
GParted is undoubtedly one of the best partition managers for Linux out there. The user interface is very simple and gets the job done.
In some cases, you end up using GParted to fix or format your USB drive as well. I had a USB disk which I couldn’t format in Ubuntu using the “Disks” app – this is where GParted came to the rescue.
So, it is a quite useful tool with plenty of good features. Let me highlight them for you.
Installing GParted on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions
Before installing GParted, let's take a look at some of its key features:
- Set Partition Flags
- Resize/Move Partitions
- Create/Remove Partitions
- Ability to Set UUIDs
So, moving on to the installation. You might have GParted pre-installed, therefore, make sure to verify that before proceeding to install it.
If you do not have it installed, you can head into the software center on your Linux distro and search for 'GParted' to get it installed.
In case you want to use the terminal, simply type in the following command (Ubuntu/Debian):
sudo apt install gpartedIf you’re using any other Linux distribution, you can either find GParted in their respective software managers, or you could head over to the official download page for further install instructions.
Using the features of GParted
You can do many things with GParted, ranging from a simple format task to important partitioning tasks. I’ll highlight the key features with some screenshots to help you know more about it before installing it.
Create partition tables
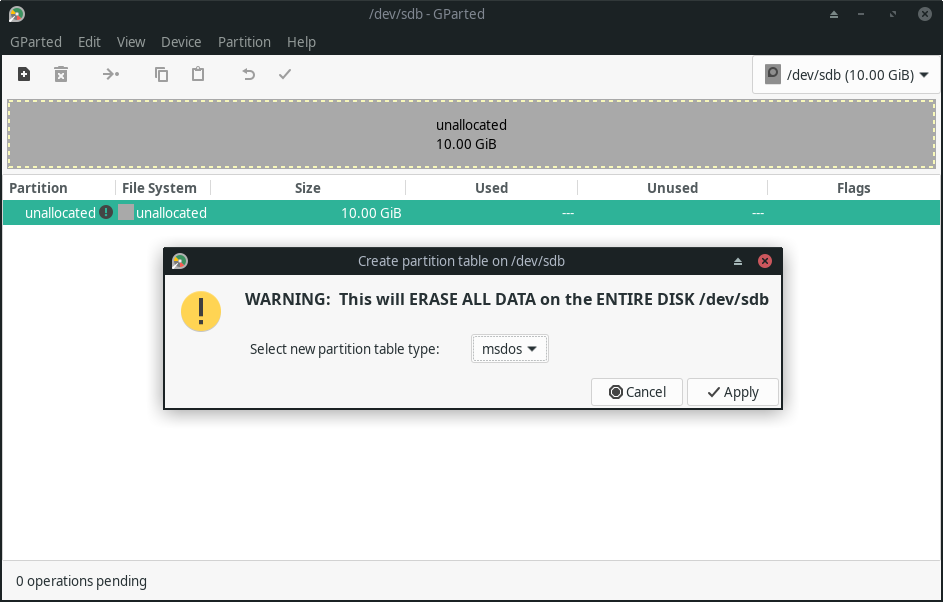
You can create a new partition table for your disks, or erase the content of your existing disk to modify the partition table.
GParted lets you choose from different types of partition tables like msdos, bsd, gpt, atari, and more.
Create, Move, Label, Delete & Modify Partitions
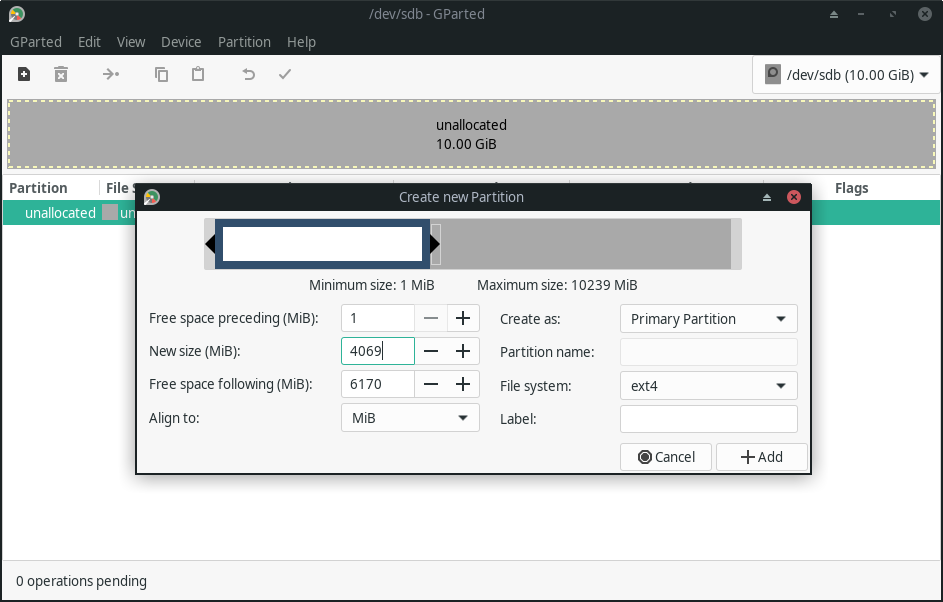
You can easily create, label, delete or modify the partitions with a bunch of options available within GParted.
Below, you can see how creating a new partition looks like. Of course, you will have to be careful about what you want to do.
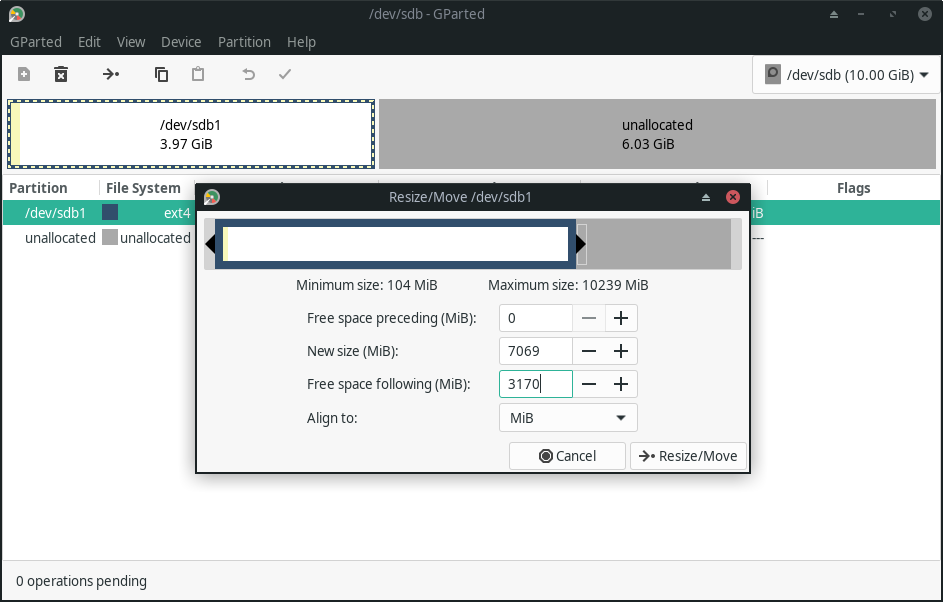
After creating a new partition, you can also Resize/Move it according to your preference.
The good thing is that GParted makes sure that you do not directly apply any changes – it queues up your selected operations/tasks and asks for another final confirmation before you hit it.
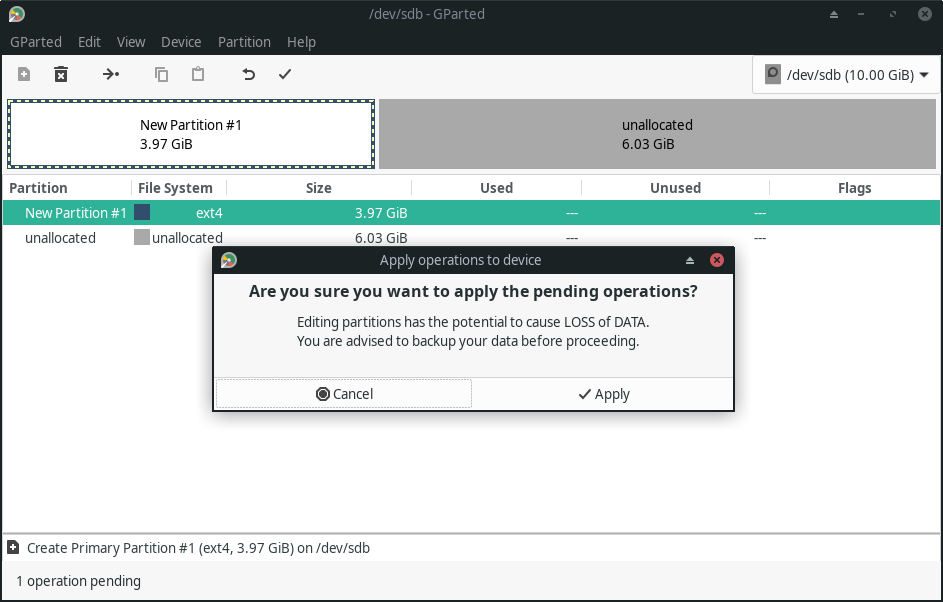
The tick mark symbol ✓ on the top allows you to confirm the changes and then only your changes take into effect.
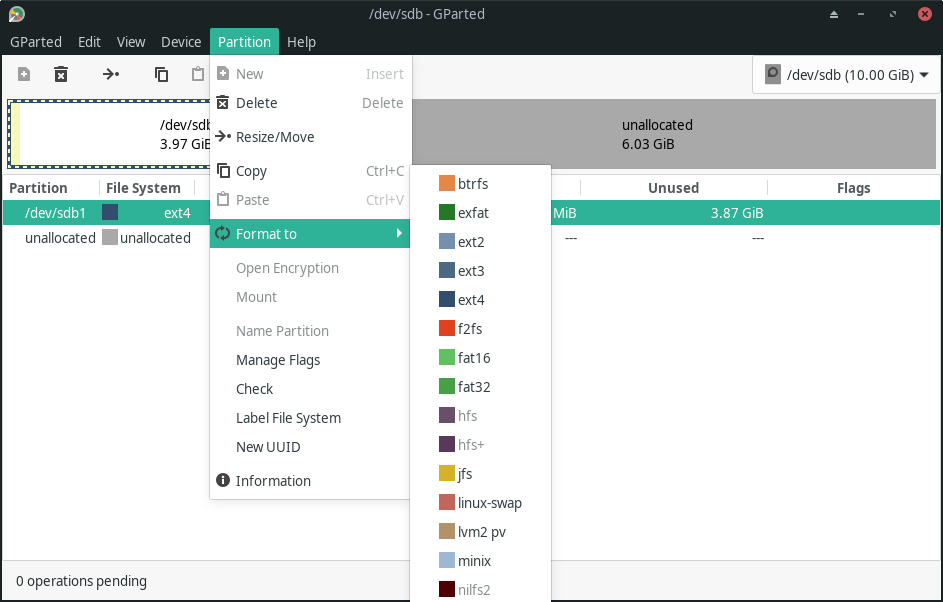
Here’s another screenshot for the format options you have available for the partitions:
Attempt Data Rescue
Apart from editing partitions, you can also try to recover your lost data in Linux using the “Attempt Data Rescue” feature, as shown in the screenshot below.
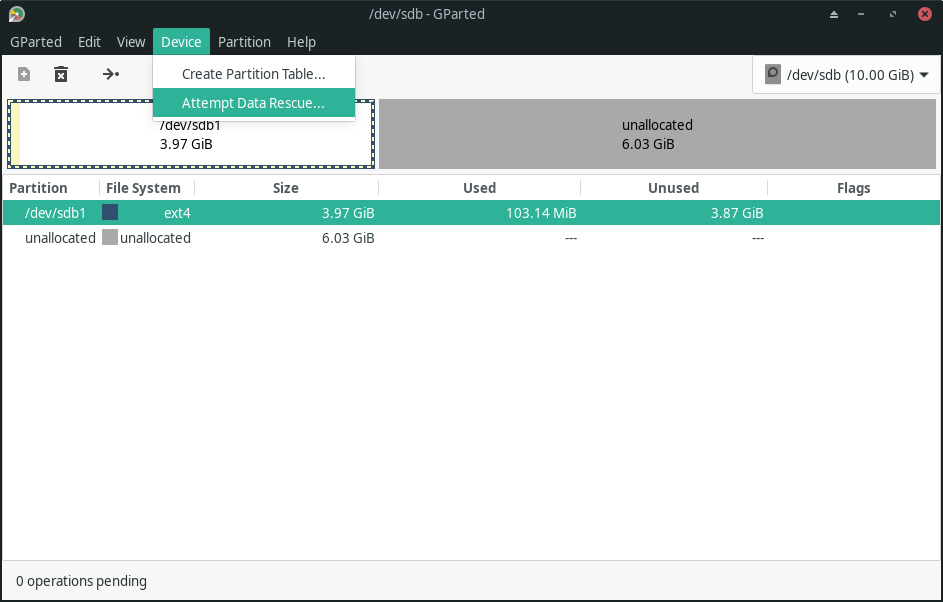
It is worth noting that you do not have this feature installed by default – you only see the option visible.
So, for the data recovery feature to work, you have to install 'gpart' separately using the following command (on Ubuntu/Debian-based distributions):
sudo apt install gpartIn addition to all the key features listed above, GParted supports a wide range of storage devices and file systems. You can learn more about it from the list of features on their official website.
Wrapping Up
GParted is a very useful and important tool when it comes to dealing with disk management and partitions. However, you will have to be careful while using it for obvious reasons.
💬 Have you tried GParted? Prefer other partitioning tools for Linux? Don't hesitate to share your experiences in the comments below!

