
Brief: Learn various ways of installing Rust programming language on Linux along with its package manager Cargo.
Ever since Mozilla dumped Rust, it has gained even more prominence and popularity. Don’t just take my words for it. Rust is going to be included in the Linux kernel, only the second programming language after C.
Many developers have also started making awesome command line based tools in Rust. These tools are often available through the Cargo package manager.
This is why it matters to install Rust support in Linux, both for the programmers and the end users.
Officially, Rust documents suggest installing Rust in Linux by downloading and executing the installer script in this manner:
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | shThat could work. However, your distribution probably already packages Rust. Using your distribution’s package manager is also an option.
Let me walk you through the Rust installation steps for both official Rust way and package manager way.
Method 1: Installing Rust on any Linux using the official method
There are a few advantages of this method:
- You get the latest Rust and Cargo version
- Rust is only installed for the current user, not system-wide
- You do not need to be root or have sudo access to install Rust for yourself this way
A few people dislike downloading and running shell scripts off the internet, even if it is coming from the official sources. However, since it does not need root access and the script is coming from the official sources, it should be safe to install it this way.
First, make sure that you have Curl installed. Use your distribution’s package manager to install it, if it is not already installed. You can install Curl on Ubuntu and Debian using the apt command:
sudo apt install curlNext, use this command to download the script and run it:
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh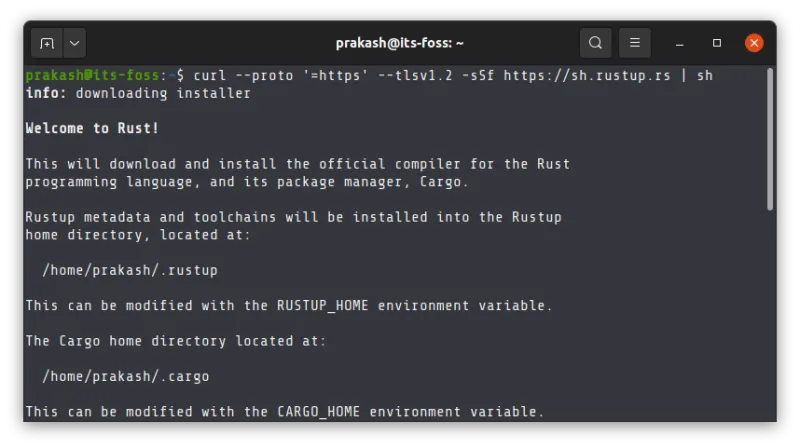
It will ask for your input on the kind of installation you want. Go with option 1:
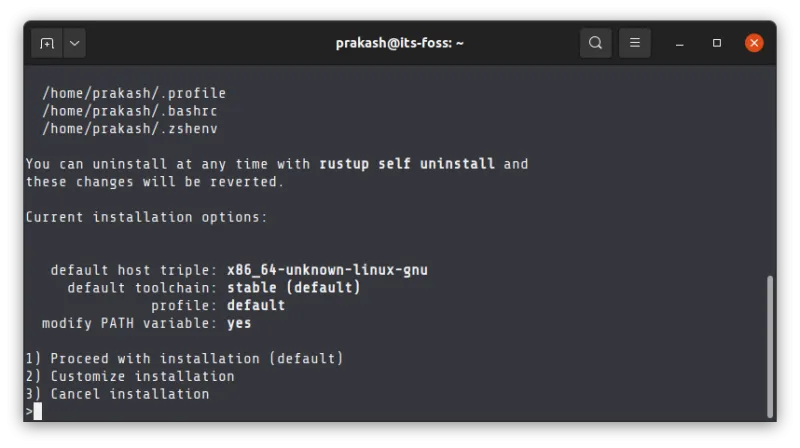
Once the script finishes the installation process, you need to source the configuration file to make the changes available for your shell.
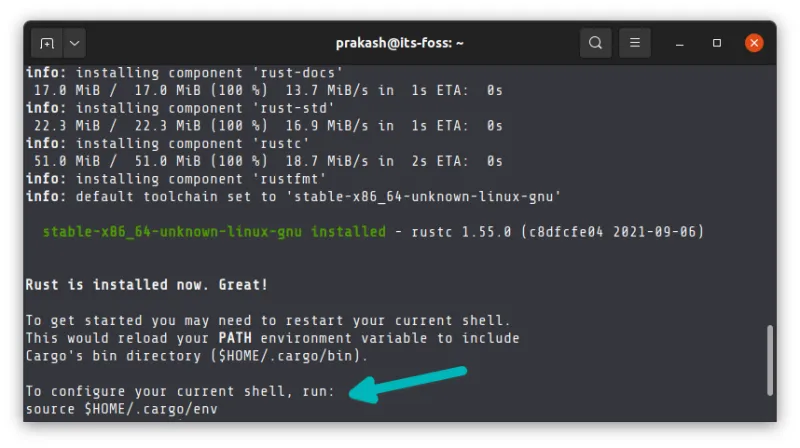
Source the file:
source $HOME/.cargo/envOnce it is done, verify that rust is available for you by checking the installed version:
rustc --version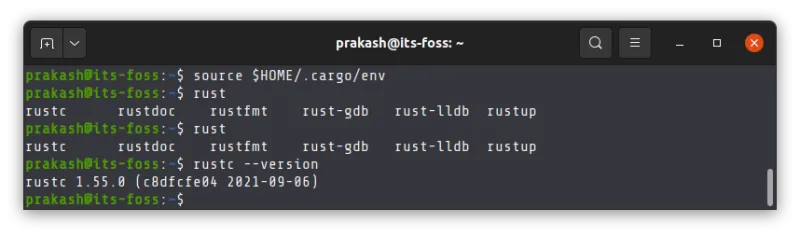
Here's a replay of the Rust installation (click to enlarge):

rustup updateLet me quickly show how to remove rust installed this way before you see the other installation method.
Removing Rust installed the official way
In a terminal, use the following command to remove Rust from your system:
rustup self uninstallPress Y when asked and you’ll have Rust removed from the system.
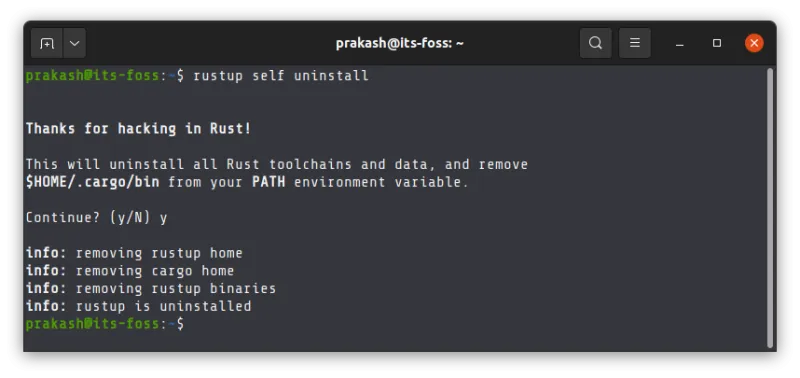
Here's a replay of removing Rust installed the official way.

That’s settled then. Let’s see how to use the apt command to install Rust on Ubuntu.
Method 2: Installing Rust support on Ubuntu using apt
Why would you want to use the package manager?
- It installs Rust system-wide and thus makes it available for all the users on the system
- It gets updated centrally with other system updates (if your distribution adds a new version of Rust)
There are two main Rust packages available in Ubuntu:
- rustc: The rust compiler used for Rust programming language
- cargo: Cargo is the Rust package manager and it automatically installs rustc
As a regular user, you would be using Cargo for installing Rust-based applications. As a programmer, you’ll need Cargo to get other Rust packages or create your own.
Since Cargo includes rustc, I would advise installing it so that all required packages are installed in one go.
sudo apt install cargoYou’ll be asked to enter your account’s password.
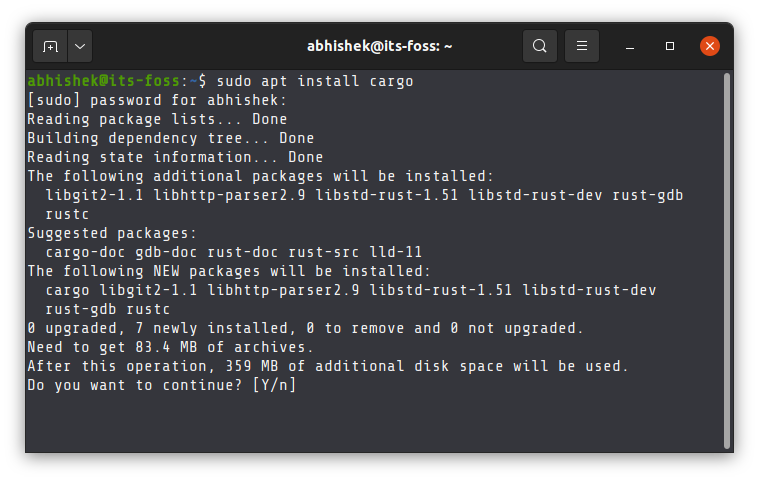
You are, of course, free to use apt install rustc and install only Rust. That choice lies with you.
You may verify that Rust is installed for you and all the other users (if you want to):
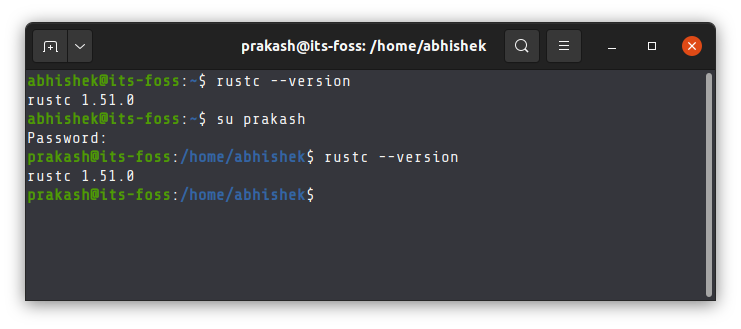
Here's a replay of Rust installation with apt in Ubuntu.

That’s good. Let me quickly show the uninstall step as well.
Removing Rust using apt remove
To remove Rust, you can remove Cargo first and then use the autoremove command to remove the dependencies installed with it.
sudo apt remove cargoNow run the autoremove:
sudo apt autoremoveHere's the replay uninstall Rust with apt command:

That’s it. You now know all the essentials about installing Rust on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions. Questions and suggestions are always welcome.

