Previously, our Open Science and AI articles have elaborately discussed the significance of Open Source Science and AI through various applications including Healthcare and Medicine. Recently, there have been promising new advancements in these fields!
Cancer Pathologists can now make use of an advanced Open Source AI system that has now achieved an extremely high level of Accuracy in detecting certain forms of Lung Cancer!
This is the realization of one of the many visions of the innovators and researchers at New York University (NYU), described two years ago in this video in great detail:
Their AI system is called DeepPATH, an Open Source framework that gathers the codes that have been used to study the use of a deep learning architecture (Google inception v3).
The future of AI-assisted therapy looks more promising than ever, now that researchers at NYU have designed the DeepPATH framework. Their algorithm has been designed to train it to differentiate and identify images of lungs that consist of both Normal and Cancer affected tissues.
Why is this
The most common form of Cancer worldwide is Lung Cancer. So far in 2018, 2.09 million cases of Lung Cancer have been reported, with 1.76 million deaths linked to Lung Cancer alone. WHO details it vividly.
There are four major Cancer risk factors:
- Tobacco use
- Alcohol use,
- Unhealthy diet
- Physical inactivity
The Nature paper (preprint available here) titled “Classification and mutation prediction from non-small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning”, highlights the effectiveness of their algorithm in identifying Lung Cancer Types with 97% Accuracy!
Why is the new study helpful for Cancer Pathologists?
The researchers achieved the new feat by teaching their AI algorithm to differentiate between two specific Lung Cancer Types, namely, Adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), which are the most prevalent subtypes of Lung Cancer.
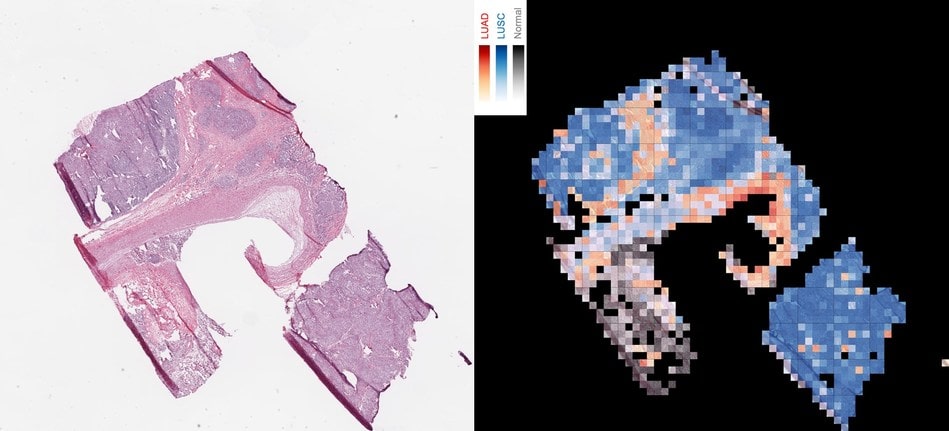
In conventional medical practice, visual inspection by an experienced pathologist is absolutely essential to distinctly identify one Lung Cancer Type from the other. Now, AI can perform the same task, as the performance of their deep learning models was comparable to each of three pathologists (two thoracic and one anatomic) who were asked to participate in this study and this is the reason why this breakthrough is so significant!
Google’s inception v3 was trained to recognize tumor areas based on the pathologists’ manual selections. The researchers at NYU trained a deep convolutional neural network (Google inception v3) on whole-slide images obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas to intelligently classify them into LUAD, LUSC or Normal Lung Tissue.
In addition to identifying cancerous tissue, the team also trained it to identify genetic mutations within the tissue. Out of the ten most commonly mutated genes in LUAD, six of them, namely STK11, EGFR, FAT1, SETBP1, KRAS and TP53 were predicted.
Not only so, but the team of AI scientists also laid out the future aspect of applying the same algorithm to extend the classification to other Types of less common Lung Cancers such as large-cell carcinoma, small-cell lung cancer and histological subtypes of LUAD and also to non-neoplastic features (neoplastic relates to neoplasms) including necrosis, fibrosis, and other reactive changes in the tumor microenvironment.
They also did mention data insufficiency at this point in time for such applications. But in future, if more such cases are eventually seen, then more datasets would also have to become available, in order for the algorithm to train with them.
The entire deep learning study by the team was accelerated by harnessing the significantly higher computational power of Graphical Processing Units or GPUs (compared to conventional Central Processing Units or CPUs). They used a single Tesla K20m GPU in particular, with the processing time being around 20 seconds. But they also highlighted that using multiple GPUs would reduce that time further down to a few seconds.
Our most favourite part of this news is of course that the entire code of DeepPATH is Open Source and readily available on GitHub. This would make it really helpful for academicians and researchers (both individuals and groups) who are working in similar research projects who would also like to apply the same system to analyze and interpret their own datasets with AI. These datasets can be of any form that could benefit our society.
We have discussed datasets in a prior article, where we described how NASA’s Open Science initiatives can be utilized to ask for dataset suggestions through submission on their Open Data Portal. Perhaps the datasets available there could also be quite resourceful for Google’s Open Source AI?
Isn’t this an amazing new milestone for Applied Open Source AI? Would you like to see more of such developments in the future of Applied AI with an Open Source Approach? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.

