
Fedora 41 is an exciting upgrade with numerous features and visual treats.
If you have already installed Fedora 41 or upgraded to Fedora 41, we recommend following a few essential things that can help enhance your desktop experience with Fedora 41.
If you still haven’t installed it, you may want to check out the feature list of Fedora 41 to explore more about it.
Suggested Read 📖

Some of the most essential things to do include:
1. Configure DNF for Faster Downloads of Packages
Several methods can enhance the speed of downloading packages in Fedora. By selecting the fastest mirrors, the package download speed can increase. Furthermore, if you have a sufficiently faster internet connection, then the number of parallel downloads can be changed to get faster downloads.
Just edit the DNF configuration files located at /etc/dnf/dnf.conf.
For this, open a terminal and type:
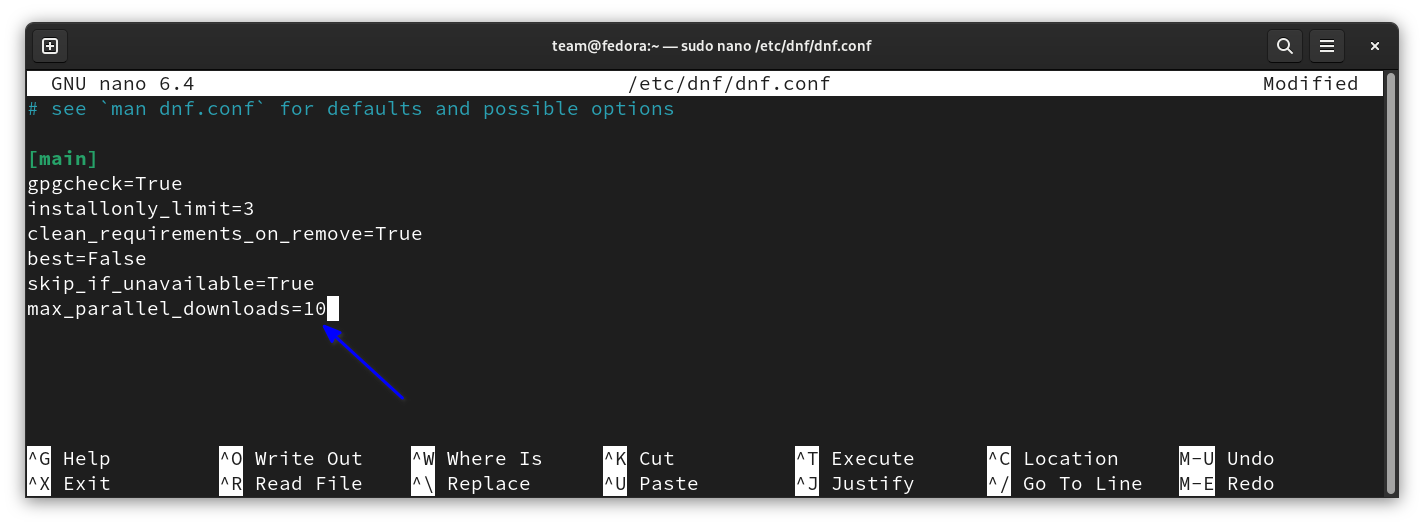
sudo nano /etc/dnf/dnf.confAppend the following line and save:
max_parallel_downloads=10The fastest mirrors work by selecting the mirror with the lowest latency. The speed difference may or may not be noticeable. So, you only choose to increase max_parallel_download as above or add the following line to pick the fastest mirror for downloads:
fastestmirror=true
2. Update the System
Whether you have the latest and greatest out-of-the-box, it is always a good thing to perform a system update, refreshing the list of repositories and upgrading any packages pushed last minute.
You can do that from the GNOME Software Center (from the Updates section) or use the terminal.
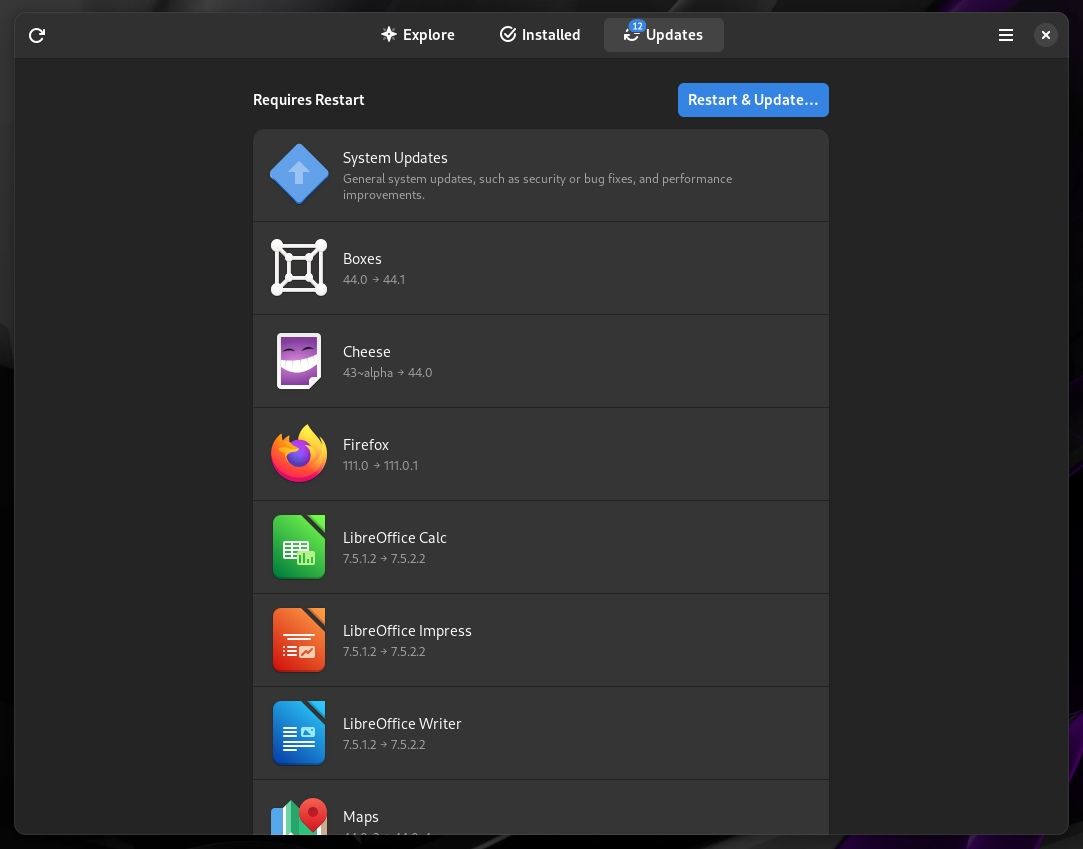
For the terminal, use the following command:
sudo dnf updateA restart may be required to complete the system update.
3. Enable RPM Fusion and Other Third-Party Repository
Fedora installer provides a method to enable additional third-party repositories for convenience. You should also get a prompt to do it in the Software Center.
You can see all the repositories available to your system. You can enable and disable them here.
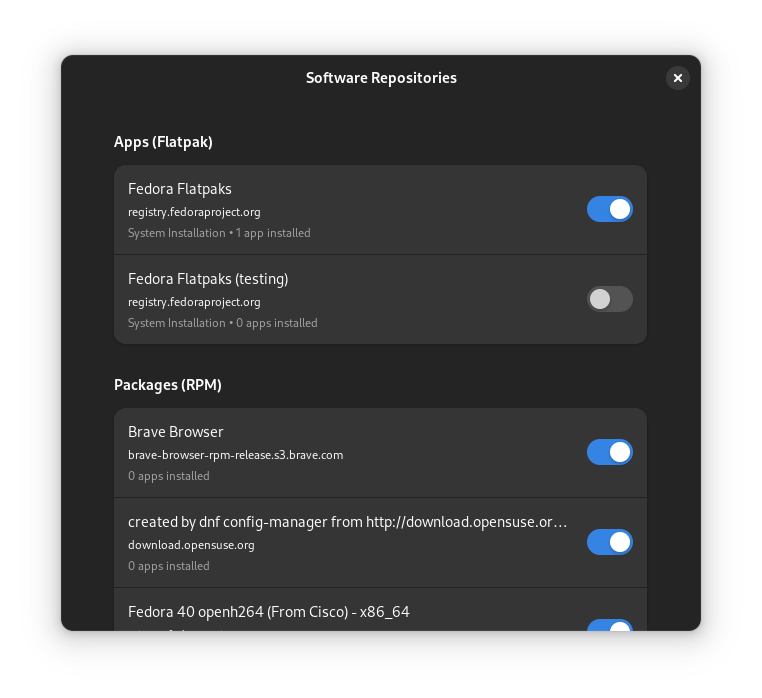
However, only the RPM repository for NVIDIA driver, Google Chrome, and Steam are added. But there are many more applications available in RPM Fusion.
So, if you need extra tools that aren’t usually available in the default repositories and the filtered RPM fusion repo, adding the RPM Fusion repo is a good idea.
To enable RPM Fusion (both free and non-free), Open a terminal and enter the following command:
sudo dnf install https://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm https://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
Popular Fedora options like Workstation (GNOME) and KDE Spin have graphical software manager, GNOME Software and KDE Discover. For these graphical package managers, RPM Fusion repositories provide Appstream metadata.
Setting this metadata will enable you to install packages from the RPM Fusion repository graphically. Once RPM Fusion is enabled, run the command:
sudo dnf update @core
sudo dnf4 update @core). This installed properly, and I was able to get RPM Fusion packages in GNOME Software.4. Enjoy the dark mode
Love the dark mode? Fedora has got you there.
In the Settings→Appearance, you can switch to the Dark style.
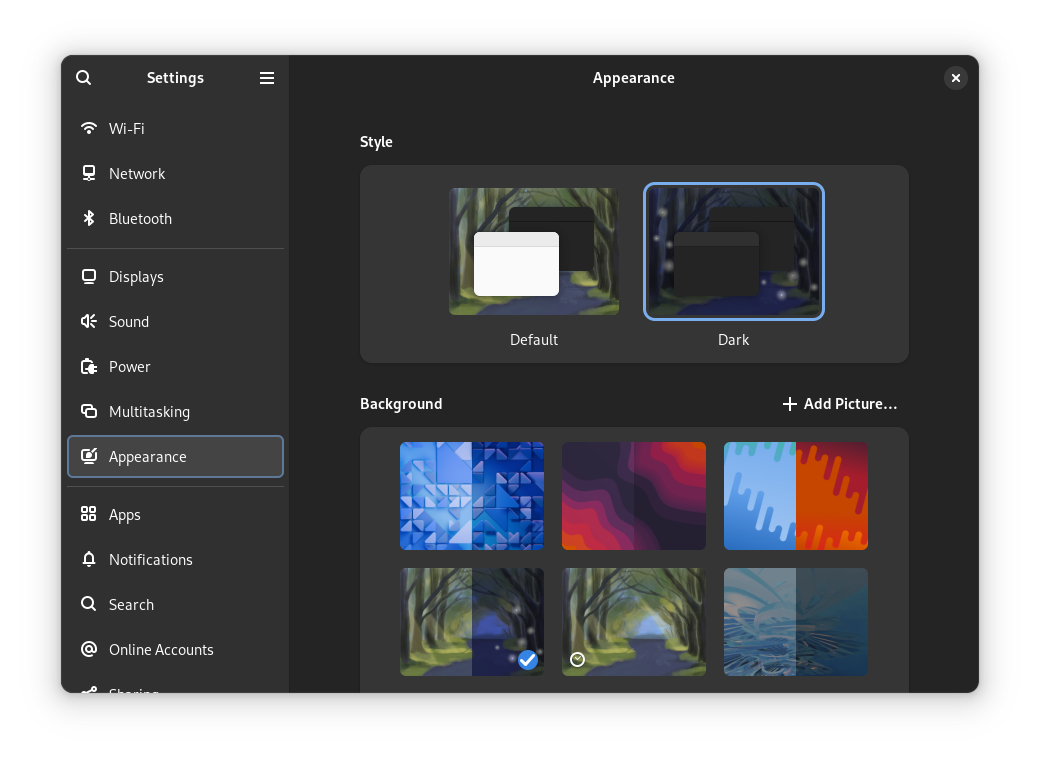
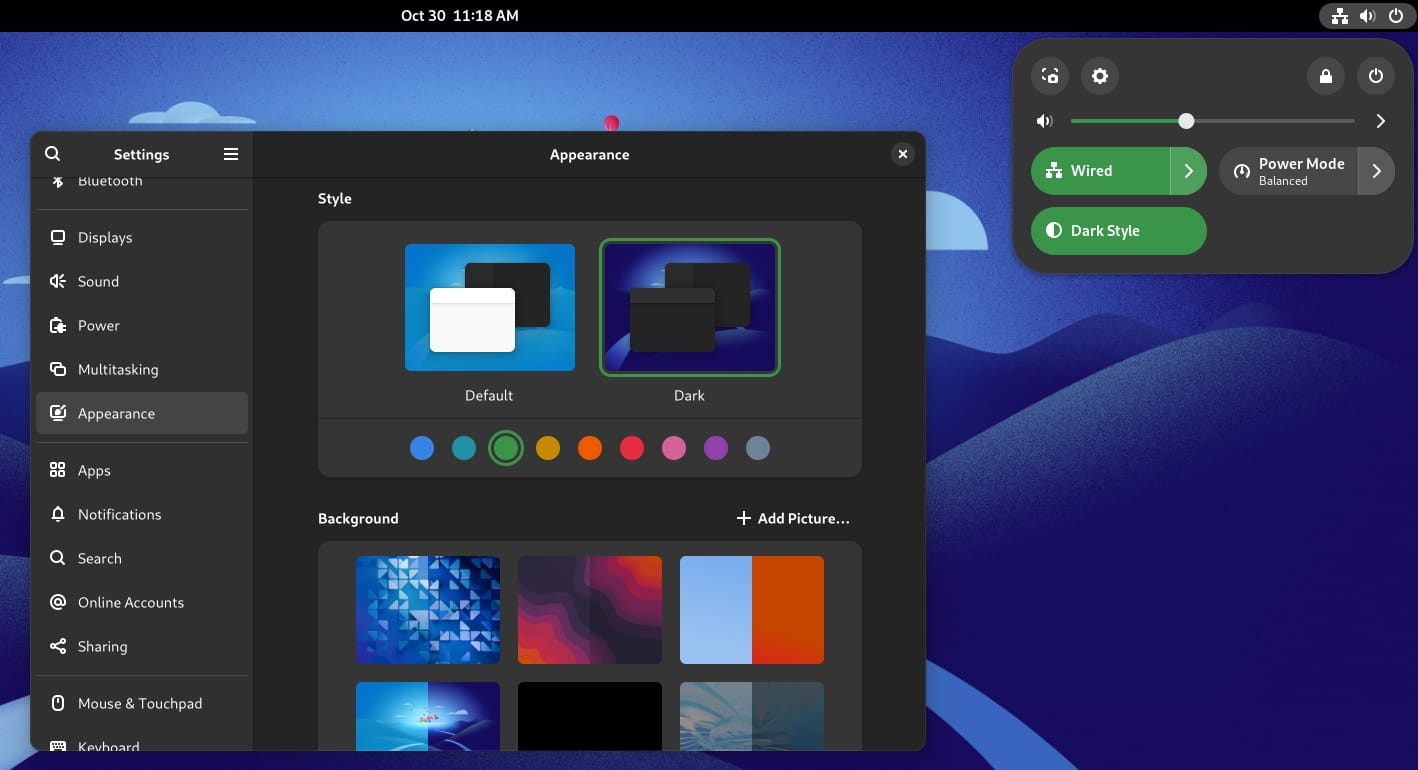
Not to forget, with this release, you finally get accent colors. So, make sure to choose the color that defines your taste! 😁
5. Install Multimedia Plugins
While you can install and use the shiny new desktop experience with Fedora 41, you cannot play videos/media on it — yet.
Of course, you can choose to install VLC, MPV with codecs packed in. Or, just manually install the multimedia codecs?
To achieve any of those, you will have to enable the RPM Fusion repository eventually.
For instance, if you want to install the VLC player after enabling the RPM fusion repo, just type the following command in the terminal:
sudo dnf install vlcIf you want to install the media codecs, use the following method.
First, change the ffmpeg-free from Fedora repository version to RPM fusion version for better support.
sudo dnf swap ffmpeg-free ffmpeg --allowerasing
Now, install additional codecs to your system:
sudo dnf update @multimedia --setopt="install_weak_deps=False" --exclude=PackageKit-gstreamer-plugin
dnf4 is used in place of dnf in Fedora 41.Similarly, you can install hardware accelerated codecs for Intel, AMD, and NVIDIA. You can take a look at the official documentation for more on this.
Refer to the GStreamer Plugins and their details for more codec installations.
6. Change Hostname After Installation
After installation, the default hostname is set up as fedora.
So, if you want to personalize your system hostname after installation, you can use the following command to set a new hostname:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname "New_Custom_Name"You can also do the same thing from the system settings. Open GNOME Settings and go to the About section. On this page, you can change the name from fedora to your liking.

7. Install Essential Applications
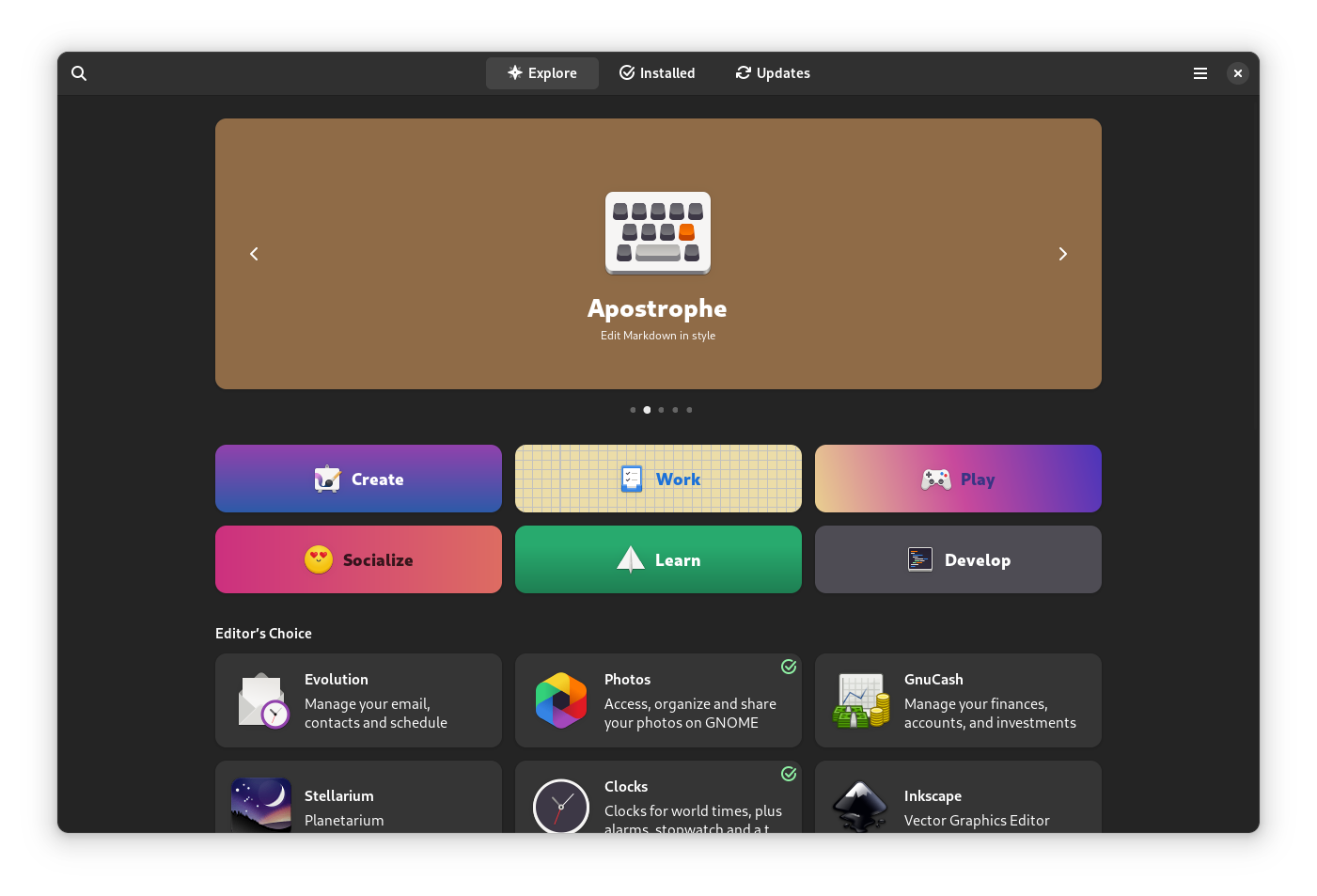
You can install essential Linux applications from the terminal using the dnf package manager or through the GNOME Software Center.
You can use the following command to install anything that you need:
sudo dnf install <package_name>
8. Install Gnome Tweaks and Extensions App
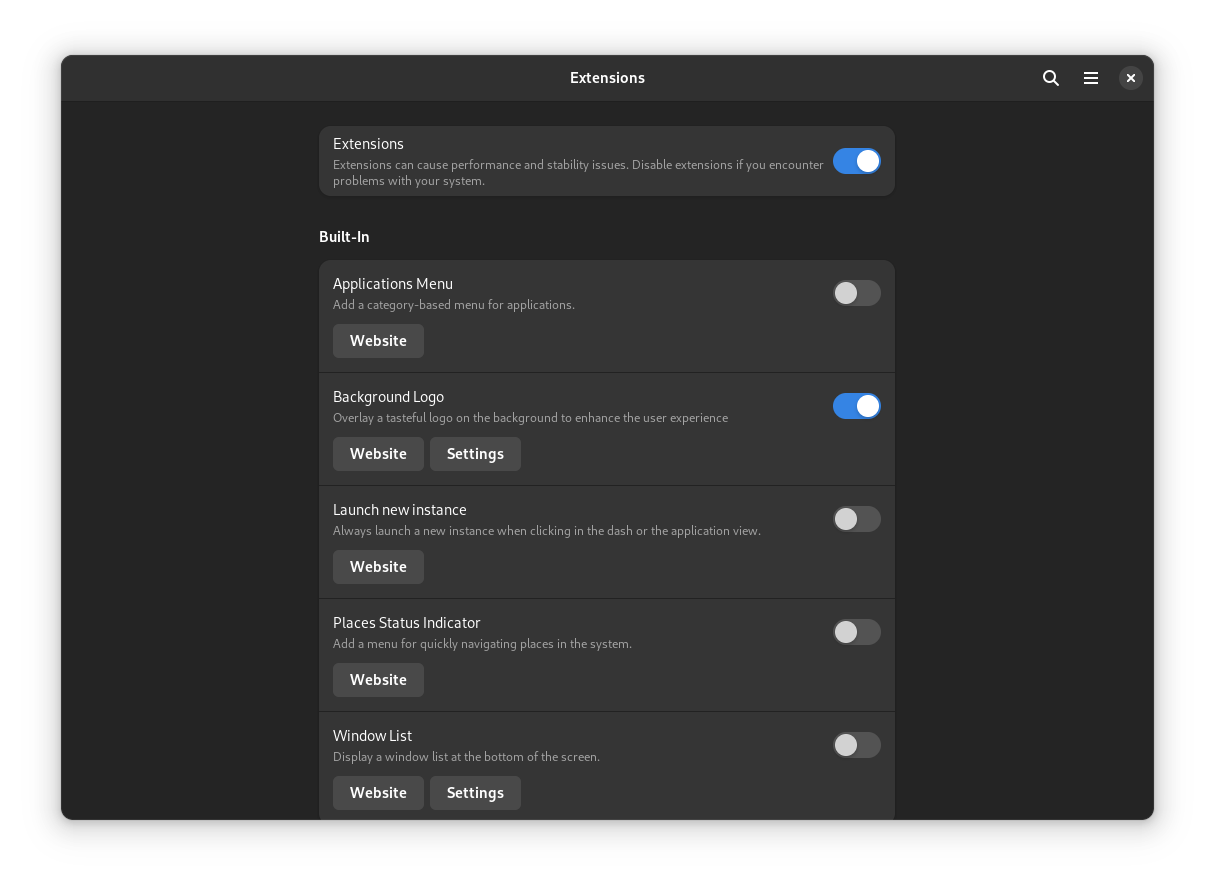
To tweak the gnome look and feel, you need to install both GNOME Tweaks and the extensions manager app. It can be done either through the software center or through the terminal using the following command:
sudo dnf install gnome-tweaks gnome-extensions-appIn my case, chrome-gnome-shell was automatically installed, which is required to make the browser extension work. You can refer to our resource on installing GNOME tweaks on Fedora if you still face issues with it.
It can be helpful to use some of the best GNOME extensions to enhance your desktop workflow.

9. Enable Minimize or Maximize Button
This isn’t for you if you are already comfortable without a minimize button in the window.
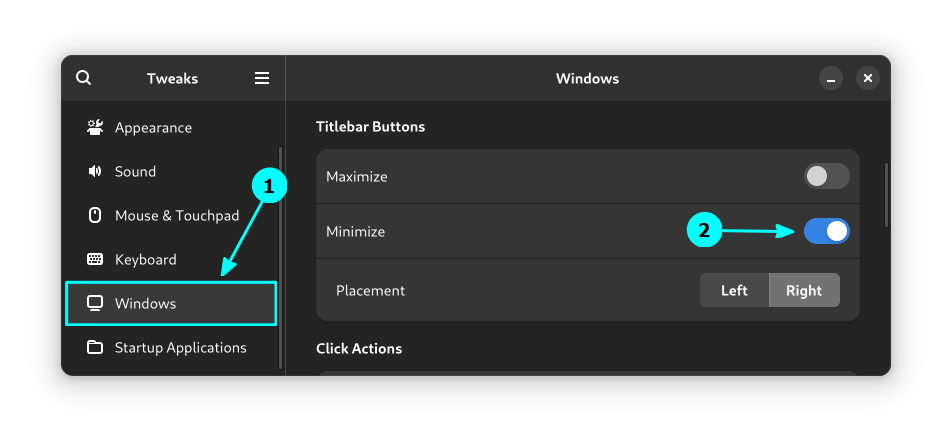
But, if you want a dedicated minimize button, you can enable it using GNOME Tweaks by heading to the Windows option and enabling the minimize button.
While you can already double-click on a window to maximize, you can still add the maximize button as well.
10. Tweak Privacy Settings
It is worth double-checking if you have the problem reporting enabled/disabled.
You can head to the Privacy settings and check if “Automatic Problem Reporting” is enabled/disabled.
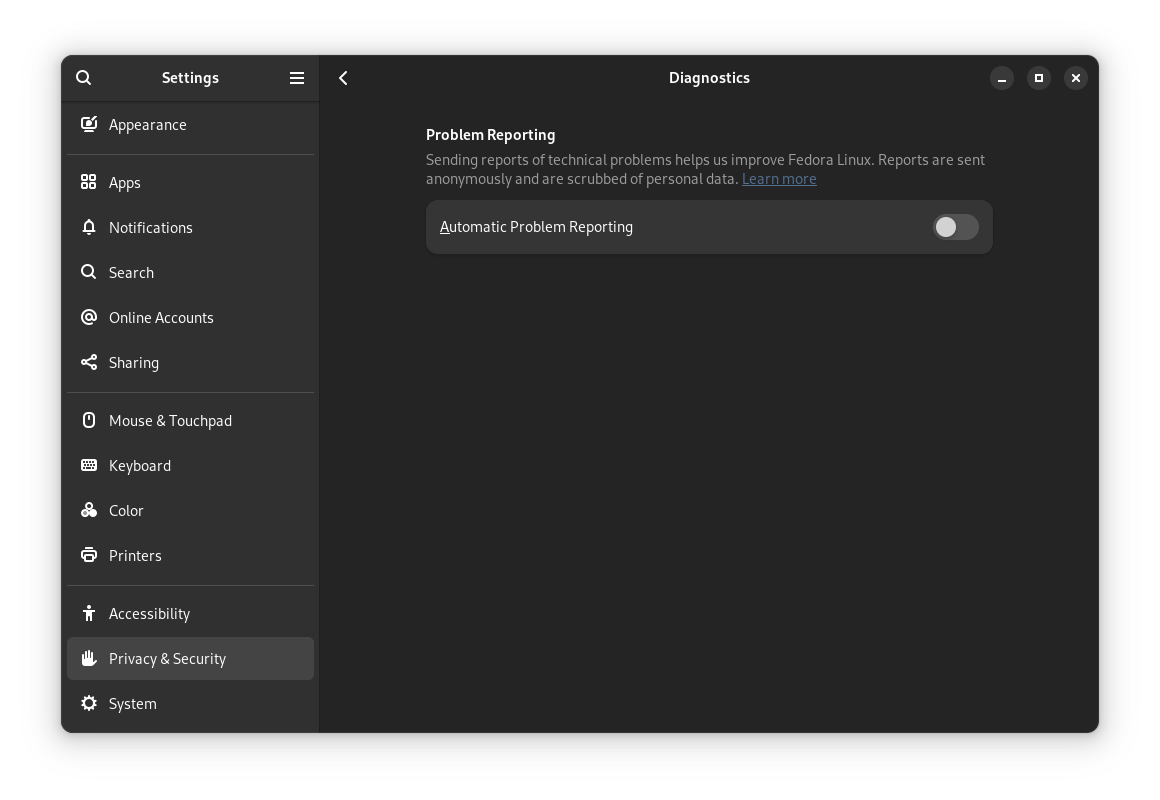
You should enable it if you do not mind sharing anonymous data for developers to improve the experience.
If you do not like the concept, disable it.
11. Screen Lock and Power Settings
If you are using a laptop, the default power saving options turn the screen blank and suspend it after a period of inactivity.
But, if you do not want that to happen, head to the power settings and disable the “Screen Blank” and “Automatic Suspend” options.
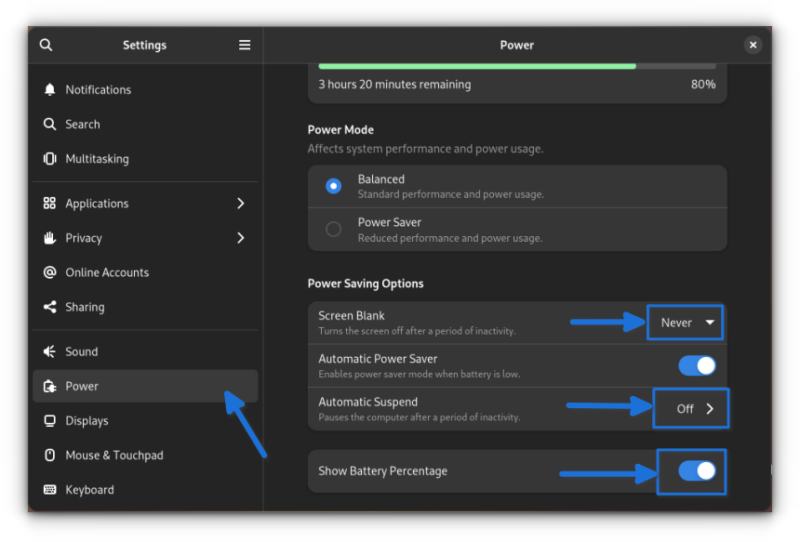
You can also choose to display the battery percentage from the same settings.
12. Use Night Light Settings
Every distribution comes packed with the night light feature to help you reduce eye strain.
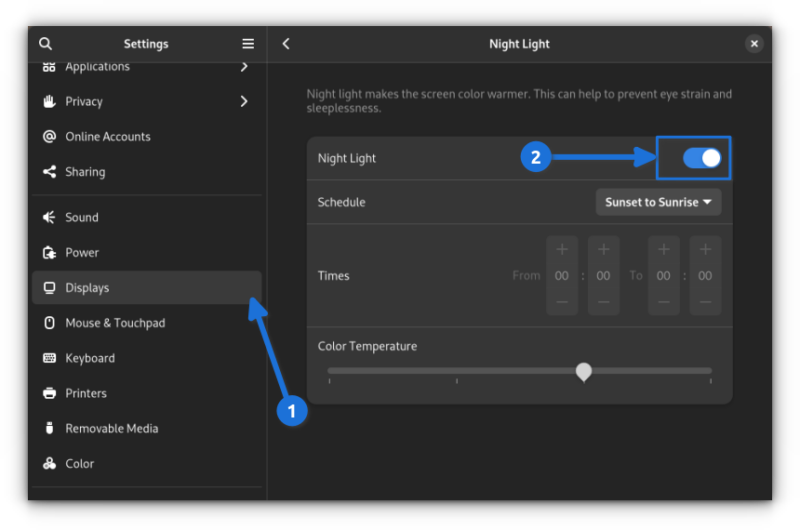
For Fedora, you can access it in the display settings and enable it or set a schedule for it to automatically enable/disable the night light as required.
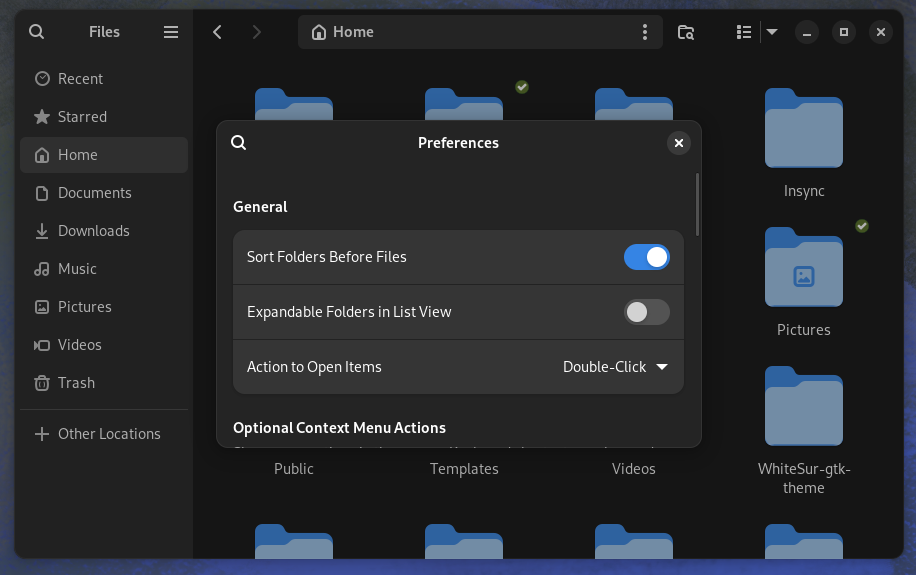
13. Sort Folder before files in Nautilus File Manager
This is rather a simple thing but may annoy a first-time user if you want to view the folders listed first.
In that case, go to preferences in Files and toggle the Sort Folders Before Files option as shown in the image below.
14. Automatically Delete Trash Content
We tend to delete things, but then forget to delete them from the trash.
In such cases, the size of the trash/bin grows, and we may end up with low storage space.
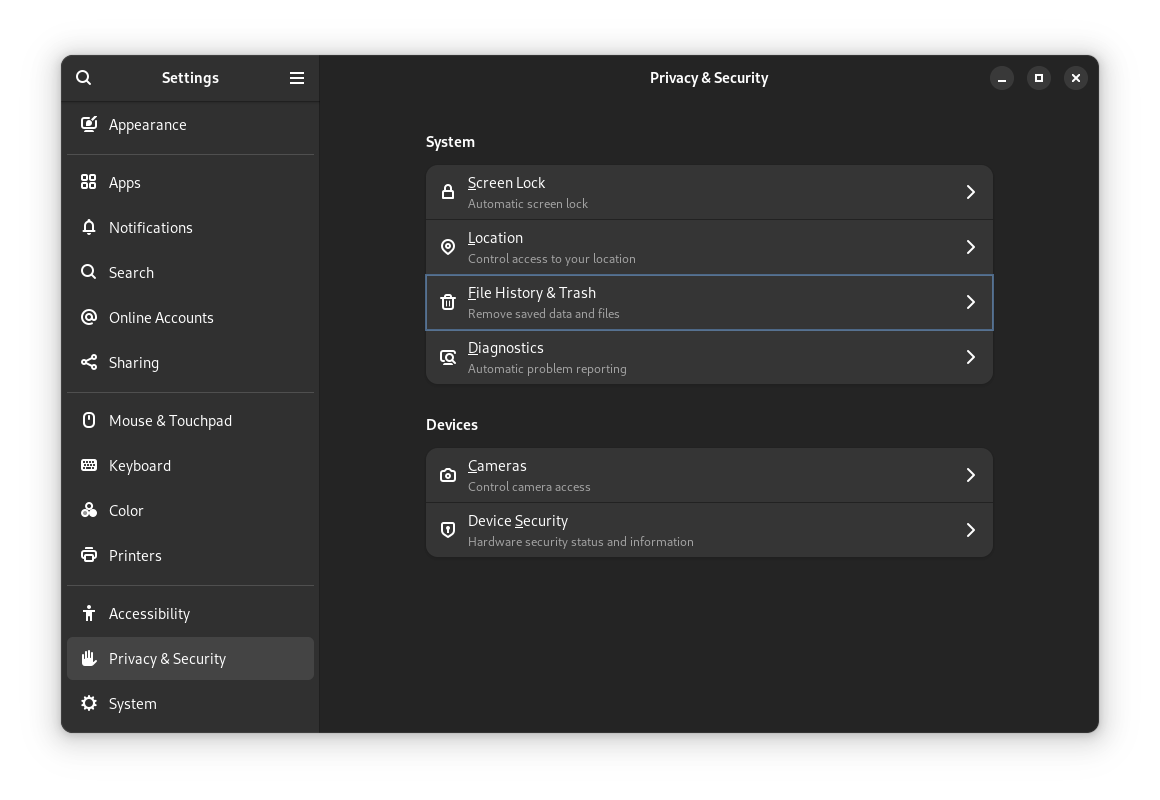
To avoid this, Go to Settings → Privacy & Security and toggle the Automatic Delete Trash Content option as required.
The automatic deletion period can be set in the same window if you want to tweak that. The default value is set to 30 days.
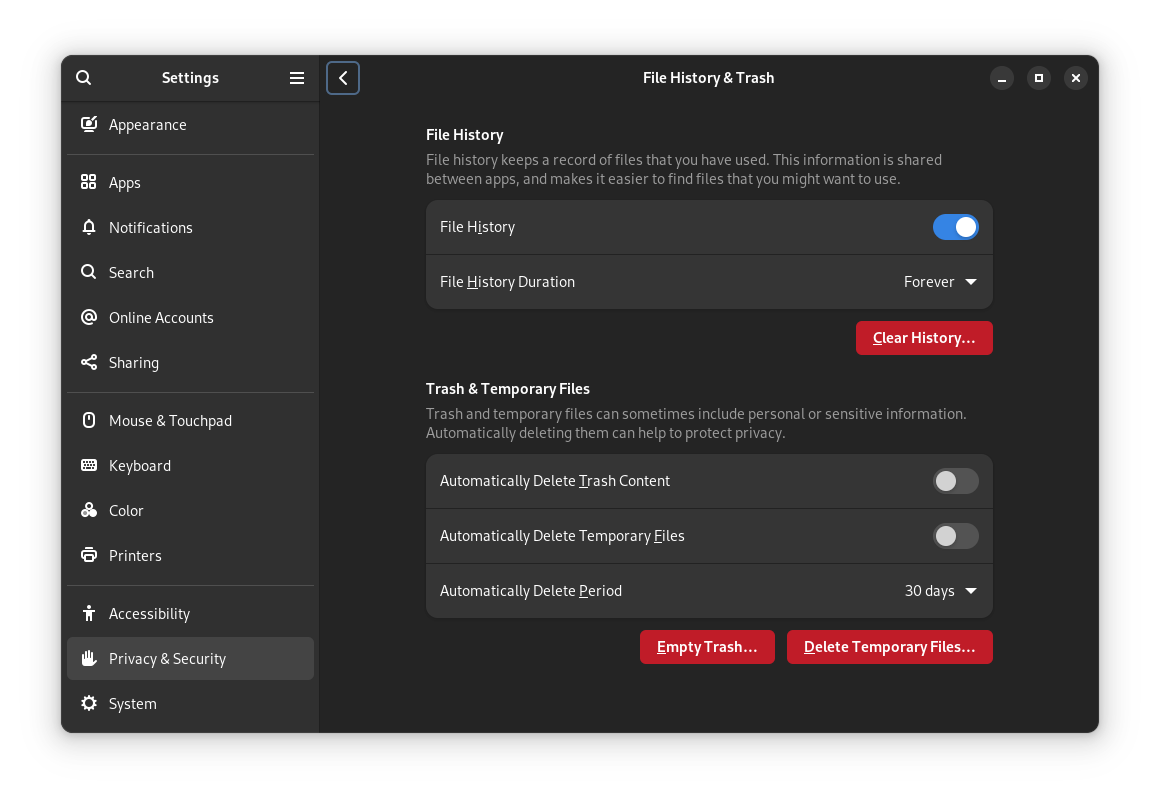
Automatically delete trash content
15. Set the Power Profiles
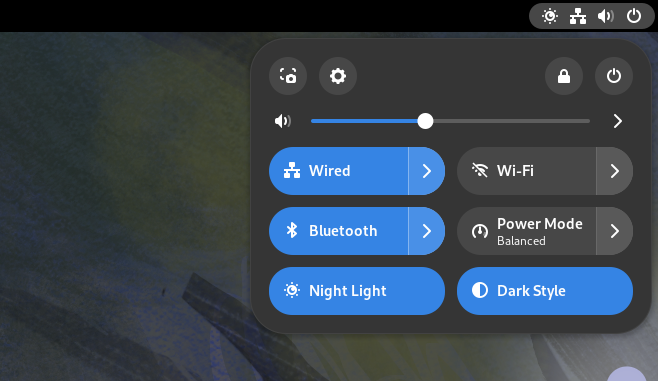
Power profiles are accessible from the Settings page and through the top panel (or the system tray).
Use the appropriate mode, like balanced (which should be the default for best performance) and power saver, for better battery savings and a minor hit to the performance.
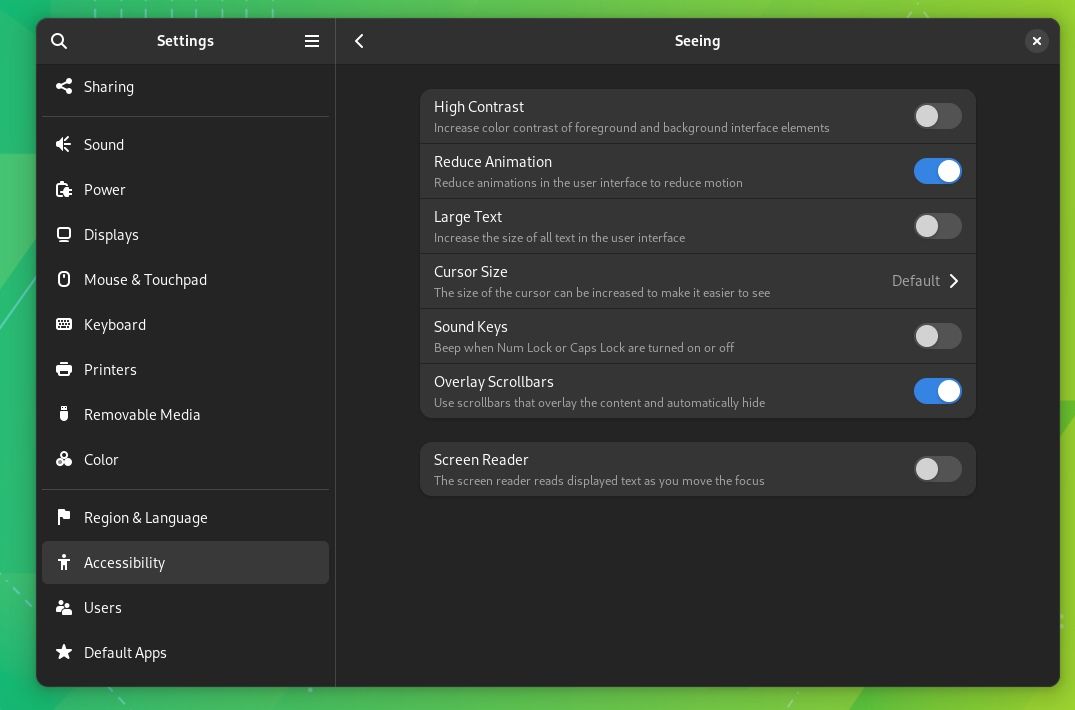
16. Reduce the animation effect for a faster response (if you need it)
If you notice any stutters with the system performance, such as launching apps or the navigation in general, try reducing the animation from accessibility settings (under Seeing) as shown in the image below.
17. Get the top panel indicator back
In the GNOME desktop, there are no applet idnicators and this makes things difficult for applications such as Spotify, Discord etc that are minimized to tray on close but keep on running.
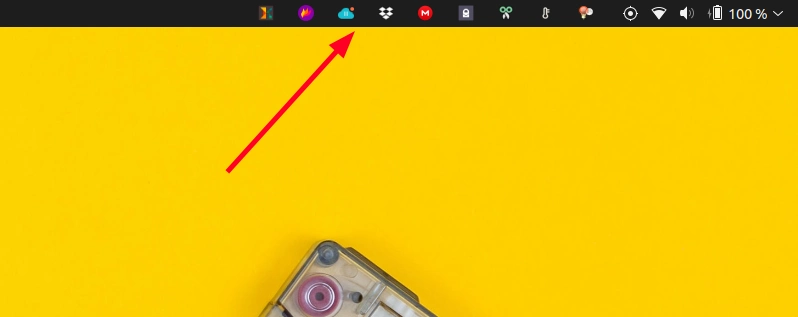
To get the top panel indicator back in GNOME, you can use an extension like AppIndicator and KStatusNotifierItem Support.
Wrapping Up
Per your use case, you can do countless more things with your Fedora 40 system.
After all, you get some of the latest and greatest packages (and kernel). So, feel free to explore more.
What do you usually do after installing/upgrading to a new version of Fedora? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below.


