If you are looking to develop applications for Ubuntu, you need to install Ubuntu SDK (Software Development Kit). Ubuntu SDK is based on Qt Creator (IDE for Qt development) and tailored for developing apps for Ubuntu and Ubuntu Touch. While I am not going to teach you Qt development, I can surely show you how to install and configure Ubuntu SDK in Ubuntu 16.04 and 14.04. You can work on your own thereafter as tons of help is available online.
Install Ubuntu SDK in Ubuntu 16.04 & 14.04
Since it relates to Ubuntu, no wonder Canonical has provided an official PPA to easily install Ubuntu SDK in Ubuntu 16.04 and 14.04. Open a terminal and use the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntu-sdk-team/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-sdkIt will download and install Ubuntu SDK. Note that it downloads around 1 GB of data for Ubuntu SDK. So keep your internet connection and data charges in mind. Installing the Ubuntu SDK is the easy part. What might confuse you as a newbie, is how to configure Ubuntu SDK for development. We are going to see it in next section.
Configure Ubuntu SDK
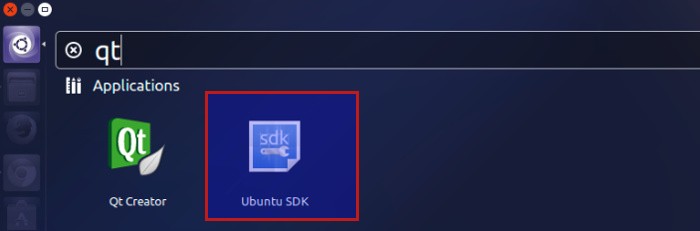
Search in Dash for Ubuntu SDK. Note that you’ll find both Qt creator and Ubuntu SDK installed. Always use Ubuntu SDK if you are aiming to develop applications for Ubuntu.
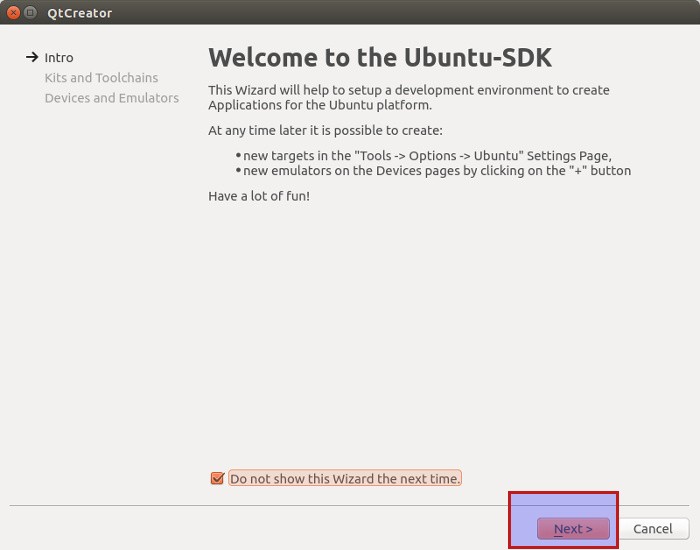
When you run the Ubuntu SDK for the first time, it will take you to a number of steps to configure the SDK.
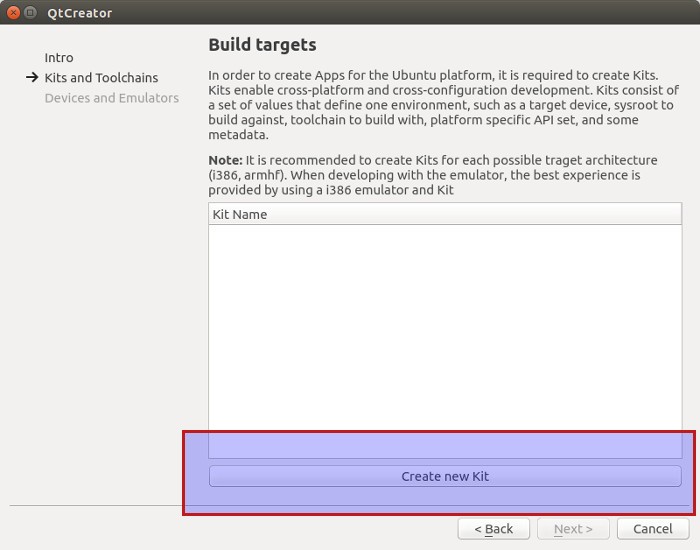
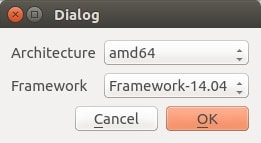
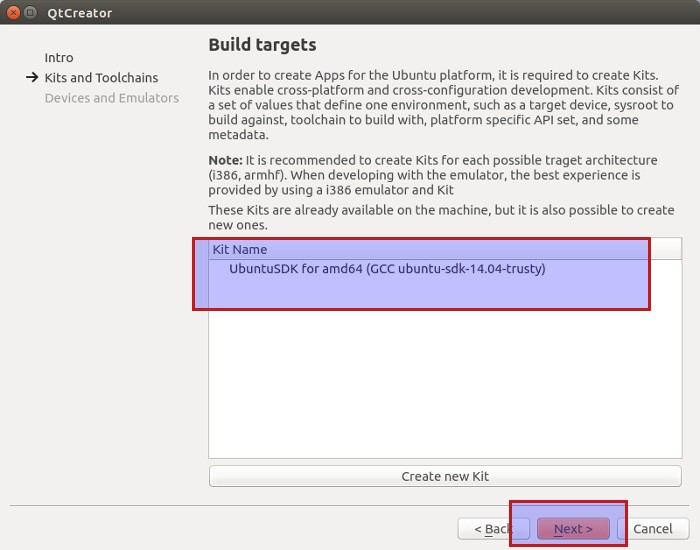
Next step is to create a kit. Basically, this means the architecture and version of Ubuntu you are targeting for. You can create and add multiple kits. It’s not a big deal. For the sake of emulator to work fine, Ubuntu suggests to use i386 architecture.
As I said, you can choose whatever architecture and Ubuntu version you want and you can add as many Kits as you want.
You’ll have to enter your admin password here:
Once you do this, you’ll see a screen like this:
It will take few minutes to generate the kit. Once generated, you’ll have the option to close this screen:
When you have generated a kit, select the kit and move to the next screen:
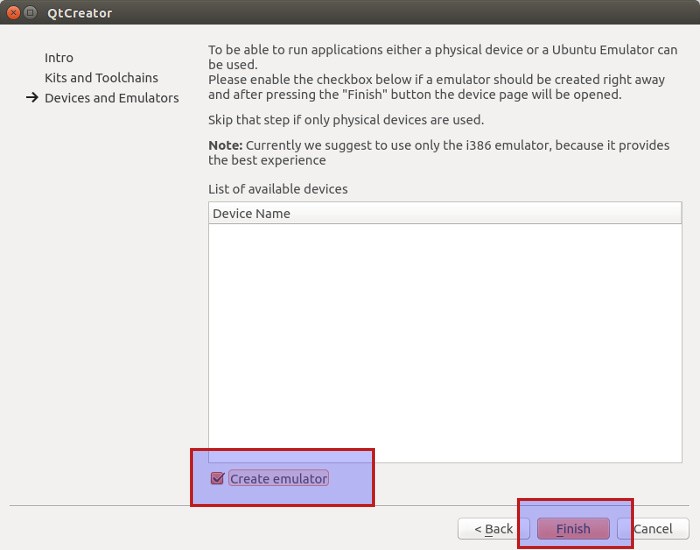
You’ll be asked to create an emulator. You should create one so that you won’t need a physical device for testing your apps.
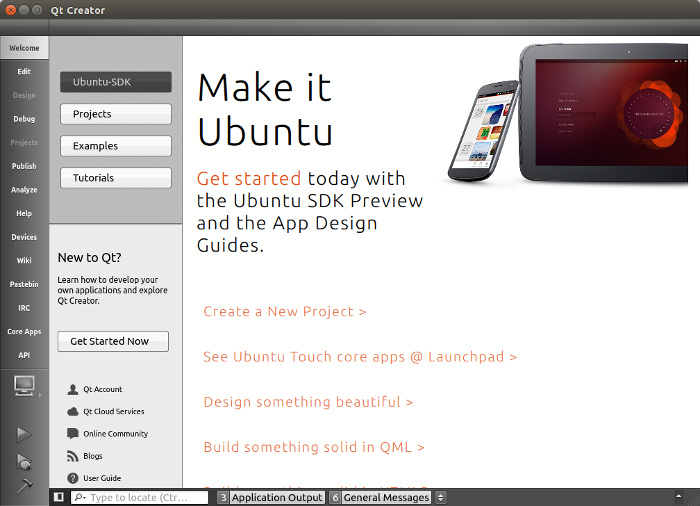
Once you do this, you’ll be greeted with welcome screen of Ubuntu SDK. You’ll see plenty of examples and tutorials here.
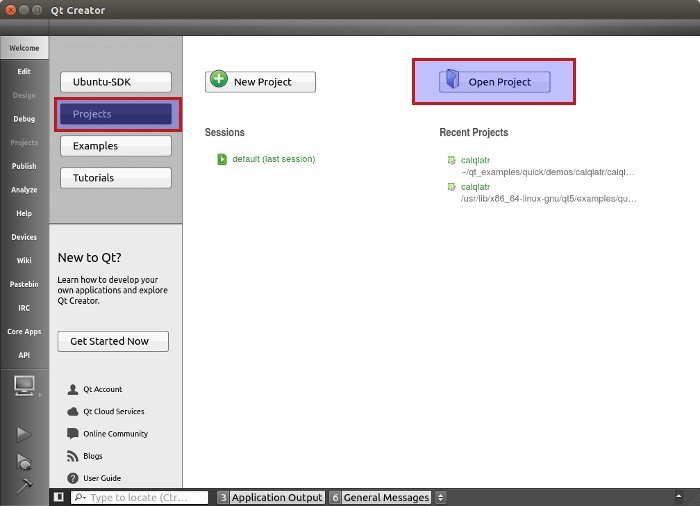
We are almost done with configuring Ubuntu SDK. We just need to verify if the SDK is working fine or not. To do this, you can open a demo project from examples and run it. The problem you’ll face here is that the examples are stored in a location that needs super user access. So, Ubuntu SDK will give you an option of copying the demo project to a location that doesn’t require super user access, such as home directory.
But the problem won’t be solved by this. Because it will copy just the demo project. And the demo project have files that are using header files from other projects. So at the en you’ll be seeing lots of error and the project won’t run successfully.
To get rid of this issue, what I did was to copy the whole examples directory from /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt5/examples/quick
cd ~
mkdir qt_examples
cp -r /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt5/examples/quick qt_examplesOnce you have copied the whole directory, in the Ubuntu SDK, go to Projects and open the project from quick/demo.
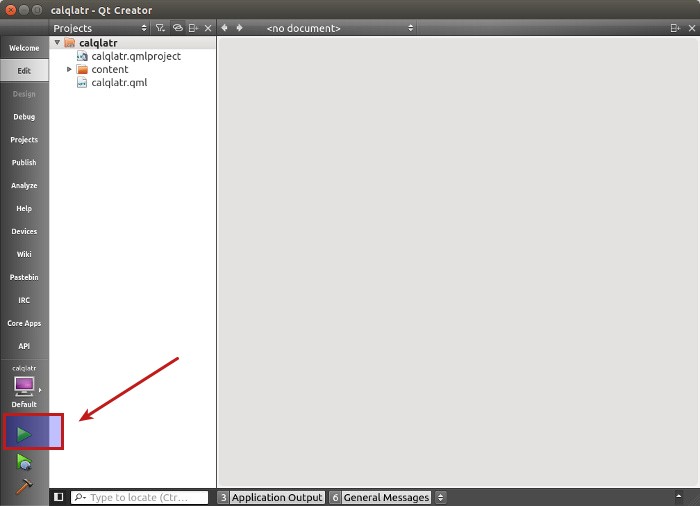
Run the demo project.
If it is properly configured, you should see the demo application screen.
That’s it. I hope this tutorial helped you to install and configure Ubuntu SDK in Ubuntu 16.04 and other higher versions. Good luck with creating new apps for Ubuntu. If interested, you can read about how to create webapp for Ubuntu Phone.