
When you do a fresh installation of Ubuntu, you are not given any option to configure a root password.
Instead, a user account is created and added as sudoer. This user can run commands as root by adding sudo before them.
You could also switch to the root user with sudo:
sudo su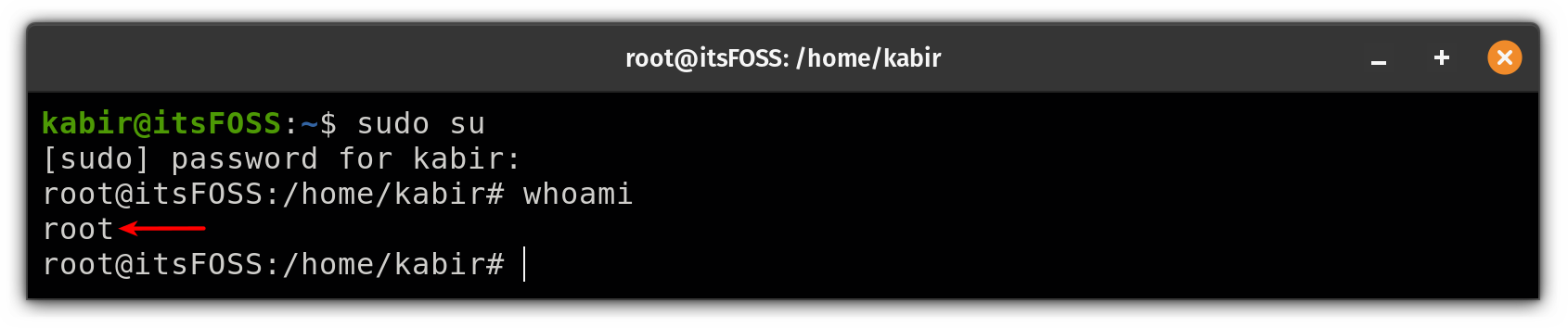
However, you may find yourself in a situation where you prefer to run as root and you would also prefer to have a dedicated password to this root user.
If that's the case, this quick tutorial will help you.
How to set a root password in Ubuntu
The strange part of this entire tutorial is even though you never configured a root password, you are going to change it with the password of your liking.
To change (or set) a root password, you can use the passwd command with sudo to change the root password:
sudo passwd rootOnce you execute the above command, it will first ask you for a sudo password and then ask you to enter the new root password two times:
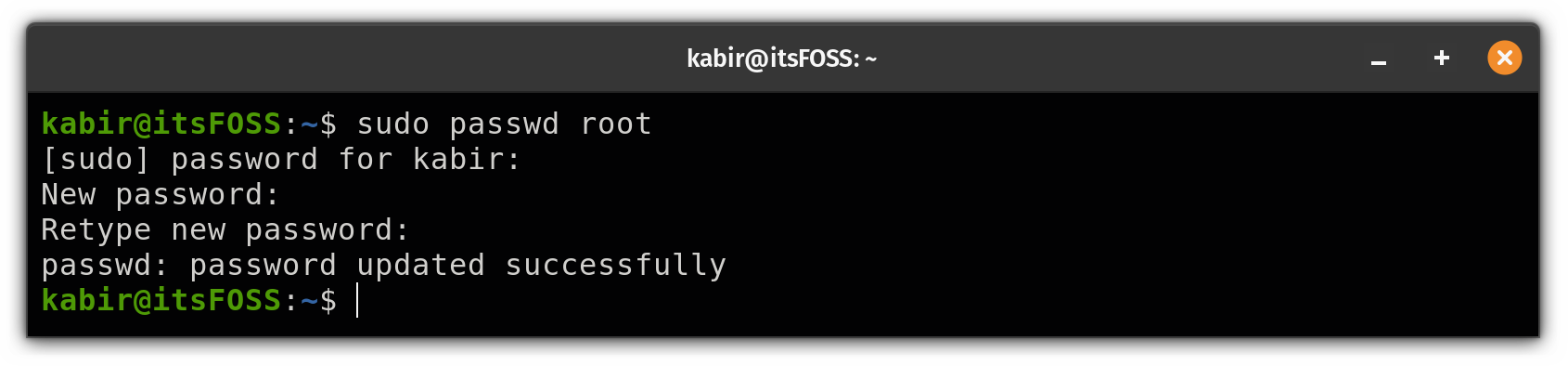
From here on, you can access the root user account without any restrictions:
su 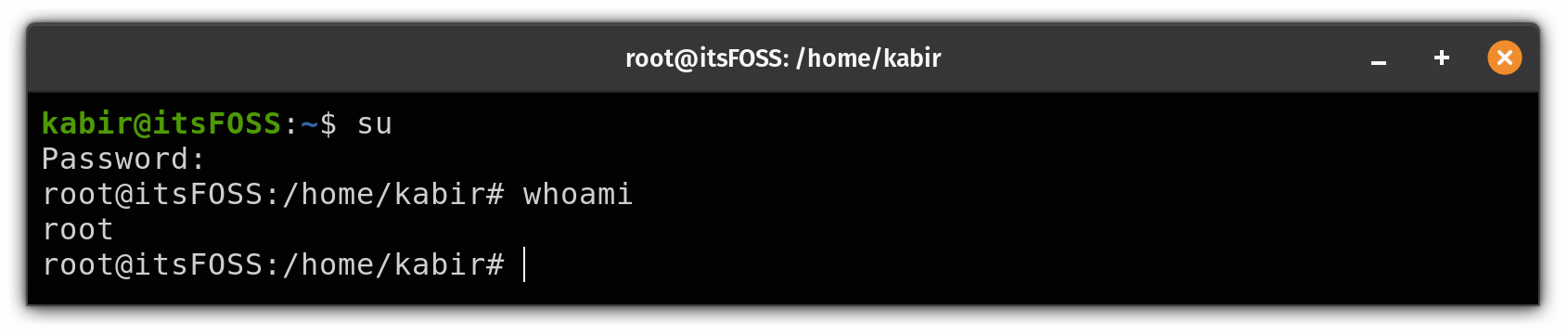
How to unset root password again
We at itsFOSS don't suggest configuring a root account unless you really want as there are various reasons why Ubuntu don't give an option for a root account during installation.
If you want to go back to the previous stage when the root user was locked and you can only access the root account with sudo, then you can lock the root account.
First, switch to the root user using the following:
su Now, use the passwd command to lock the root user and delete the root password as shown here:
passwd -dl root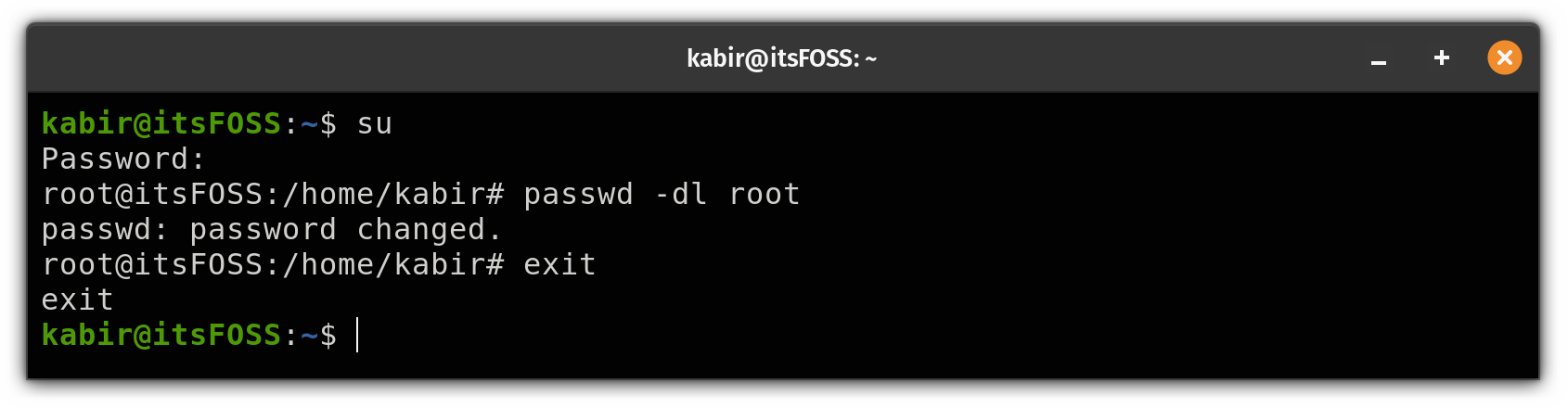
From here, you can't access the root account directly and if you want to access it, you can still access it as you used to do with sudo su command:

Wrapping Up...
In this quick tutorial, I went through how you can set the root password and how to revert to the previous state. I don't recommend setting up a root account unless you know what you are up to.
That's it from my side. If you have any queries, leave us a comment.
It's FOSS turns 13! 13 years of helping people use Linux ❤️
And we need your help to go on for 13 more years. Support us with a Plus membership and enjoy an ad-free reading experience and get a Linux eBook for free.
To celebrate 13 years of It's FOSS, we have a lifetime membership option with reduced pricing of just $76. This is valid until 25th June only.
If you ever wanted to appreciate our work with Plus membership but didn't like the recurring subscription, this is your chance 😃


