
There are hundreds of Linux distributions available.
But most of them fall into these three categories: Debian, Red Hat (Fedora) and Arch Linux.
Using a distribution based on Debian/Ubuntu, Red Hat/SUSE or Arch Linux has its advantages. They are popular and hence their package manager offers a huge range of software.
However, some users prefer to use Linux distributions built from scratch and be independent of DEB/RPM packaging system.
In this article, we will list some of the best Linux distributions developed independently.
Note: Obviously, this list excludes popular options like Debian, Ubuntu, and Fedora, which are used as bases for creating new distros. Moreover, the distributions are in no particular order of ranking.
1. NixOS
Initially released in 2003, Nix OS is built on top of the Nix Package Manager. It provides two releases every year, usually scheduled in May and November.
NixOS may not be a distribution directly geared to new and average users. However, its unique approach to package management attracts various kinds of users.
Additionally, 32-bit support systems are also supported.
Other Features:
- Builds packages isolated
- Reliable upgrade with rollback feature
- Reproducible system configuration

2. Gentoo Linux
Gentoo Linux is an independently developed distribution aimed mainly at system experts. It is built for users who want the freedom to customize, fine-tune and optimize the operating system to suit their requirements.
Gentoo uses Portage package management that lets you create and install packages, often allowing you to optimize them for your hardware. Chromium OS, the open-source version of Chrome OS, uses Gentoo at its core.
Not to forget, Gentoo is one of those distributions that still support 32-bit architectures.
Other Features:
- Incremental Updates
- Source-based approach to software management
- Concept of overlay repositories like GURU (Gentoo’s user repository), where users can add packages not yet provided by Gentoo
3. Void Linux
Void Linux is a rolling release distribution with its own X Binary Package System (XBPS) for installing and removing software. It was created by Juan Romero Pardines, a former NetBSD developer.
It avoids systemd and instead uses runit as its init system. Furthermore, it gives you the option to use several desktop environments.
Other Features:
- Minimal system requirements
- Offers an official repository for non-free packages
- Support for Raspberry Pi
- Integration of OpenBSD’s LibreSSL software
- Support for musl C library
- 32-bit support

4. Solus Linux

Formerly EvolveOS, Solus Linux offers some exciting features while built from scratch. Solus features its own homegrown budgie desktop environment as its flagship version.
Compared to other options, Solus Linux is one of the few independent distributions that new Linux users can use. It manages to be one of the best Linux distributions available.
It uses eopkg package management with a semi-rolling release model. As per the developers, Solus is exclusively developed for personal computing purposes.
Other Features:
- Available in Budgie, Gnome, MATE, and KDE Plasma editions
- Variety of software out of the box, which reduces setup efforts
5. Mageia
Mageia started as a fork of Mandriva Linux back in 2010. It aims to be a stable and secure operating system for desktop and server usage.
Mageia is a community-driven project supported by a non-profit organization and elected contributors. You will notice a major release every year.
Other Features
- Supports 32-bit system
- KDE Plasma, Gnome, and XFCE editions are available from the website
- Minimal system requirements
6. Clear Linux
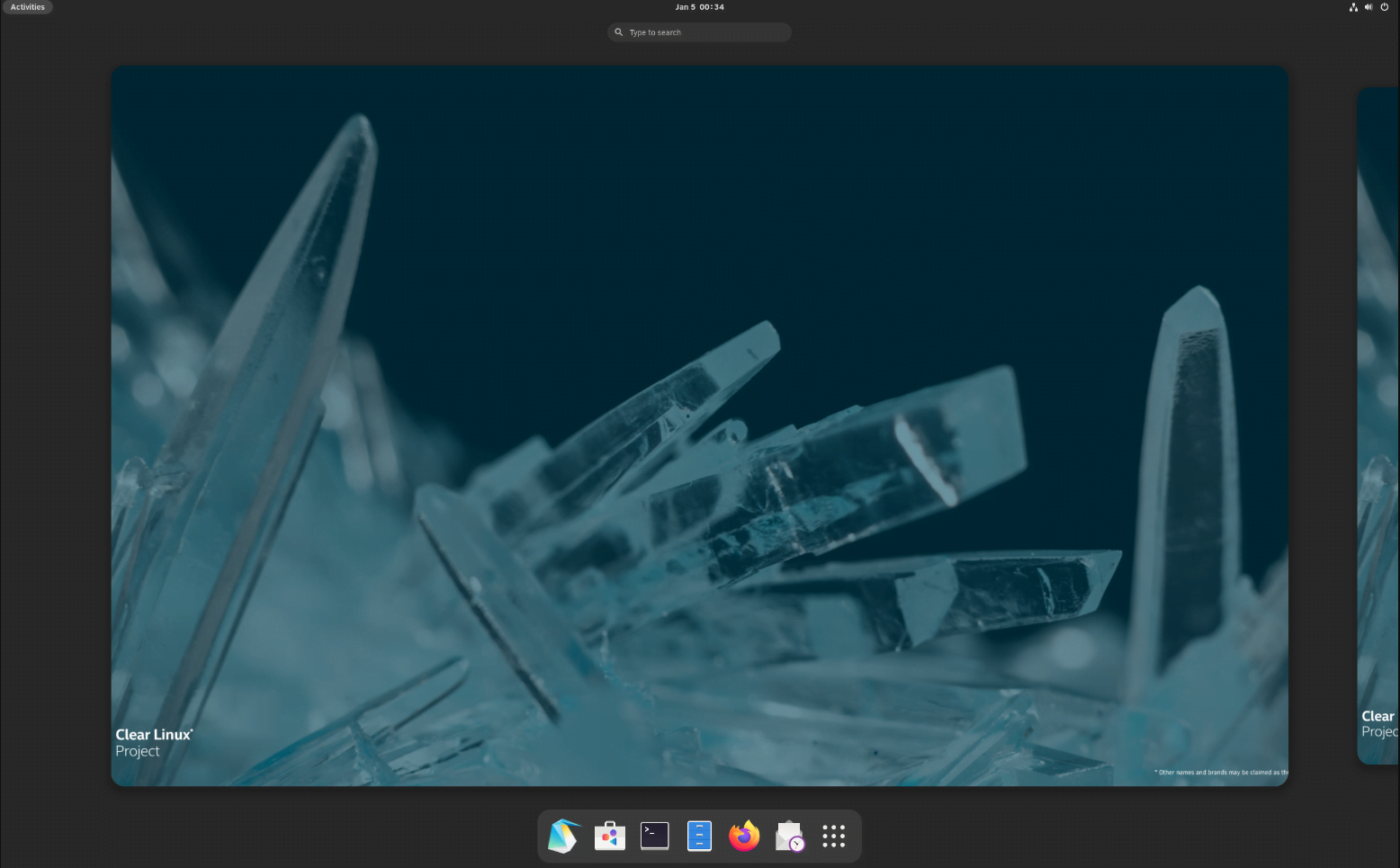
Clear Linux is a distribution by Intel, primarily designed with performance and cloud use cases in mind.
One interesting thing about Clear Linux is the operating system upgrades as a whole rather than individual packages. So, even if you mess up with the system accidentally, it should boot correctly, performing a factory reset to let you set it up again.
It is not geared toward personal use. But it can be a unique choice to try.
Other Features:
- Highly tuned for Intel platforms
- A strict separation between User and System files
- Constant vulnerability scanning
7. PCLinuxOS

PCLinuxOS is an x86_64 Linux distribution that uses APT-RPM packages. You can get KDE Plasma, Mate, and XFCE desktops, while it also offers several community editions featuring more desktops.
Locally installed versions of PCLinuxOS utilize the APT package management system thanks to Synaptic package manager. You can also find rpm packages from its repositories.
Other Features:
- mylivecd script allows the user to take a ‘snapshot’ of their current hard drive installation (all settings, applications, documents, etc.) and compress it into an ISO CD/DVD/USB image.
- Additional support for over 85 languages.
8. 4MLinux
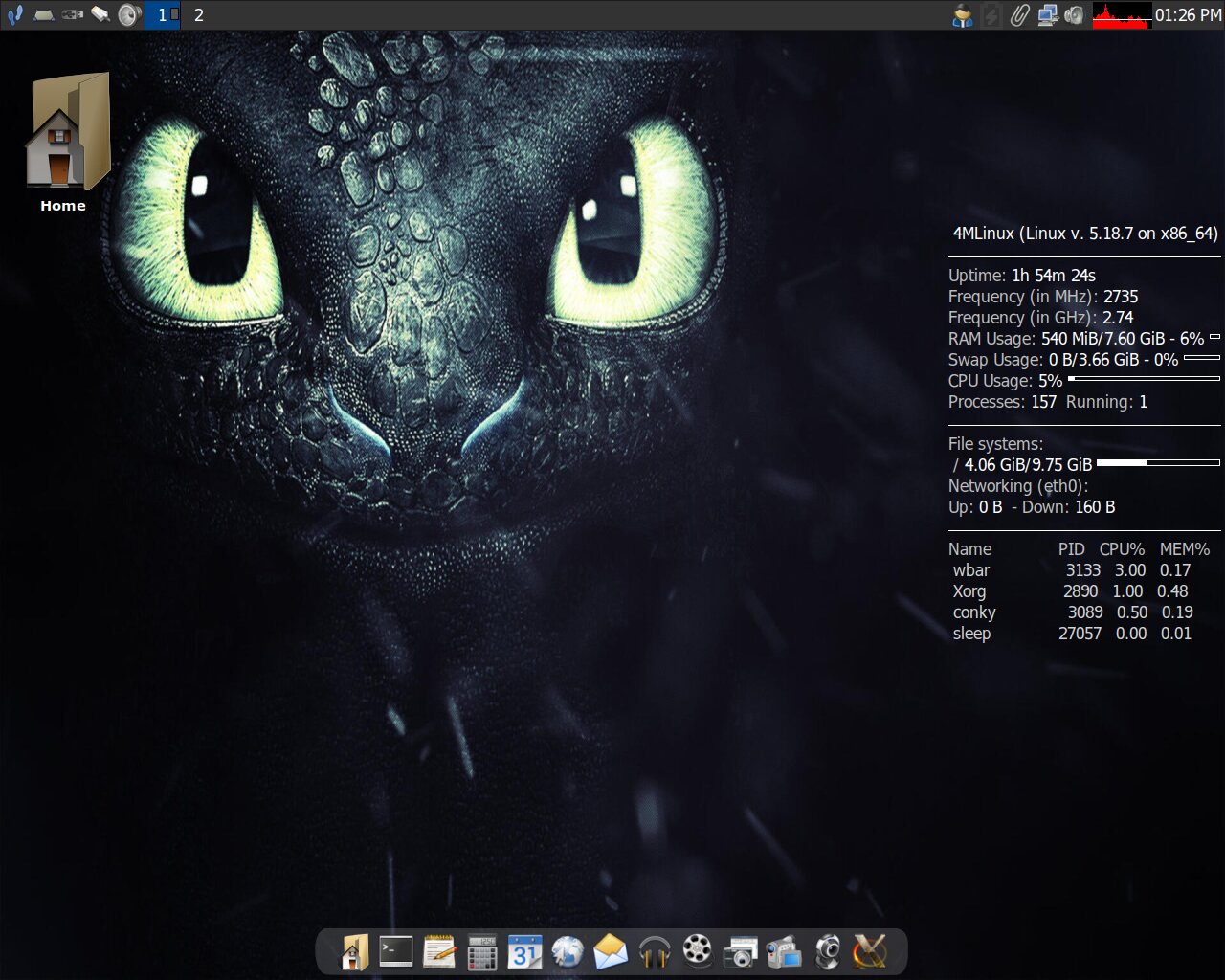
4MLinux is a general-purpose Linux distribution with a strong focus on the following four “M” of computing:
- Maintenance (system rescue Live CD)
- Multimedia (full support for a huge number of image, audio and video formats)
- Miniserver (DNS, FTP, HTTP, MySQL, NFS, Proxy, SMTP, SSH, and Telnet)
- Mystery (meaning a collection of classic Linux games)
It has a minimal system requirement and is available as a desktop and server version.
Other Features
- Support for large number of image, audio/video formats
- Small and general-purpose Linux distribution
9. Tiny Core Linux
Tiny Core Linux focuses on providing a base system using BusyBox and FLTK. It is not a complete desktop. So, you do not expect it to run on every system.
It represents only the core needed to boot into a very minimal X desktop, typically with wired internet access.
The user gets great control over everything, but it may not be an easy out-of-the-box experience for new Linux users.
Other Features
- Designed to run from a RAM copy created at boot time
- By default, operates like a cloud/internet client
- Users can run appbrowser to browse repositories and download applications
10. Linux From Scratch
Linux From Scratch is a way to install a working Linux system by building all its components manually. Once completed, it provides a compact, flexible and secure system and a greater understanding of the internal workings of the Linux-based operating systems.
If you need to dive deep into how a Linux system works and explore its nuts and bolts, Linux From Scratch is the project you need to try.
Other Features
- Customised Linux system, entirely from scratch
- Extremely flexible
- Offers added security because of self compile from source
11. Slackware
Slackware is the oldest distribution that is still being maintained. Originally created in 1993, with Softlanding Linux System as base, Slackware later became the base for many Linux distributions.
Slackware aims at producing the most UNIX-like Linux distribution while keeping simplicity and stability.
Other Features
- Available for 32-bit and 64-bit systems
- Extensive online documentation
- Can run on Pentium system to latest machines
12. Alpine Linux
Alpine Linux is a community-developed operating system designed for routers, firewalls, VPNs, VoIP boxes, and servers. It began as a fork of the LEAF Project.
Alpine Linux uses apk-tools package management, initially written as a shell script and later written in C programming language. This is a minimal Linux distribution, which still supports 32-bit systems and can be installed as a run-from-RAM operating system.
Other Features:
- Provides a minimal container image of just 5 MB in size
- 2-year support for the main repository and support until the next stable release for the community repository
- Made around musl libc and Busybox with resource-efficient containers
In case you are interested, you can refer to our tutorial on installing Alpine Linux in virtual box.

13. KaOS
KaOS is a Linux distribution built from scratch and inspired by Arch Linux. It uses pacman for package management. It is built with the philosophy “One Desktop Environment (KDE Plasma), One Toolkit (Qt), One Architecture (x86_64)“.
It has limited repositories, but still, it offers plenty of tools for a regular user.
Other Features:
- Most up-to-date Plasma desktop
- Tightly integrated rolling and transparent distribution for the modern desktop
Wrapping Up
If you need a unique experience, these independent Linux distributions should serve the purpose.
However, if you want to replace it with a mainstream distribution like Ubuntu for your desktop…
You might want to think twice, considering most of the options (if not all) above are not ideal options for day-to-day desktop usage.
But then again, if you have a fair share of experience with Linux distributions, you can undoubtedly take up the task for an adventure!
If you were to try one of these indie distros, which one would it be? Share with us in the comments.


