
So you installed Ubuntu and started using it extensively. Somewhere down the line, you are bound to lose the track of the software that you had installed over the time.
That’s perfectly normal. No one expects you to remember all the packages installed on your system. But the question arises, how to know what packages have been installed? How to see the installed packages?
To list all the installed packages using apt:
apt list –installedRead the rest of the tutorial to know more about other ways and some more tips to fine tune your search for installed packages.
List installed packages in Ubuntu and Debian
If you use apt command extensively, you would probably expect a command like apt list installed packages. You are not entirely wrong here.
While apt-get command doesn’t have a straightforward option like apt-get list installed packages, apt has a command for this.
apt list --installedThis will list all the packages that have been installed using apt. It will also list the packages that were installed as a dependency. Which means that not only you’ll have the applications you installed, you’ll also have a huge list of libraries and other packages that you didn’t install directly.
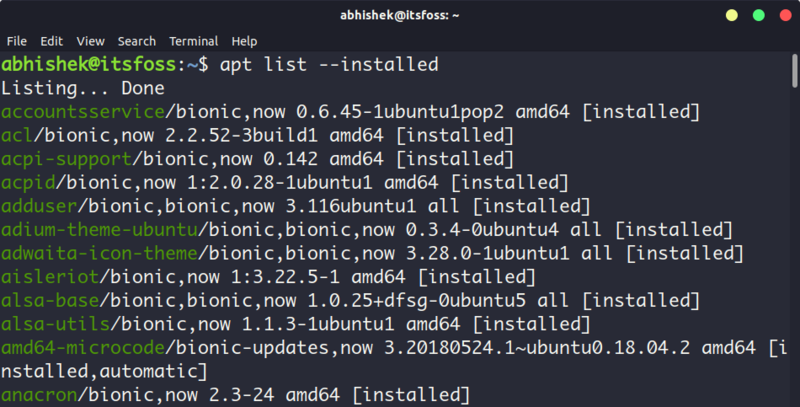
Check whether a specific package is installed in Ubuntu
Since the list of installed packages is a huge one, it would be a better idea to use grep and filter the output for a certain package.
apt list --installed | grep program_nameA better way is to use this command:
apt -qq list program_name --installedBoth q options are for quiet mode. And this way, it only looks for programs that are installed.
Note that the above method also lists the applications installed with .deb files. That’s cool, isn’t it?
Other ways to check installed packages in Ubuntu/Debian
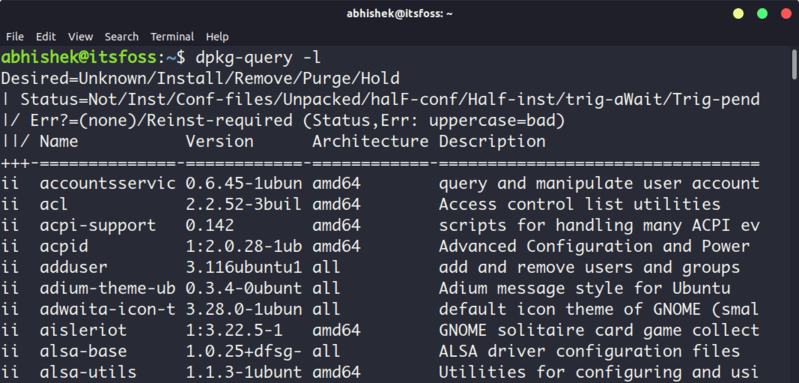
If you have read my apt vs apt-get comparison article, you probably already know that both apt and apt-get basically use dpkg. This means you can use dpkg command to list all the installed packages in Debian.
dpkg-query -lYou can filter the output with grep again to search for a specific package.
So far, you have dealt with applications installed with Debian’s package manager. What about Snap and Flatpak applications? How to list them because they are not accessible with apt and dpkg?
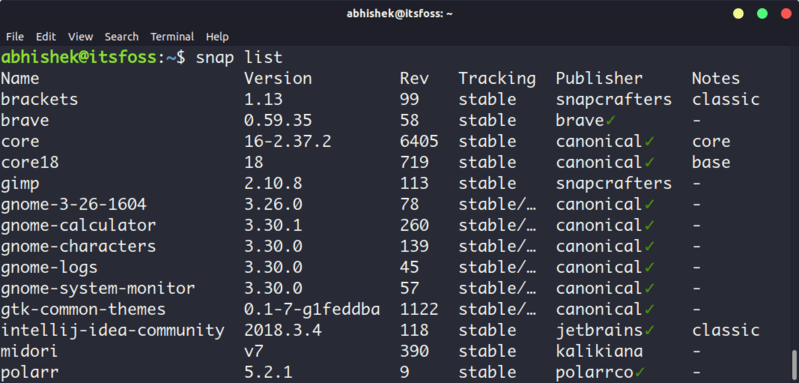
To show all the Snap packages installed on your system, use this command:
snap listSnap list also indicates which applications are from a verified publisher with a green tick.
To list all the Flatpak packages installed on your system, use this:
flatpak listLet me summarize it for you.
Summary
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| apt list --installed | List installed deb packages using apt command |
| dpkg-query -l | List installed deb packages using dpkg command |
| snap list | List installed snap packages |
| flatpak list | List installed Flatpak packages |
List the recently installed packages
So far, you have seen the list of installed packages in alphabetical order. What if you want to see the packages that have been installed recently?
Thankfully, a Linux system keeps a log of everything that happens in your system. You can refer to the logs to see the recently installed packages.
There are a couple of ways to do this. You can either use the dpkg command’s log or the apt command’s log.
You’ll have to use grep command to filter the result to list the installed packages only.
grep " install " /var/log/dpkg.logThis will list all the packages including the dependencies that were installed recently on your system along with the time of installation.
2019-02-12 12:41:42 install ubuntu-make:all 16.11.1ubuntu1
2019-02-13 21:03:02 install xdg-desktop-portal:amd64 0.11-1
2019-02-13 21:03:02 install libostree-1-1:amd64 2018.8-0ubuntu0.1
2019-02-13 21:03:02 install flatpak:amd64 1.0.6-0ubuntu0.1
2019-02-13 21:03:02 install xdg-desktop-portal-gtk:amd64 0.11-1
2019-02-14 11:49:10 install qml-module-qtquick-window2:amd64 5.9.5-0ubuntu1.1
2019-02-14 11:49:10 install qml-module-qtquick2:amd64 5.9.5-0ubuntu1.1
2019-02-14 11:49:10 install qml-module-qtgraphicaleffects:amd64 5.9.5-0ubuntu1You can also use the history of apt command. This will show only the programs that you installed using apt command. It won’t show the dependencies installed with it, though the details are present in the logs. Sometimes, you just want to see that, right?
grep " install " /var/log/apt/history.logThe output should be something like this:
Commandline: apt install pinta
Commandline: apt install pinta
Commandline: apt install tmux
Commandline: apt install terminator
Commandline: apt install moreutils
Commandline: apt install ubuntu-make
Commandline: apt install flatpak
Commandline: apt install cool-retro-term
Commandline: apt install ubuntu-software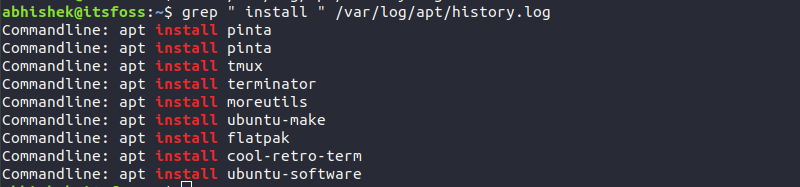
The history log of apt is quite useful because it shows the time when the apt command was run, the user who ran the command and the packages that were installed by a command.
Bonus Tip: Show installed applications in Software Center
If you are not comfortable with the terminal and the commands, you still has a way to see the applications installed on your system.
You can open the Software Center and click on the Installed tab. You’ll see the list of applications that have been installed on your system.
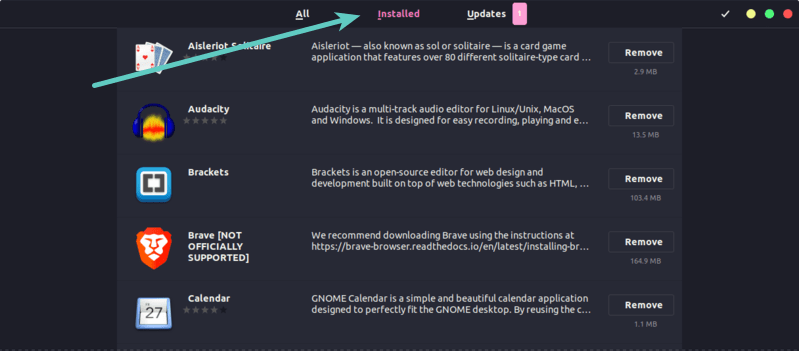
It won’t show the libraries and other command line stuff though but perhaps you don’t want to see that as you are more GUI centric. Otherwise, you can always use the Synaptic Package Manager.
That’s it
I hope this quick little tutorial helped you to see the list of installed packages on Ubuntu and Debian based distributions.
If you have questions or suggestions to improve this article, please leave a comment below.

