
python3-pip package like this:sudo add-apt-repository universe
sudo apt install python3-pip
There are numerous ways to install software on Ubuntu. You can install applications from the software center, from downloaded deb files, from PPAs, from Snap packages, using Flatpak, using AppImage and even from the good old source code.
Here’s another way to install packages on Ubuntu. It’s called PIP and you can use it to install Python-based applications.
What is pip?
Pip stands for “Pip Installs Packages”. Pip is a command-line based package management system. It’s used to install and manage software written in the Python language. You can use pip to install packages listed in the Python Package Index (PyPI).
As a software developer, you can use pip to install various Python modules and packages for your own Python projects.
As an end user, you may need pip for installing some applications that are developed using Python and can be installed easily using pip. One such example is the Stress Terminal application, which you can easily install with pip.
Let’s see how you can install pip on Ubuntu and other Ubuntu-based distributions.
How to install pip on Ubuntu, Linux Mint and other Ubuntu-based distributions
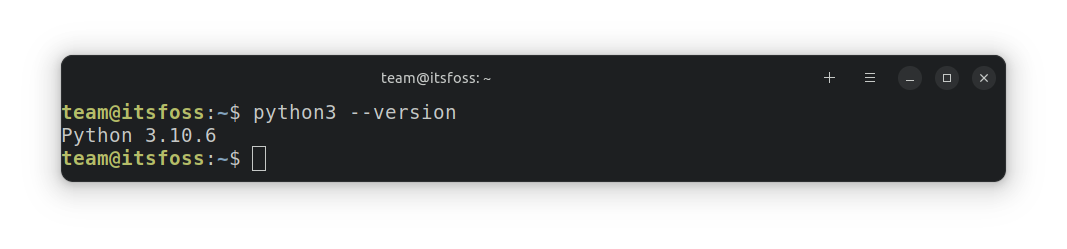
First, make sure that Python 3 is installed on Ubuntu. To check that, use this command:
python3 --versionIf it shows you a number like Python 3.x.y, Python 3 is installed on your Linux system.
Now you can install pip3 using the command below:
sudo apt install python3-pipYou should verify that pip3 has been installed correctly using this command:
pip3 --versionIt should show you a number like this:
pip 22.0.2 from /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/pip (python 3.10)This means that pip3 is successfully installed on your system.

pip command defaults to pip3 in Ubuntu 20.04 and above.Installing Python packages [Recommended Way]
Recently, a change has been done on distributions like Ubuntu 23.04 and upcoming Debian 12, regarding the installation of python packages.
From now on, you should install Python packages either from native repositories, install in a virtual environment or use pipx.

This was implemented to avoid the conflict between OS package managers and Python-specific package management tools like pip. These conflicts include both Python-level API incompatibilities and conflicts over file ownership.
Using pip commands
Now that you’ve installed pip, let’s quickly see some basic pip commands. These commands will help you use pip commands for searching, installing and removing Python packages.
Install a package with pip
There are two ways to install a package with PIP. You either install it for the currently logged-in user, or you install system-wide.
If you use --user option, it installs the package for the logged-in user, i.e., you, without needing sudo access. The installed python software is available only for you. Other users on your system (if any) cannot use it.
pip3 install --user python_package_nameIf you remove the --user option, the package will be installed system-wide, and it will be available for all the users on your system. You’ll need sudo access in this case.
sudo pip3 install python_package_name
PIP doesn’t support tab completion by default. So you need to know the exact package name that you want to install. How do you get that? I show that to you in the next section.
Search for packages in PyPI
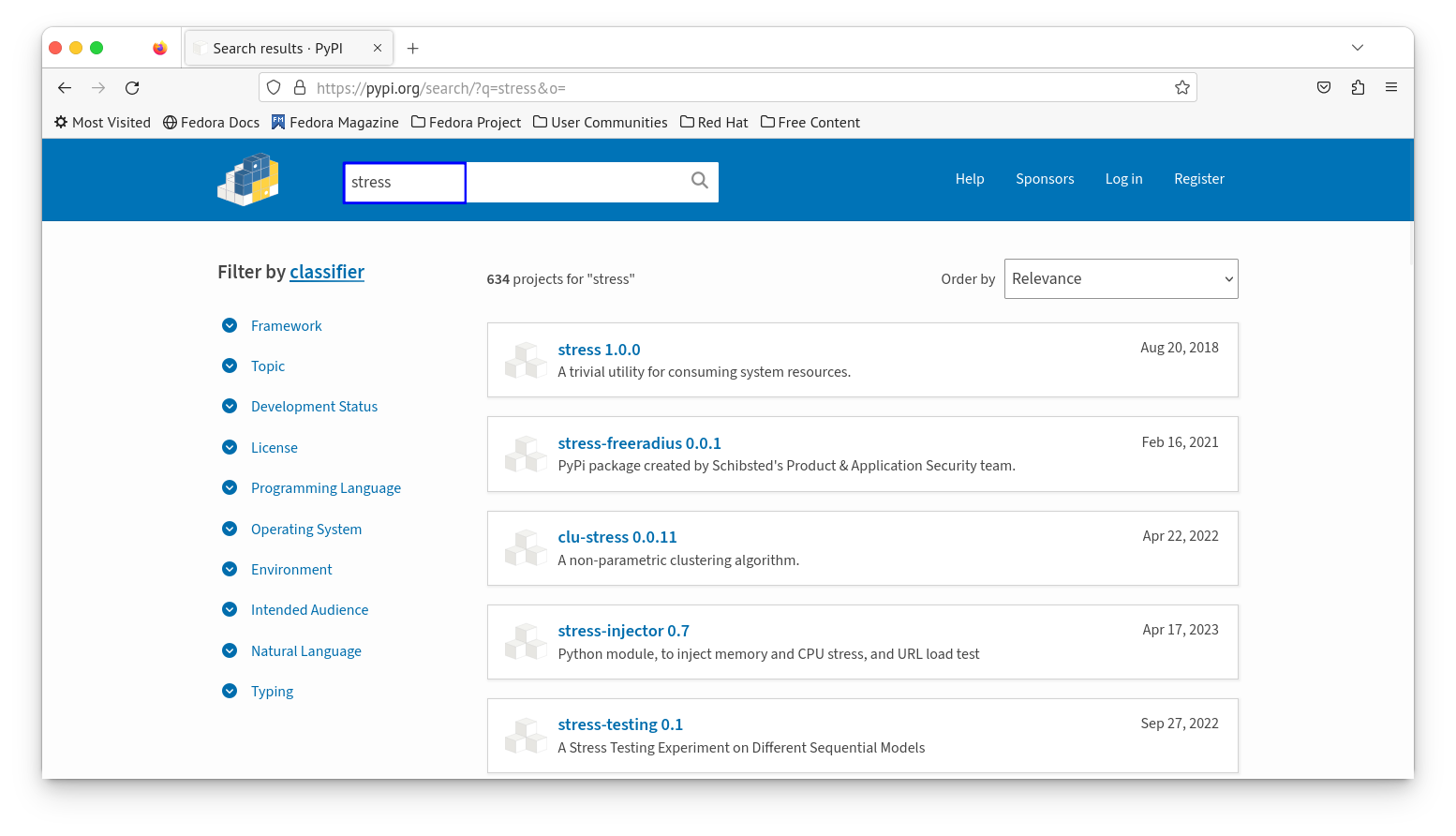
To search for packages in the Python Package Index, you can go to their official package search website.
For example, if you search on ‘stress’, it will show all the packages that have the string ‘stress’ in their name or description.
Pip had provided a command line search option, which was disabled due to excessive web traffic issues. So, if you try to use pip search package-name, you will come across an error, as shown in the screenshot below.
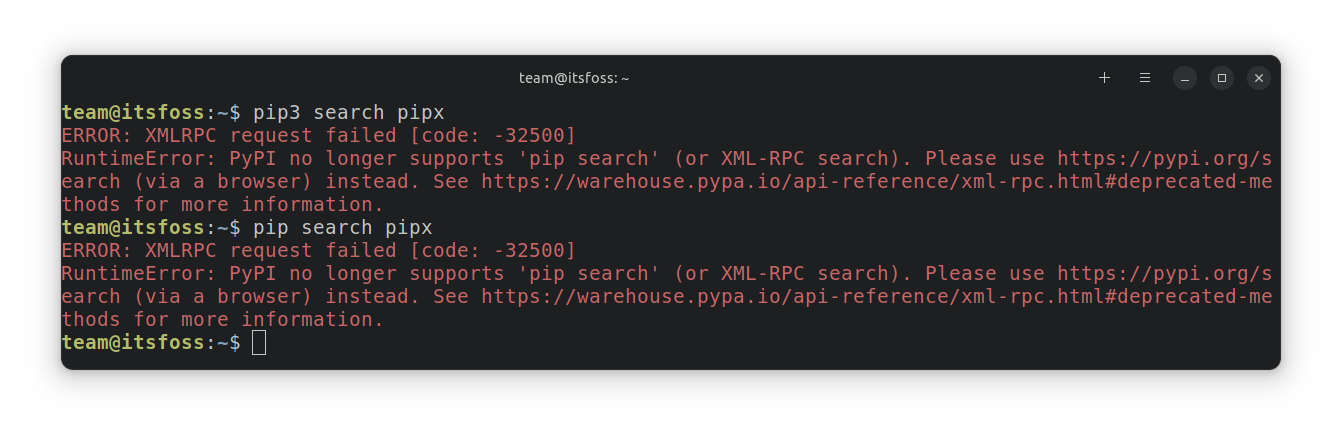
pip search errorSo, use the PyPI website instead, as mentioned above.
Upgrade Packages installed via pip
To upgrade packages installed via pip, use the command below:
pip3 install --upgrade <package-name>Remove packages installed via pip
If you want to remove a Python package installed via pip, you can use the remove option.
pip3 uninstall <installed_package_name>Uninstall Pip from Ubuntu
To remove pip from Ubuntu, open a terminal and run:
sudo apt remove python3-pip
sudo apt autoremovePipx is better! Start using it instead of Pip
Actually, if you want to use Pip for installing Python-based GUI applications, you should use Pipx. It complies with the new Python guidelines.
Using Pipx is similar to Pip so it should feel familiar.

I hope you like this tutorial on installing and using Pip on Ubuntu and hopefully on other distributions, too. Let me know if you have questions or suggestions.
It's FOSS turns 13! 13 years of helping people use Linux ❤️
And we need your help to go on for 13 more years. Support us with a Plus membership and enjoy an ad-free reading experience and get a Linux eBook for free.
To celebrate 13 years of It's FOSS, we have a lifetime membership option with reduced pricing of just $76. This is valid until 25th June only.
If you ever wanted to appreciate our work with Plus membership but didn't like the recurring subscription, this is your chance 😃


