
How do you program in C on Linux? It is indeed very easy and consists of three simple steps.
Step 1: Write your program and save the file with a .c extension. For example, my_program.c.
Step 2: You compile the program and generate the object file using gcc compiler in a terminal like this:
gcc -o my_program my_program.cStep 3: You run the generated object file to run your C program in Linux:
./my_program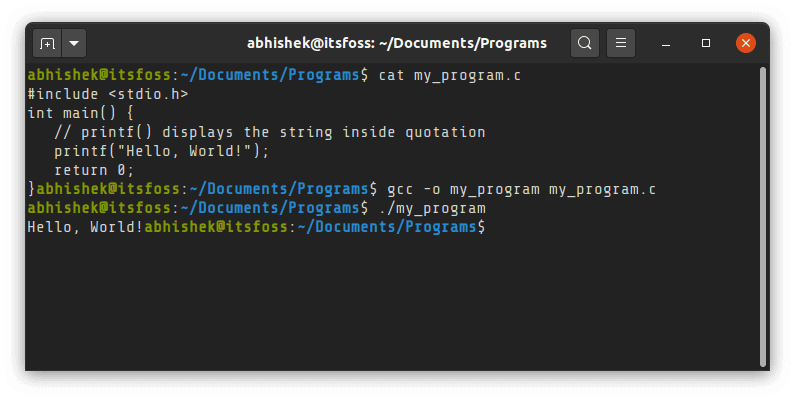
This was just a quick summary of how to compile and run a C program in Linux. If you are new to either C or Linux, I’ll show these steps in detail to make you comfortable coding C programs in a Linux environment.
I’ll discuss how to run C programs in a Linux terminal and a code editor.
Method 1: How to run C programs in a Linux terminal
In order to run a C program in Linux, you need to have a C compiler present on your systems. The most popular compiler is gcc (GNU Compiler Collection).
You can install gcc using your distribution package manager. In Debian and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, use the apt command:
sudo apt install gccSwitch to the directory where you have kept your C program (or provide the path) and then generate the object file by compiling the program:
gcc -o my_program my_program.cKeep in mind that it is optional to provide the output object file (-o my_program). If you won’t do that, an object file named a.out will be automatically generated. But this is not good because it will be overwritten for each C program and you won’t be able to know which program the a.out object file belongs to.
Once your object file is generated, run it to run the C program. It is already executable. Simply use it like this:
./my_programAnd it will display the desired output if your program is correct. As you can see, this is not very different from running C++ programs in Linux.

Method 2: How to run C programs in Linux using a code editor like Visual Studio Code
Not everyone is comfortable with the command line and terminal and I totally understand that.
You can use a proper C/C++ IDE like Eclipse or Code Blocks but they are often too heavy programs and more suitable for large projects.
I recommend using an open-source code editor like Visual Studio Code or Atom. These are basically text editors and you can install add-ons to compile and run programs directly from the graphical code editor.
I am using Visual Studio Code editor in this example. It’s a hugely popular open-source code editor from Microsoft.
First thing first, install Visual Studio Code in Ubuntu from the software centre. For other distributions, please check your Linux distribution’s package manager or software centre. You may also check the official website for more information.
Start Visual Studio Code and open/create a project and create your C program here. I am using a sample Hello World program.
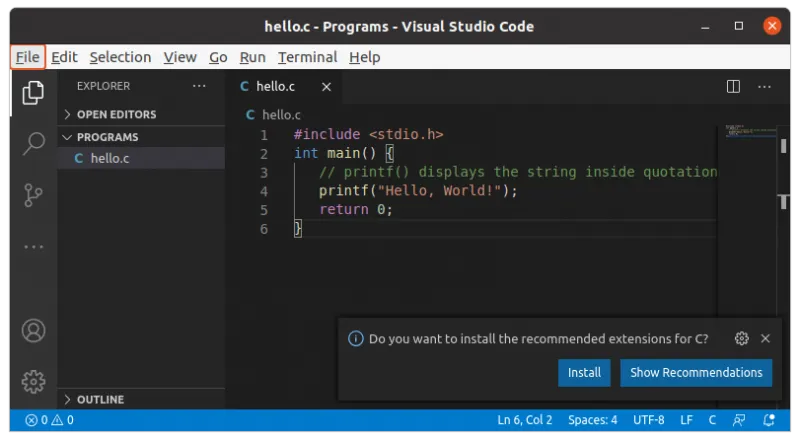
You must ensure the gcc compiler is installed on your Linux system.
sudo apt install gccNext, you would want to use an extension that allows you to run the C code. Microsoft may prompt you for installing its own extension for the C/C++ programs but it is complicated to set up and hence I won’t recommend it.
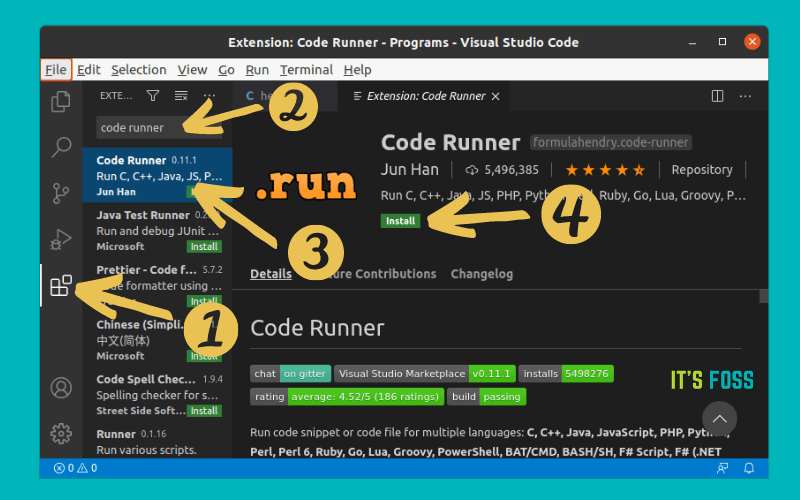
Instead, I suggest using the Code Runner extension. It’s a no-nonsense extension and you can run C and C++ code easily without additional configuration.
Go to the Extensions tab, search for ‘Code Runner,’ and install it.
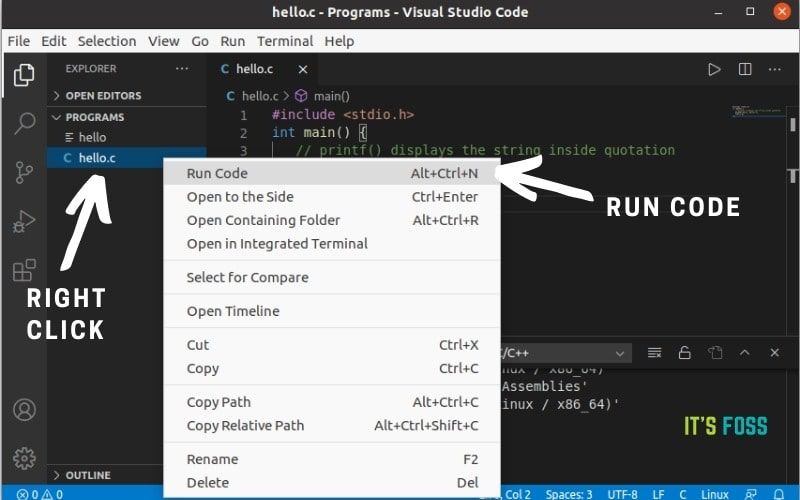
Restart Visual Studio Code. Now, you should be able to run the C code by using one of the following ways:
- Using the shortcut Ctrl+Alt+N.
- Press F1 and then select or type Run Code.
- Right-click the text editor and click Run code from the context menu.
When you run the program, it is compiled automatically and then run. You can see the output in the terminal that is opened at the bottom of the editor. What could be better than this?
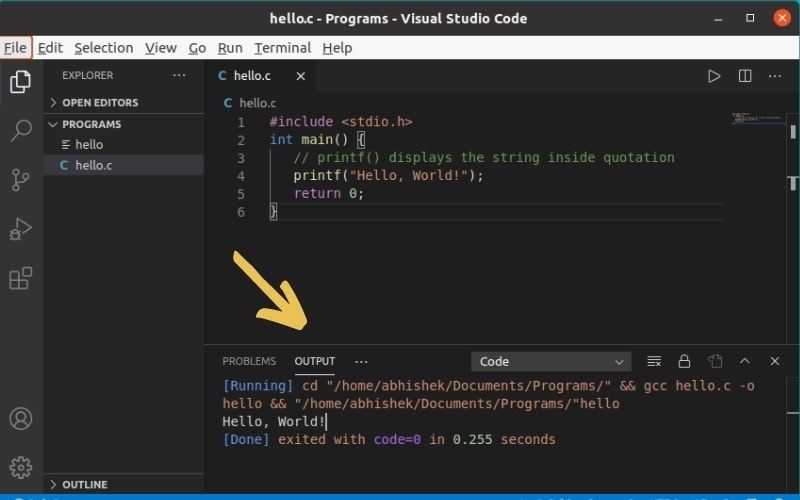
Which method do you prefer?
If you prefer a video to learn about installing and running C programs in Linx, check out the below Video tutorial.
Running a few C programs in the Linux command line is okay but using a code editor is much easier and saves time. Won’t you agree?
I will let you decide whichever method you want to use.

