
The snap packages are now an integral part of Ubuntu.
I mean, you can remove Snap from Ubuntu but they are still at the core of Ubuntu.
When it comes to updating Ubuntu, you'll come across apt update and apt upgrade commands. No one really talks about snap update command.
That's because Snap updates are automatically updated to newer versions. It's built-in to the Snap mechanism. Your system checks for the updates multiple times daily and updates Snap applications automatically.
But this does not mean you cannot update Snap packages manually. Knowing about Snap updates also help you understand some of the underlying mechanism.
Let me show you how Snap update works and how you can control various parameters.
snap refresh command is used for updating Snap packages.Check Snap update schedule
As I mentioned earlier, the snapd daemon checks for updates on installed Snap packages multiple times a day. By default, it checks for updates four times a day.
You can see all these details using this command:
snap refresh --timeIt gives me the following output:
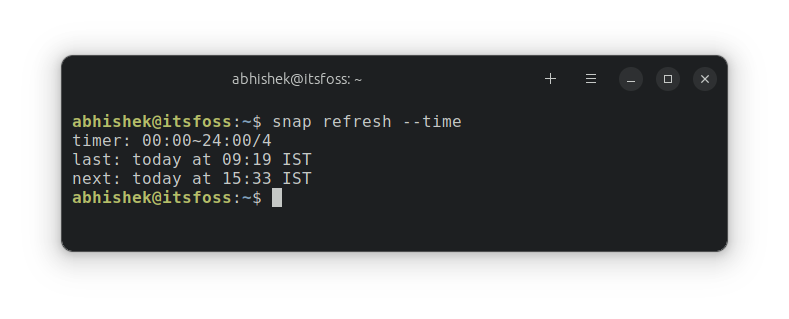
In here, timer: 00:00~24:00/4 tells you that the refresh check takes place 4 times in the span of 24 hours.
It also shows that the last Snap update check took place at 09:19 and the next one is scheduled at 15:33.
refresh.timer option. For example, sudo snap set system refresh.timer=6:00-8:00,20:00-22:00 will make the Snap update check to happen between 6 and 8 in the morning and 8 and 10 at night.See which Snap applications can be updated
You can check which Snap packages have updates available with the following command:
snap refresh --listIf no Snap package has updates, you'll see this message.
All snaps up to date.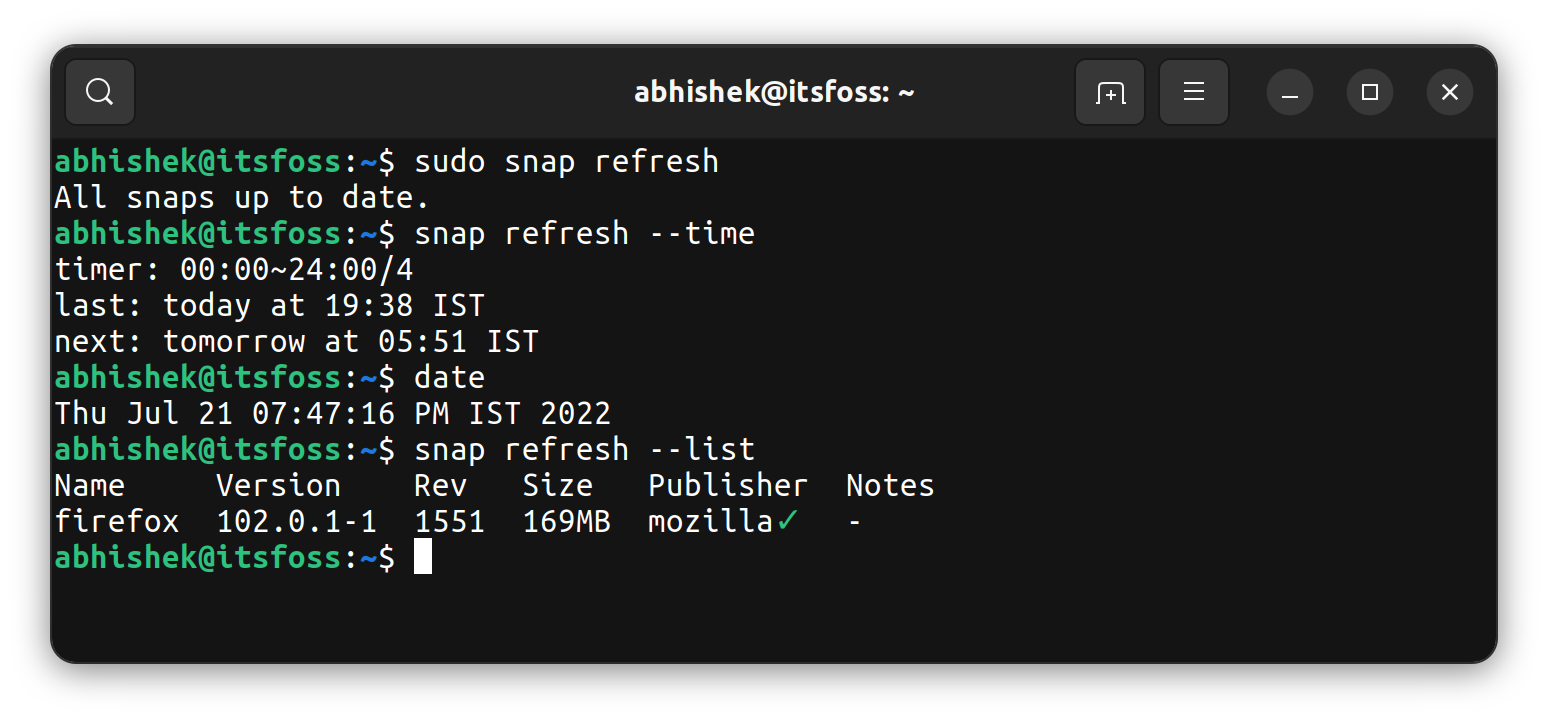
Update all Snap packages manually
If you don't want to wait till the next Snap refresh, you can surely manually update all the Snap packages that can be updated.
All you have to do is to run this command:
sudo snap refreshAnd see the updates take place.
Update specific Snap packages
If you only want to update a specific Snap package, use:
sudo snap refresh package_nameYou'll need to be precise with the package name, of course. You can also provide multiple packages to be updated.
sudo snap refresh package_1 package_2Please note that some Snap applications (that are usually installed in classic mode) are not updated in the background. You have to close the running Snap applications and then update them.
Check changes made by Snap updates
Since Snap updates mostly work in the background, you may wonder what changes were made
snap changesIt should show what changes Snap made in the last refresh.
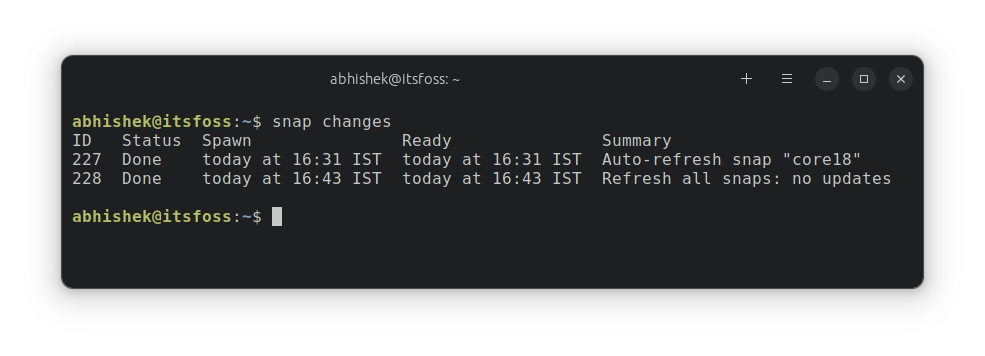
You can see the details of each change by using the ID it shows.
snap change change_ID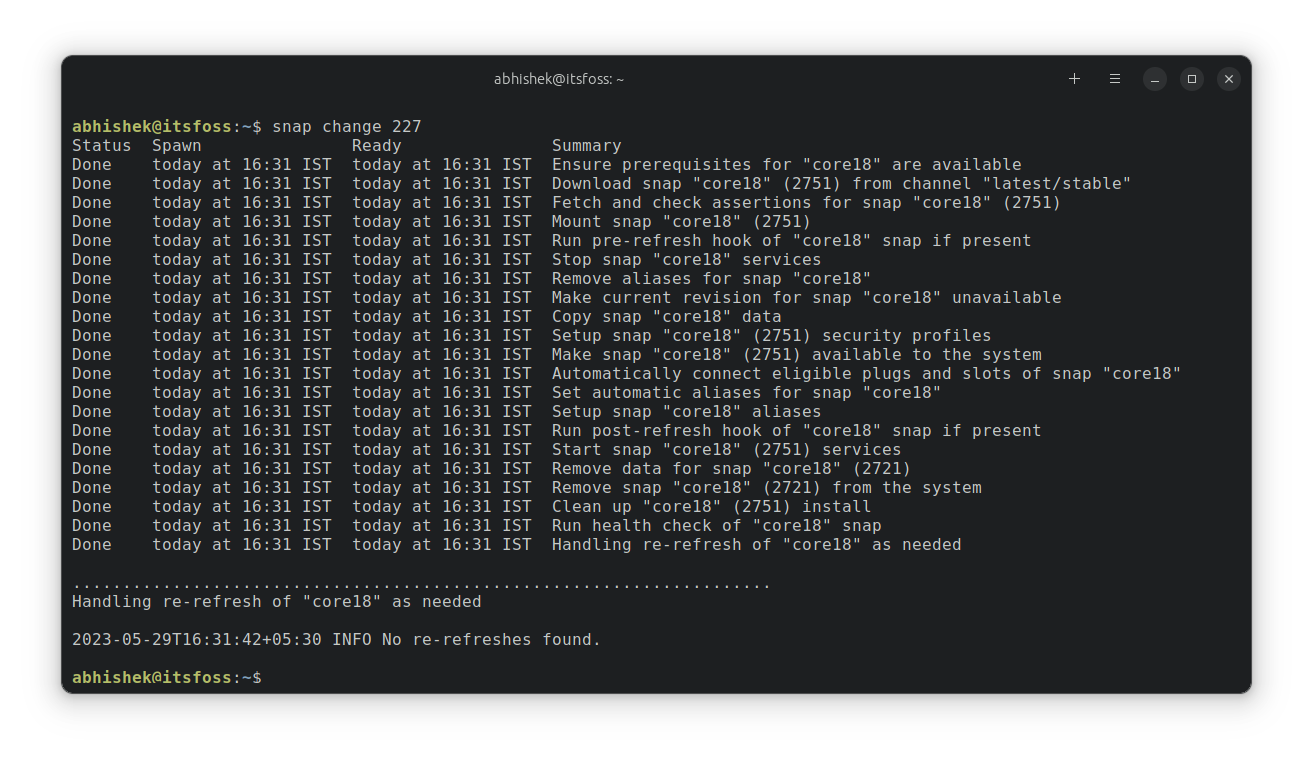
Revert the updated Snap application
By default, Snap saves one older version of the Snap packages. If you do not like the newly updated version, you can go back to the previous one with the revert option.
sudo snap revert package_name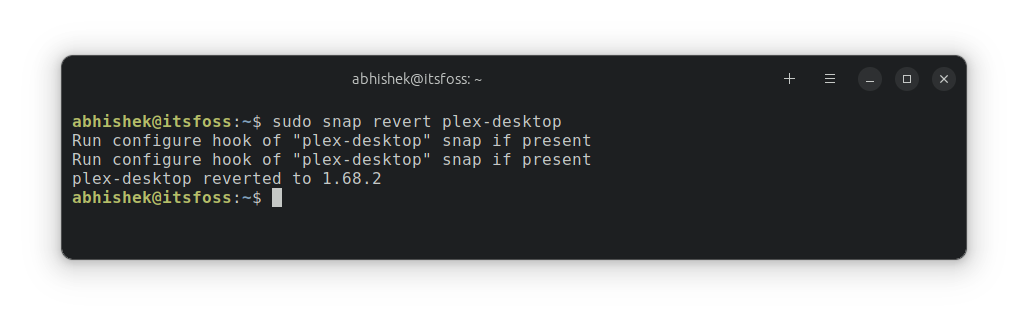
Prevent a package from updates
If you would like to stay on the current version for a particular package, you can hold it to prevent it from automatic updates.
sudo snap refresh --hold package_nameYou can stop the automatic update for all snap packages:
sudo snap refresh --holdWhen you are ready to accept updates on the package, you can unhold it.
sudo snap refresh --unhold package_nameYou may also unhold all the held packages in one go:
sudo snap refresh --unholdsudo snap refresh --hold=duration package_name. The duration can be in hours, minutes or even seconds.In the end...
If you use mobile data from time to time and do not want Snap auto-updates to eat away all your precious data, here's a trick for that.
The command below will prevent Snap updates on metered connections. In network settings, you can set your mobile network as metered.
sudo snap set system refresh.metered=holdMore about Snap updates can be found in the official documentation.

And that's it. I guess you know a lot more about Snap updates than you did earlier. Let me know what new stuff you learned in the comments. Any other question or suggestion is also weclome.



