
Here's the scenario. You can connect to a remote Linux system over SSH and you find yourself in a situation where you have to copy some files from the remote server to your local system.
How do you do that? You can use the good old scp command in the following manner:
scp remote_username@remote_server_IP:/dir/location/filename local_dir_pathIf you want to copy some files from local to remote system:
scp local_dir_path/filename remote_username@remote_server_IP:/dir/location Pay attention to the use of colon (:) between the remote server details and the path.
You can also use the rsync command here. Let me go over these steps in detail in this tutorial.
My environmental setup consists of a Raspberry Pi working as the remote server. I can SSH into the Pi easily from my TUXEDO laptop.
Using scp command
The scp command, short for secure copy, uses the SSH connection to transfer files between remote systems. I like it because its syntax is similar to the cp command.
Copy files from local machine to remote server
I have a sample.txt file in the Documents directory. I want to send this file to the remote server in its Template directory.
Do you remember the syntax:
scp local_dir_path/filename remote_username@remote_server_IP:/dir/location It will ask for a password which is the password for the user on the remote server.
Let's use it in the example here:
scp Documents/sample.txt [email protected]:~/TemplatesAnd here is the output for the command:
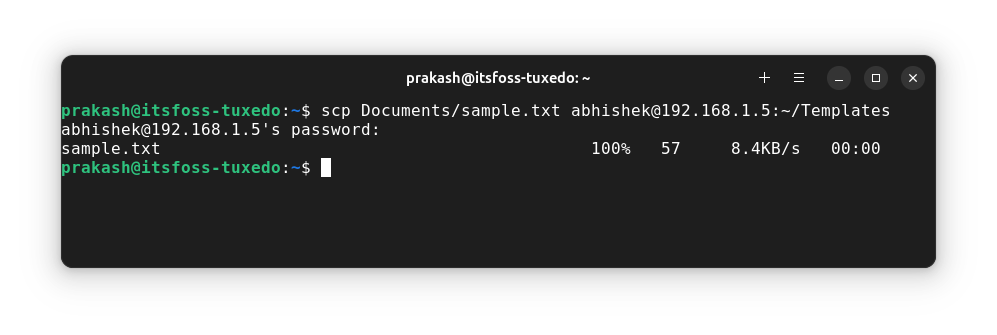
I used the ~ notation for the home directory of the user as it is shorter to write than /home/username.
You can verify it by connecting to the remote server via SSH. This is why I keep a separate terminal session open.
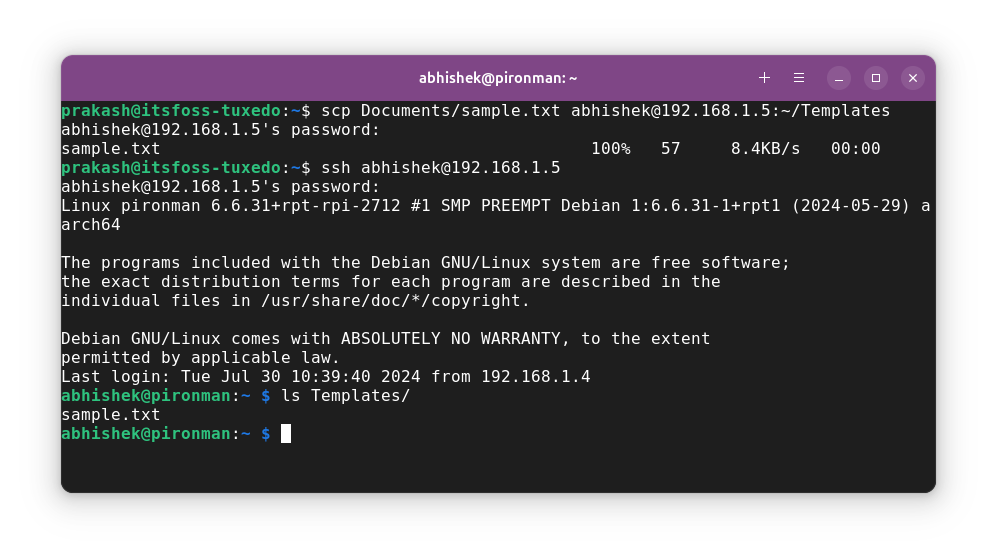
Copying multiple files
Use the same logic as the cp command:
scp file1 file2 fileN remote_username@remote_server_IP:/dir/location Copy a folder to remote system
Like you do with the cp command, use the recursive option -r:
scp -r Dir1 remote_username@remote_server_IP:/dir/location Copy files from remote server to local machine
Let's turn the tables now. Let's copy files from the remote server to the local machine. Here's the syntax:
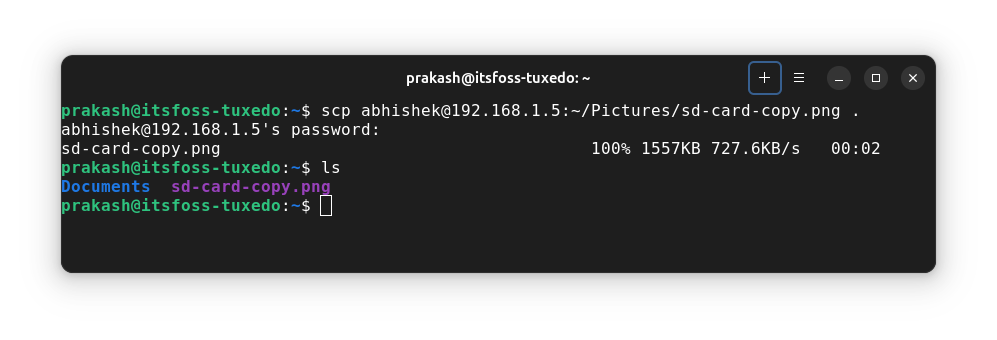
scp remote_username@remote_server_IP:/dir/location/filename local_dir_pathLet's say I have a few screenshots on the Pi and I want them on my laptop.
scp [email protected]:~/Pictures/sd-card-copy.png .I copied the remote file to my current working directory.
Copying multiple files?
This gets tricky as copying multiple files will mean providing full path (including user name and IP address) for all the files. If you can use wild card matching, go for it otherwise, copy the desired files in a new temp directory and copy this temp directory to the local system.
scp -r remote_username@remote_server_IP:/dir_location local_dir_pathUsing rsync command
rsync is another powerful command that gives you the ability to copy files between remote systems. Unlike scp, rsync is more than just a simple transfer command, it has more powerful features that make it a good backup tool when used in combination with cron jobs.
Here, I'll only show you how to use it for simple file transfers.
Copy files/directories from local to remote
To copy a file from local system to the remote server, you can use rsync command in this fashion:
rsync local_file_path remote_username@remote_server_IP:/dir/location
Let's take an example where I want to copy a local directory NewDir into the Documents directory of the remote Raspberry Pi:
rsync -r Documents/NewDir [email protected]:~/Documents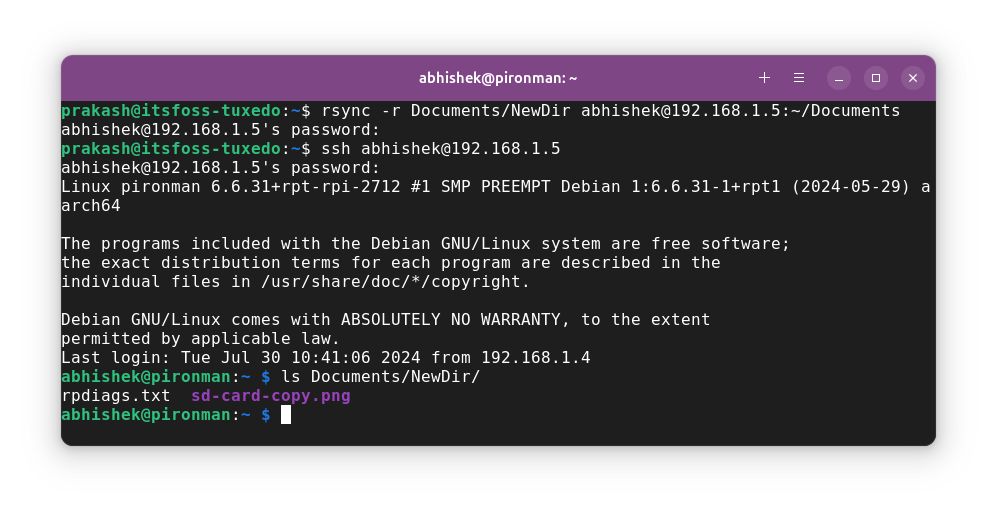
Copy files/directories from remote to local
To copy a file or directory from the remote machine to the local, use rsync in this fashion:
rsync remote_username@remote_server_IP:/file_location local_dir_pathLet's say I want to copy rpdiags.txt from the home directory of the remote system to my current working directory on the local:
rsync [email protected]:~/rpdiags.txt .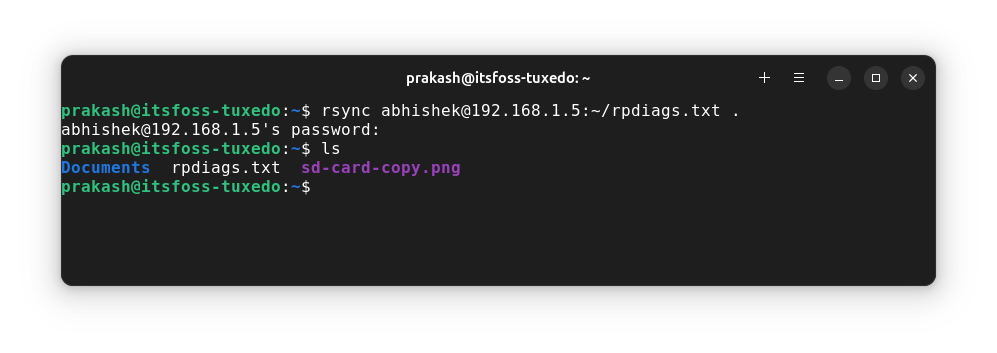
Conclusion
If you have an SFTP server setup, you can use a GUI tool like FileZilla.

I prefer using the scp command for quick file transfer over SSH connection. I use rsync when I have to make a backup of a folder that consists of numerous files. More on that in some other article. Enjoy 😄


