
You may find yourself in a situation where you need to know the exact Linux kernel version used on your system. You can easily find that out thanks to the powerful Linux command line.
How do I find the Linux kernel version?
You can use the following command to get the Linux kernel version:
uname -rYou'll see an output like this:
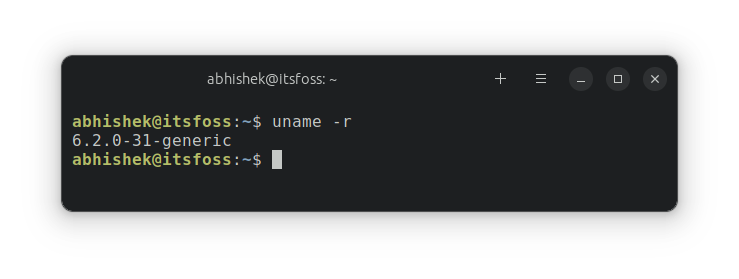
Which shows that the kernel version in use is 6.2. I'll share what does generic means in the output along with tips on getting even more detailed information about kernels.
1. Find Linux kernel using uname command
uname is the Linux command for getting system information. You can also use it to find out whether you’re using a 32-bit or 64-bit system.
Open a terminal and type in the following command:
uname -r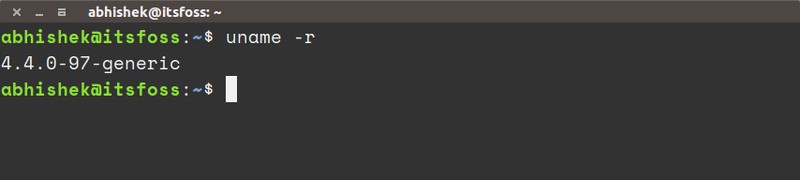
The output will be something similar to this:
4.4.0-97-genericThis means that you’re running Linux kernel 4.4.0-97, or in more generic terms, you are running Linux kernel version 4.4.
But what do the other digits mean here? Let me explain:
- 4 – Kernel version
- 4 – Major revision
- 0 – Minor revision
- 97 – Bug fix
- generic – Distribution-specific string. For Ubuntu, it means I’m using the desktop version. For Ubuntu server edition, it would be ‘server’.
Get even more details on the Linux kernel
You can also use the uname command with the option -a. This will provide more system information if you need it.
uname -a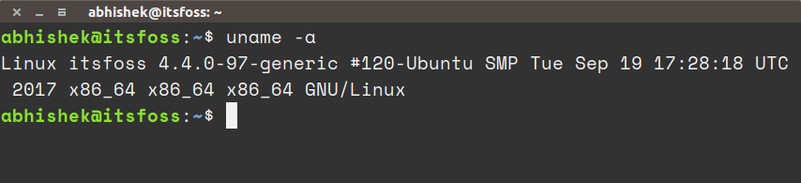
The output of the command should look like this:
Linux itsfoss 4.4.0-97-generic #120-Ubuntu SMP Tue Sep 19 17:28:18 UTC 2017 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/LinuxLet me explain the output and what it means:
- Linux – Kernel name. If you run the same command on BSD or macOS, the result will be different.
- itsfoss – Hostname.
- 4.4.0-97-generic – Kernel release (as we saw above).
- #120-Ubuntu SMP Tue Sep 19 17:28:18 UTC 2017 – This means that Ubuntu has compiled 4.4.0-97-generic 120 times. A timestamp for the last compilation is also there.
- x86_64 – Machine architecture.
- x86_64 – Processor architecture.
- x86_64 – Operating system architecture (you can run a 32-bit OS on a 64-bit processor).
- GNU/Linux – Operating system (and no, it won’t show the distribution name).
But I’ll save you from information overload. Let’s see some other commands to find your Linux kernel version.
2. Find Linux kernel using /proc/version file
In Linux, you can also find the kernel information in the file /proc/version. Just look at the contents of this file:
cat /proc/version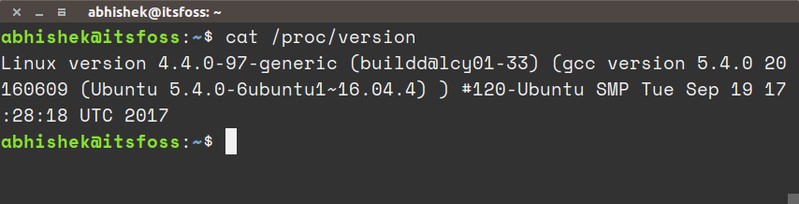
You’ll see an output similar to what you saw with uname.
Linux version 4.4.0-97-generic (buildd@lcy01-33) (gcc version 5.4.0 20160609 (Ubuntu 5.4.0-6ubuntu1~16.04.4) ) #120-Ubuntu SMP Tue Sep 19 17:28:18 UTC 2017You can see the kernel version 4.4.0-97-generic here.
3. Find Linux kernel version using dmesg command
dmesg is a powerful command used for writing kernel messages. It’s also very useful for getting system information.
Since dmesg provides an awful lot of information, you should normally use a command like less to read it. But since we’re here just to check the Linux kernel version, grepping on ‘Linux’ should give the desired output.
dmesg | grep Linux
The output will have a few lines but you should be able to identify the Linux kernel version there easily.
[ 0.000000] Linux version 4.4.0-97-generic (buildd@lcy01-33) (gcc version 5.4.0 20160609 (Ubuntu 5.4.0-6ubuntu1~16.04.4) ) #120-Ubuntu SMP Tue Sep 19 17:28:18 UTC 2017 (Ubuntu 4.4.0-97.120-generic 4.4.87)
[ 0.182880] [Firmware Bug]: ACPI: BIOS _OSI(Linux) query ignored
[ 1.003861] Linux agpgart interface v0.103
[ 1.007875] usb usb1: Manufacturer: Linux 4.4.0-97-generic xhci-hcd
[ 1.009983] usb usb2: Manufacturer: Linux 4.4.0-97-generic xhci-hcd
[ 5.371748] media: Linux media interface: v0.10
[ 5.399948] Linux video capture interface: v2.00
[ 5.651287] VBoxPciLinuxInitGet more Linux system information
Of the three ways discussed here, I use uname all the time. It’s the most convenient.
If you are interested, here are a few more articles to learn more about your Linux system.


What about you? Which command do you prefer for getting Linux kernel information?


