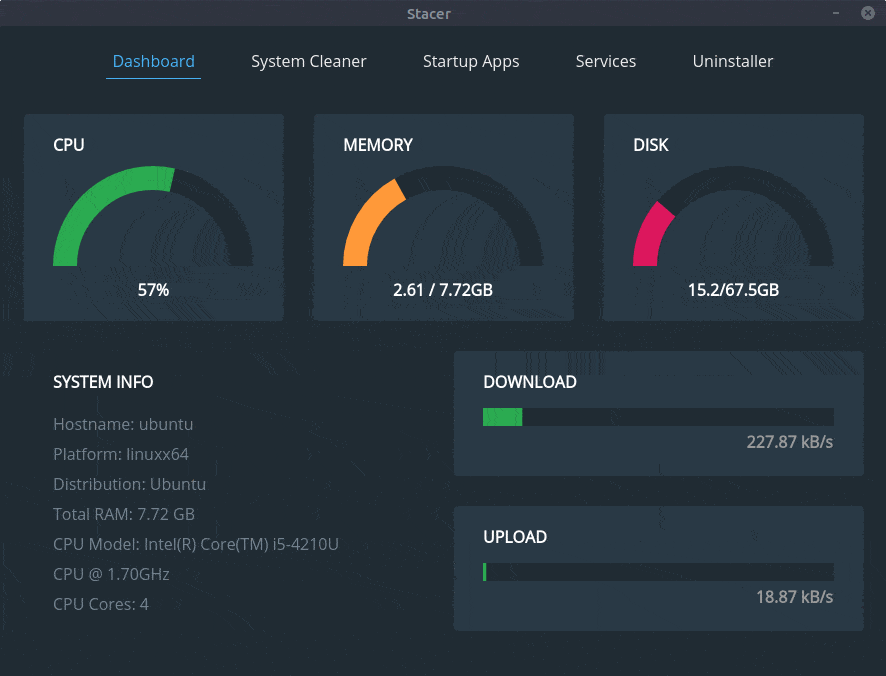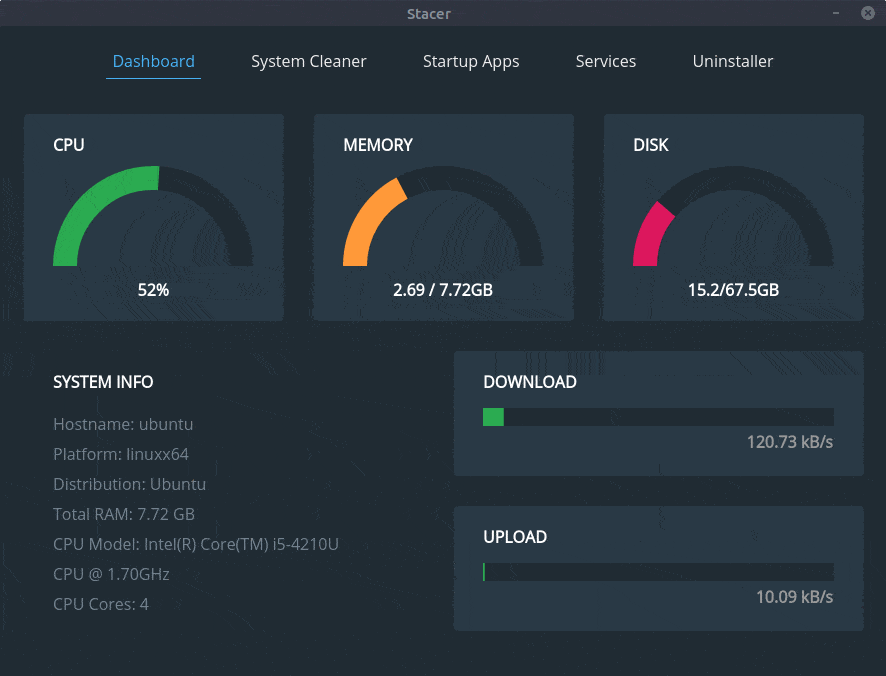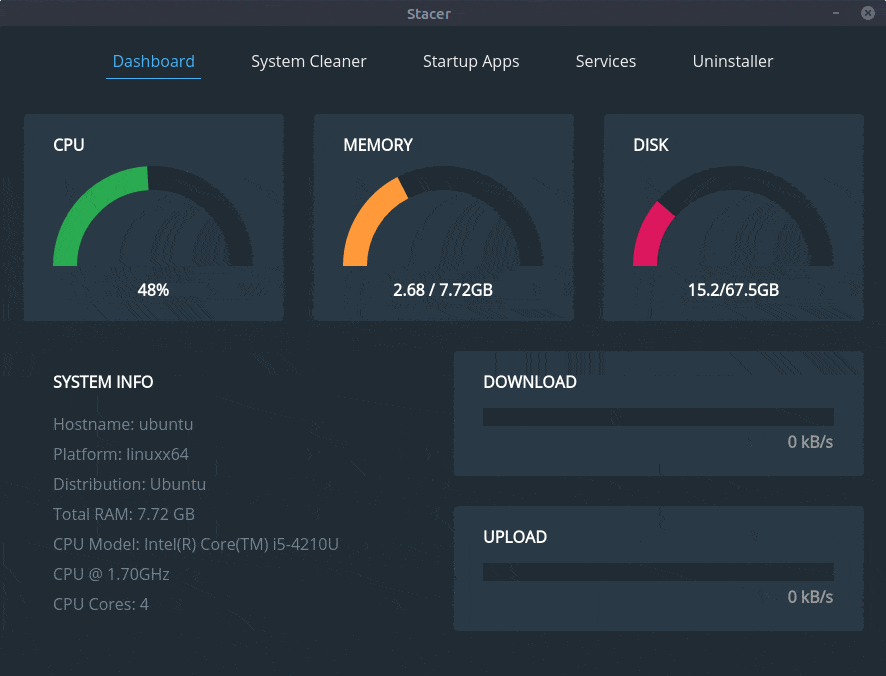
2. System Cleaner: To free up space
The system Cleaner section gives you the option to search for and clean potentially unnecessary files of four types:
- Apt Cache: If you read our guide to apt-get commands, you already know that every time you install packages with the
aptcommand, the downloaded package files are cached. This is helpful for reinstalling the same version of those packages without downloading them again. But you may want to remove them to free up disk space. - Crash Reports: Whenever any application crashes, a crash report is automatically generated to be sent to the developer of that application for debugging purposes. You can remove those reports from here.
- System Logs: This contains log files from various processes and the system.
- App Cache: Applications stores cache files for performance improvements. You can remove cache files for various applications from here.
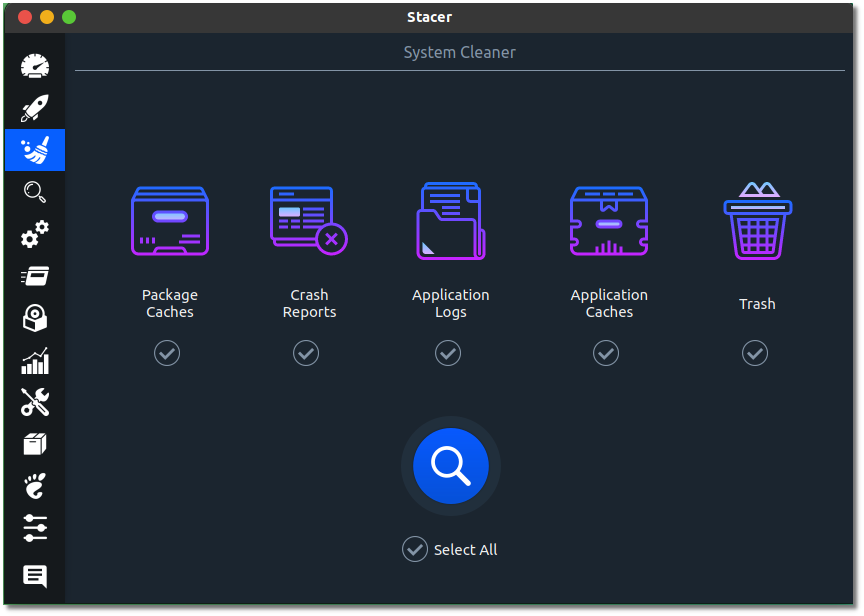
Be careful while removing the App Caches though. You might encounter performance penalties and unwanted behaviors, for example — clearing Web Browsers cache will cause you to sign-out from all signed-in websites etc.
3. Startup Apps: To manage startup applications
Startup Applications have a performance impact on system startup time. The more applications load during system startup, the more time it will take the system to be ready for use.
This is why effectively managing startup applications in Ubuntu is one of the many ways to make Ubuntu faster.
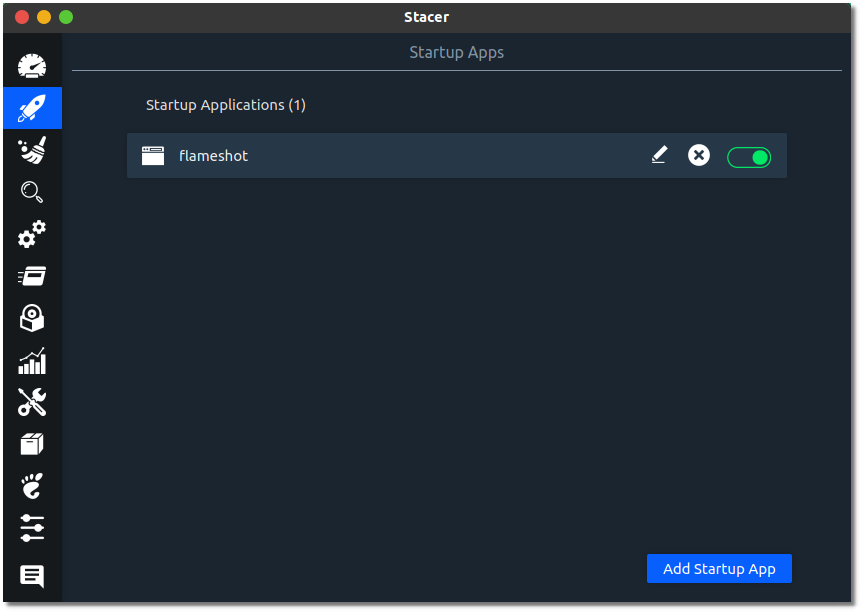
The startup Apps section lets you decide which applications you want to keep here and delete other entries.
4. Services: Manage services
The Services section lets you search for available system services in your system. You can toggle them to enable or disable them from here. Disabling services will help free up memory.
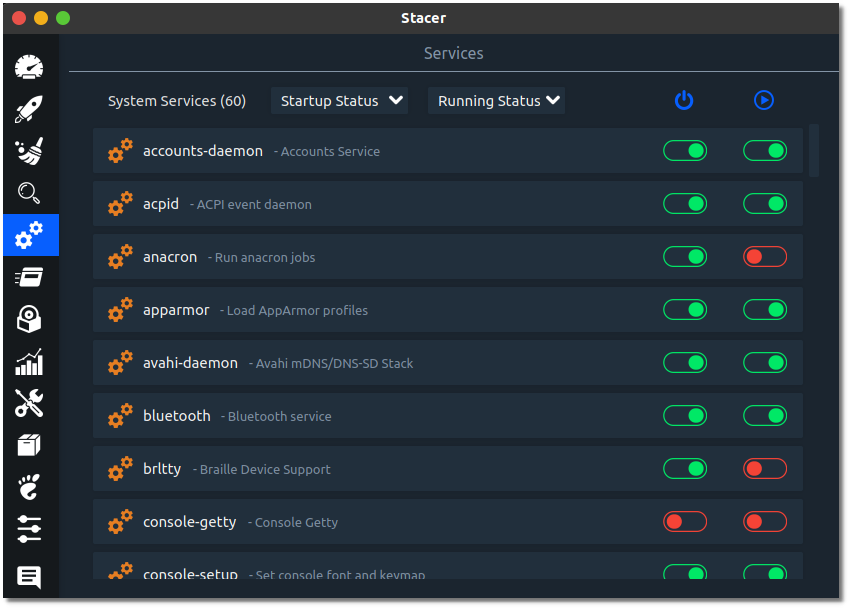
But, be careful about which services you disable, as it might be a critical service that is needed for the system.
5. Processes: Find and Manage processes
The Processes section lists all the processes currently running on the system.
This is similar to system monitoring tools like top where users can find PID of processes, CPU usage, memory usage, etc., of various processes.

You can end processes that you find unnecessary or unresponsive. Use this feature with care, because ending some processes may affect the working of your system.
6. Uninstaller: Find and remove software
The Uninstaller section lists every package installed on your Ubuntu system. You can search for any package you want and uninstall it.
I would also suggest reading our complete guide to installing and removing software in Ubuntu.
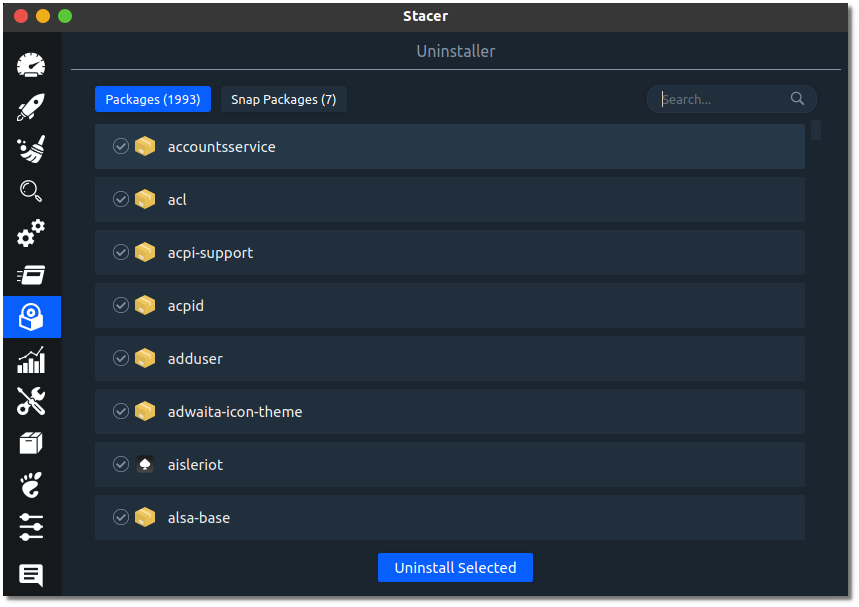
Again, be careful about this section too. You might end up uninstalling packages that are necessary for the system to operate properly.
How to Install Stacer in Ubuntu
You can install Stacer using AppImage or using the DEB package. Head to its GitHub releases section to download the packages available.
Is Stacer worth using?
For new Ubuntu users, Stacer is of course very helpful because it gathers various system optimization features under a single application. So, new users can get things done without digging too deep. Give it a try!
What do you think about Stacer? Will you give it a try? Have you tried it already?

