
I have been using Linux for a decade now and this is why sometimes I take things for granted.
Copy-pasting in the Linux terminal is one such thing.
I thought everyone already knew this until one of the It’s FOSS readers asked me this question. I gave the following suggestion to the Ubuntu user:
I thought of elaborating on this topic especially when there is no single universal way of copying and pasting in the Linux terminal.
How to copy and paste text and commands in the Linux terminal
There are several ways to do this.
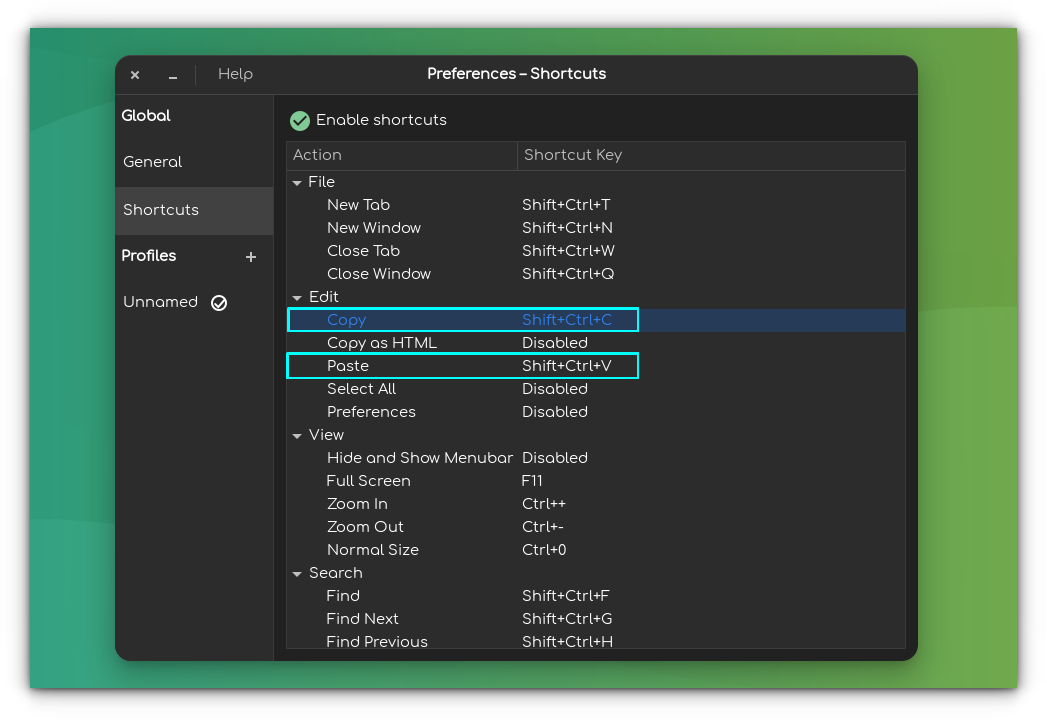
Method 1: Using keyboard shortcuts for copy-pasting in the terminal
On Ubuntu and many other Linux distributions, you can use Ctrl+Insert or Ctrl+shift+C for copying text and Shift+Insert or Ctrl+shift+V for pasting text in the terminal.

The copy-pasting also works for external sources. If you copy a command example from It’s FOSS website (using the generic Ctrl+C keys), you can paste this command into the terminal using the Ctrl+Shift+V into the terminal.
Similarly, you can use Ctrl+shift+C to copy text from the terminal and then use it to paste in a text editor or web browser using the regular Ctrl+V shortcut.
Basically, when you are interacting with the Linux terminal, you use the Ctrl+Shift+C/V for copy-pasting.
Method 2: Using right-click context menu for copy-pasting in the terminal
Another way of copying and pasting in the terminal is by using the right-click context menu.
Select the text in the terminal, right click and select Copy. Similarly, to paste the selected text, right-click and select Paste.
Method 3: Use the mouse to copy and paste into the Linux terminal
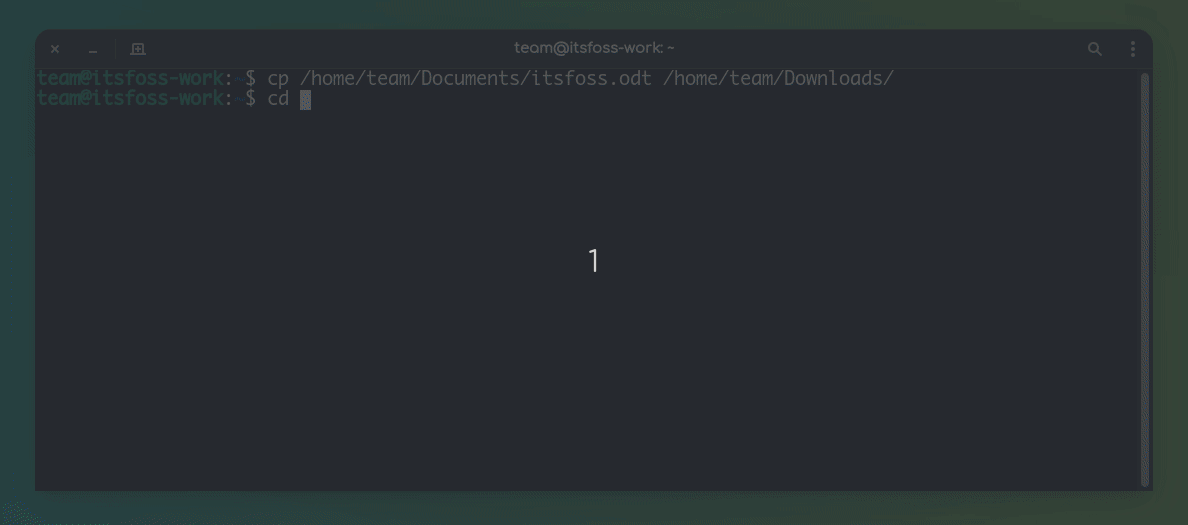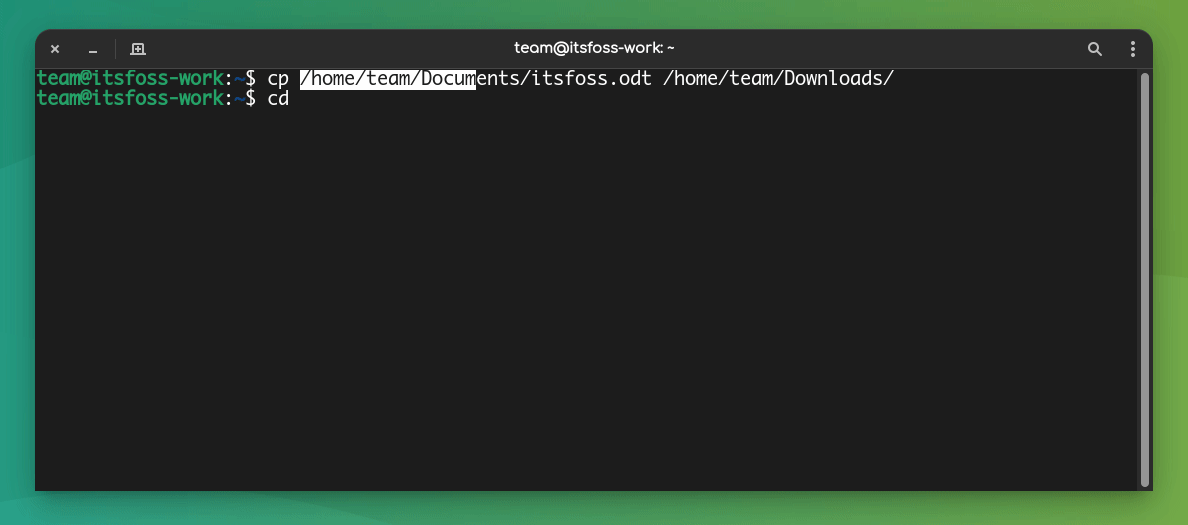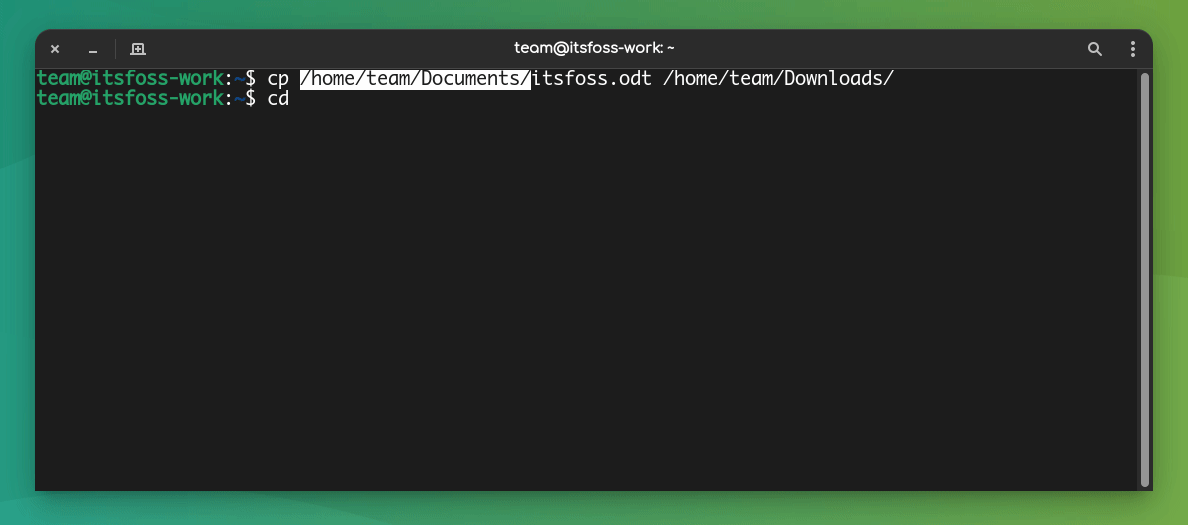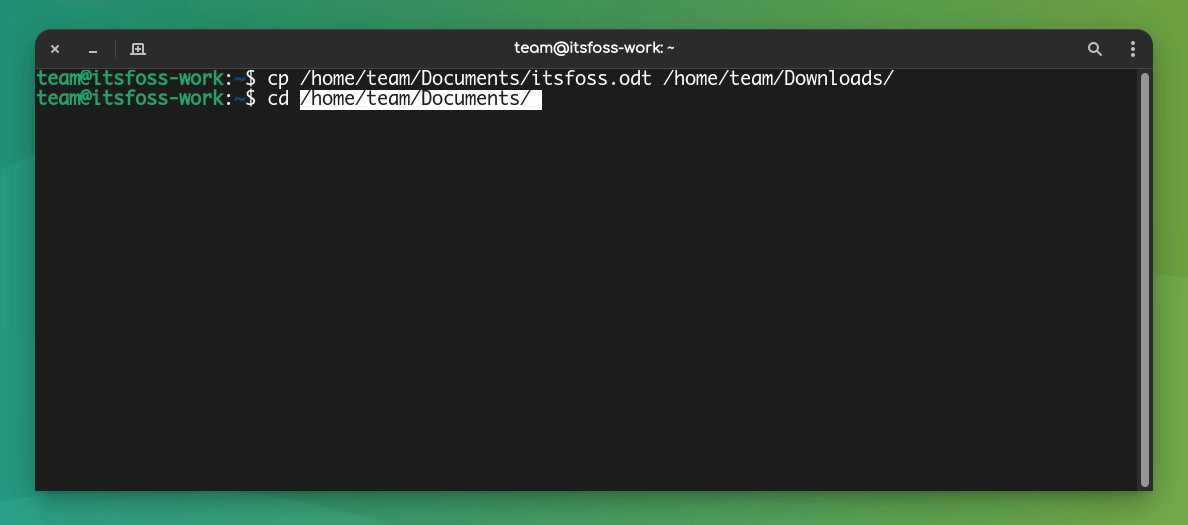
Another way to copy-paste in a Linux terminal is by using only the mouse.

You can select the text you want to copy and then press the middle mouse button (scrolling wheel) to paste the copied text.
Please keep in mind that these methods may not work in all the Linux distributions for a specific reason that I explain in the next section.
Why Linux terminals do not use the ‘universal’ Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V for
No Linux terminal will give you Ctrl+C for copying the text. This is because by default Ctrl+C keybinding is used for sending an interrupt signal to the command running in the foreground. This usually stops the running command.

This behaviour has been existing long before Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V started being used for copy-pasting text.
Since the Ctrl+C keys are ‘reserved’ for stopping a command, they cannot be used for copying.
The keyboard shortcut CTRL + S in the Linux terminal is used to send a "stop" signal to the terminal, which results in a frozen terminal. Just use Ctrl+Q and you can use the terminal again.
There are no universal key shortcuts for copy-paste in the Linux terminal. Here’s why!
The keybindings for copy-pasting are dependent on the terminal emulator (commonly known as terminal) you are using.
If you didn’t know that already, a terminal is just an application, and you can install other terminals like Guake or Terminator.
Different terminal applications may have their own keybindings for copying and pasting like Alt+C/V or Ctrl+Alt+C/V.
Most Linux terminals use the Ctrl+Shift+C/V keys but if it doesn’t work for you, you may try other key combinations or configure the keys from the preferences of the terminal emulator.
Conclusion
I know this is elementary for the Sherlock Holmes of the Linux world but it could still be useful to the Watsons.
If you are absolutely new to the terminal, this is going to help you a great deal.

New or not, you may always use shortcuts in the Linux terminal to make your life easier.

If you really care about increasing productivity through the Linux terminal, these handy Linux command tips and tricks will be a good starting point.

💬 Do you still have questions? The comment section is all yours.



