
If you have this habit of downloading everything from the web like me, you will end up having multiple duplicate files. Most often, I can find the same songs or a bunch of images in different directories or end backing up some files at two different places. It’s a pain locating these duplicate files manually and deleting them to recover the disk space.
If you want to save yourself from this pain, there are various Linux applications that will help you in locating these duplicate files and removing them. In this article, we will cover how you can find and remove these files on Ubuntu.
Czkawka: GUI tool to find and remove duplicate files
Czkawka helps you search and remove duplicate files, empty directories. It is written in Rust and has both GUI and CLI interfaces. Also, the tool is cross-platform.
Install Czkawka on Ubuntu and other Linux Distributions
Czkawka can be installed on Linux as an AppImage or download and use the precompiled binaries. If you are not sure on using AppImage on Linux, refer to our complete guide on using AppImage on Linux. You can get the installation files from their official release page.
Once downloaded the AppImage/binary, make it executable. You can do this by right-clicking on the file and select properties.
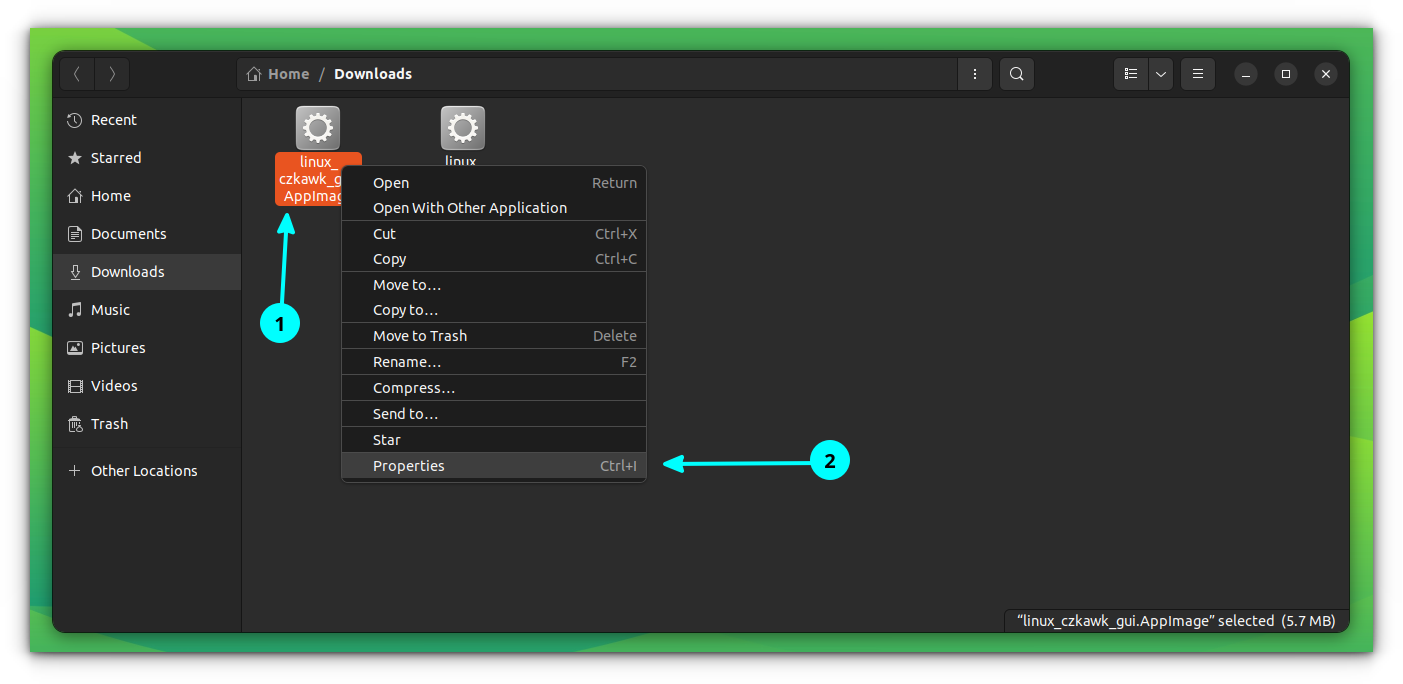
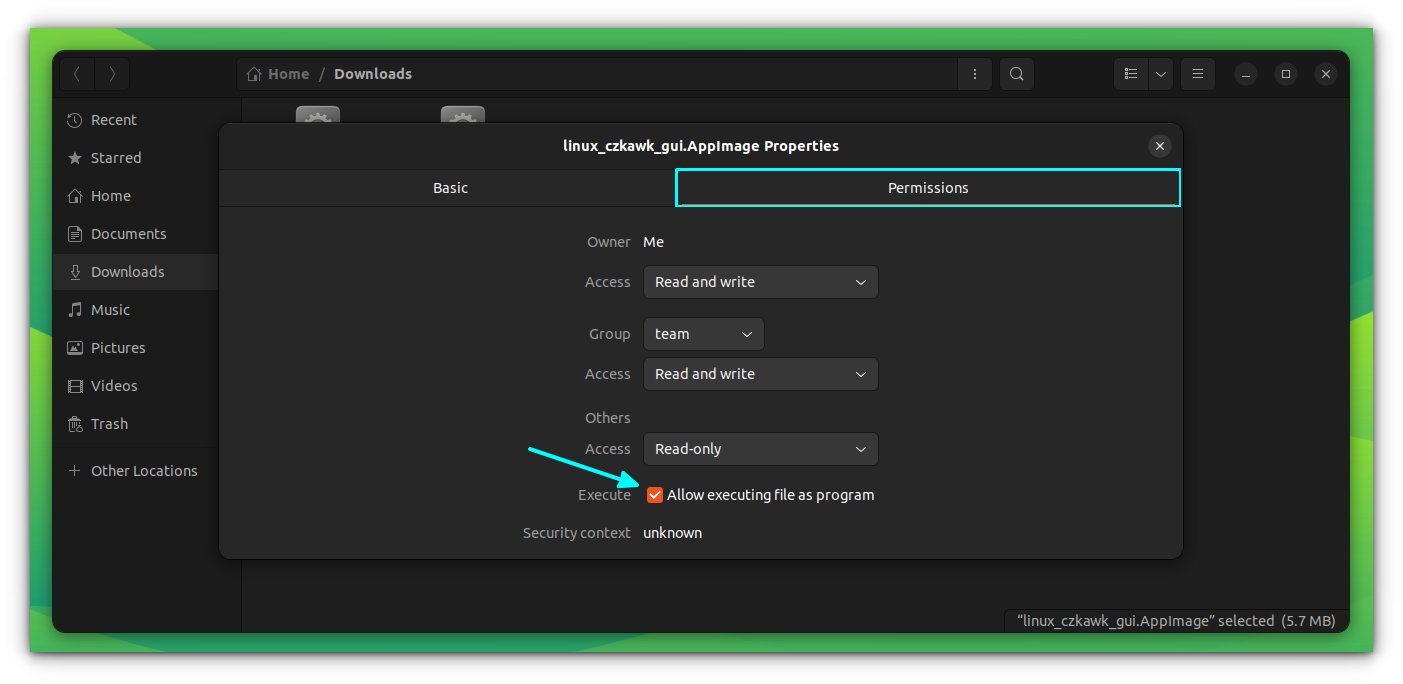
On the “Properties” dialog box, go to permissions and select “Allow executing as program” option as shown in the screenshot below.
Now, open the app by double-clicking on the AppImage file.
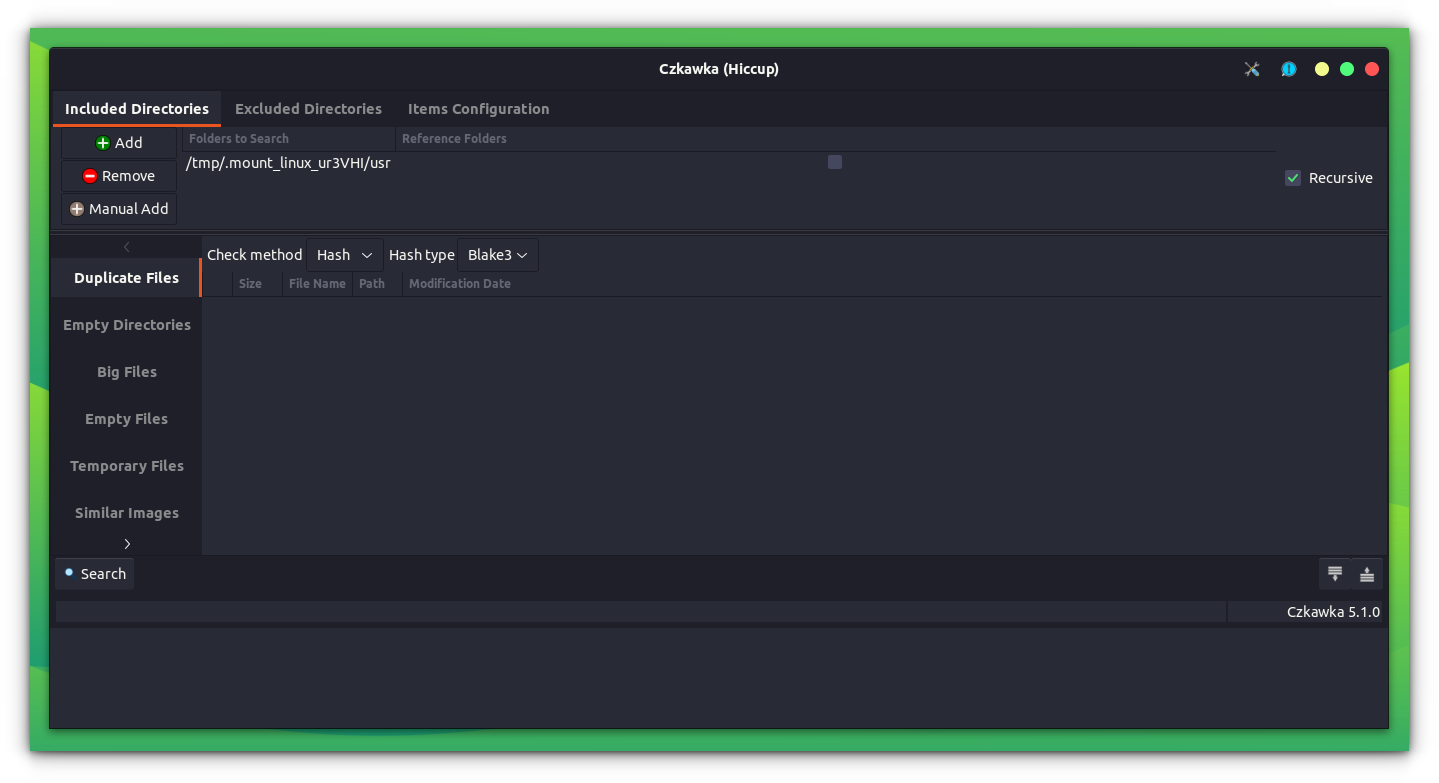
Czkawka includes a number of options to choose from. There are options to find duplicate files, installed packages, big files, temp files, empty directories, bad extensions etc.
Using Czkawka
First, select the Search Path and the task which you want to perform from the left panel. Also, you can set any of the three modes on Czkawka for searching:
- Hash: Find files which have same content.
- Size: Find files which have the same size.
- Name: Find files which have same name.
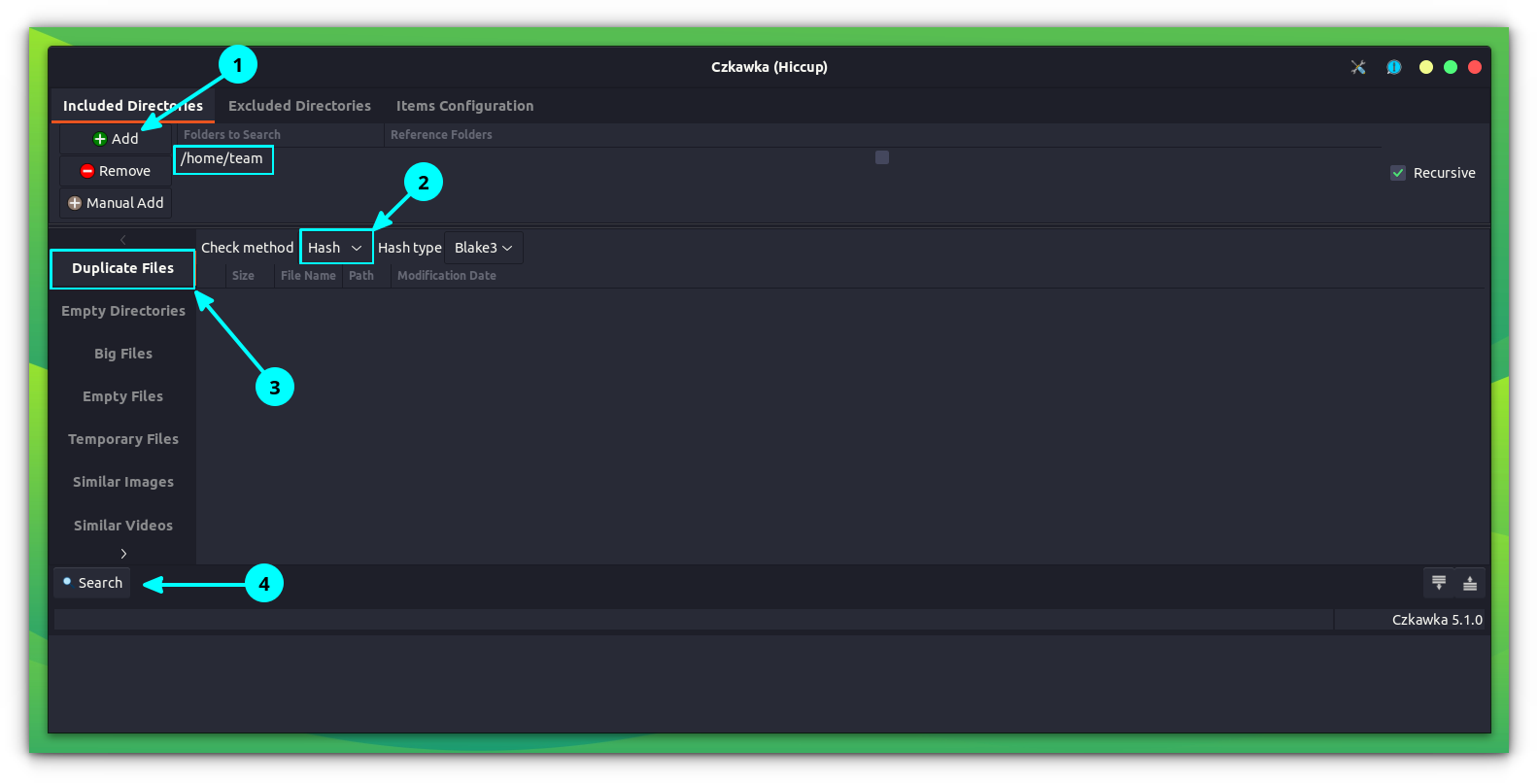
Click on Search to locate the files. Once done, you can select the files you want to remove and delete it.
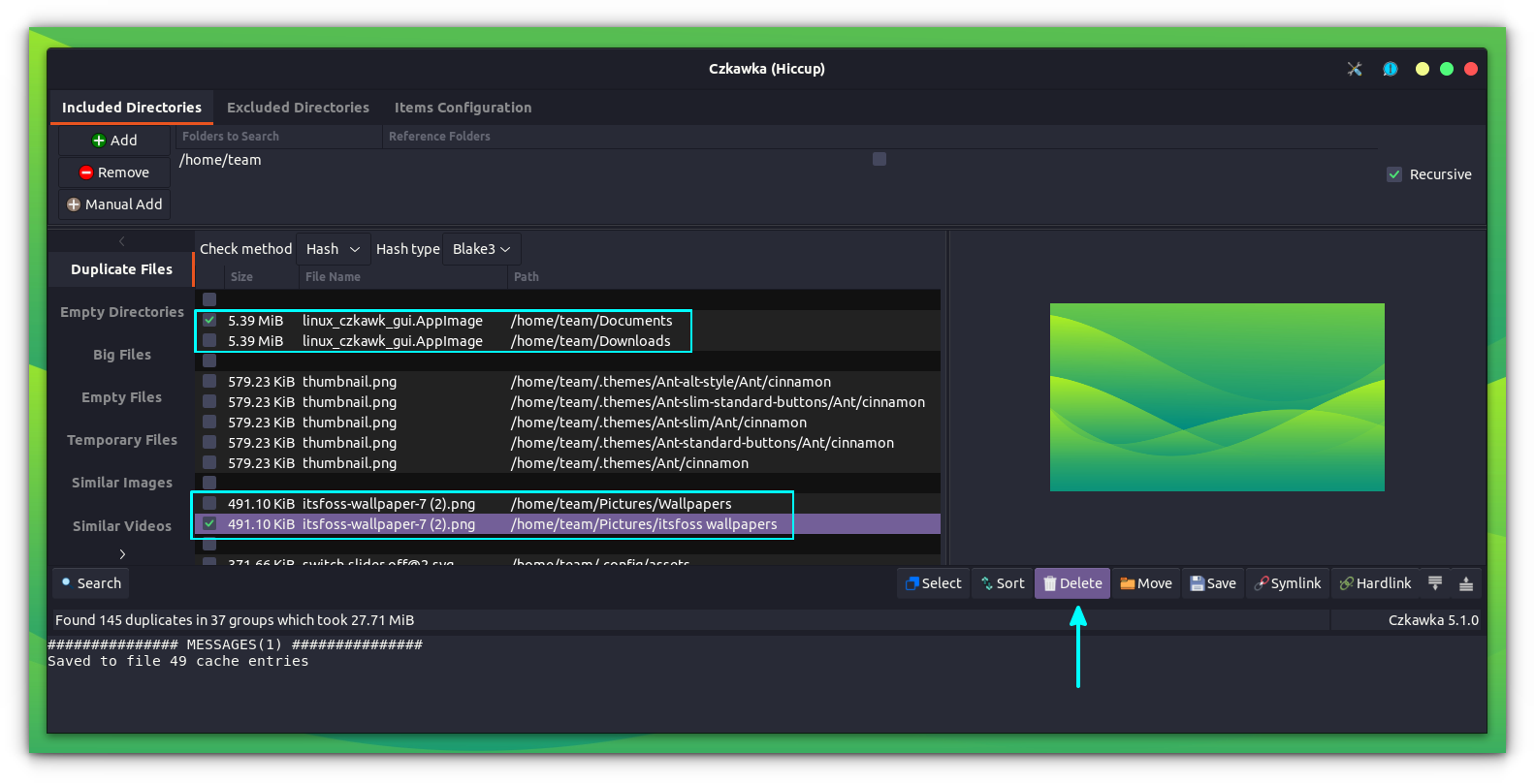
As you can see in the above screenshot, Czkawka groups the duplicate files along with locations. It also offers a preview of the file up on selecting it from the list, on the right side.
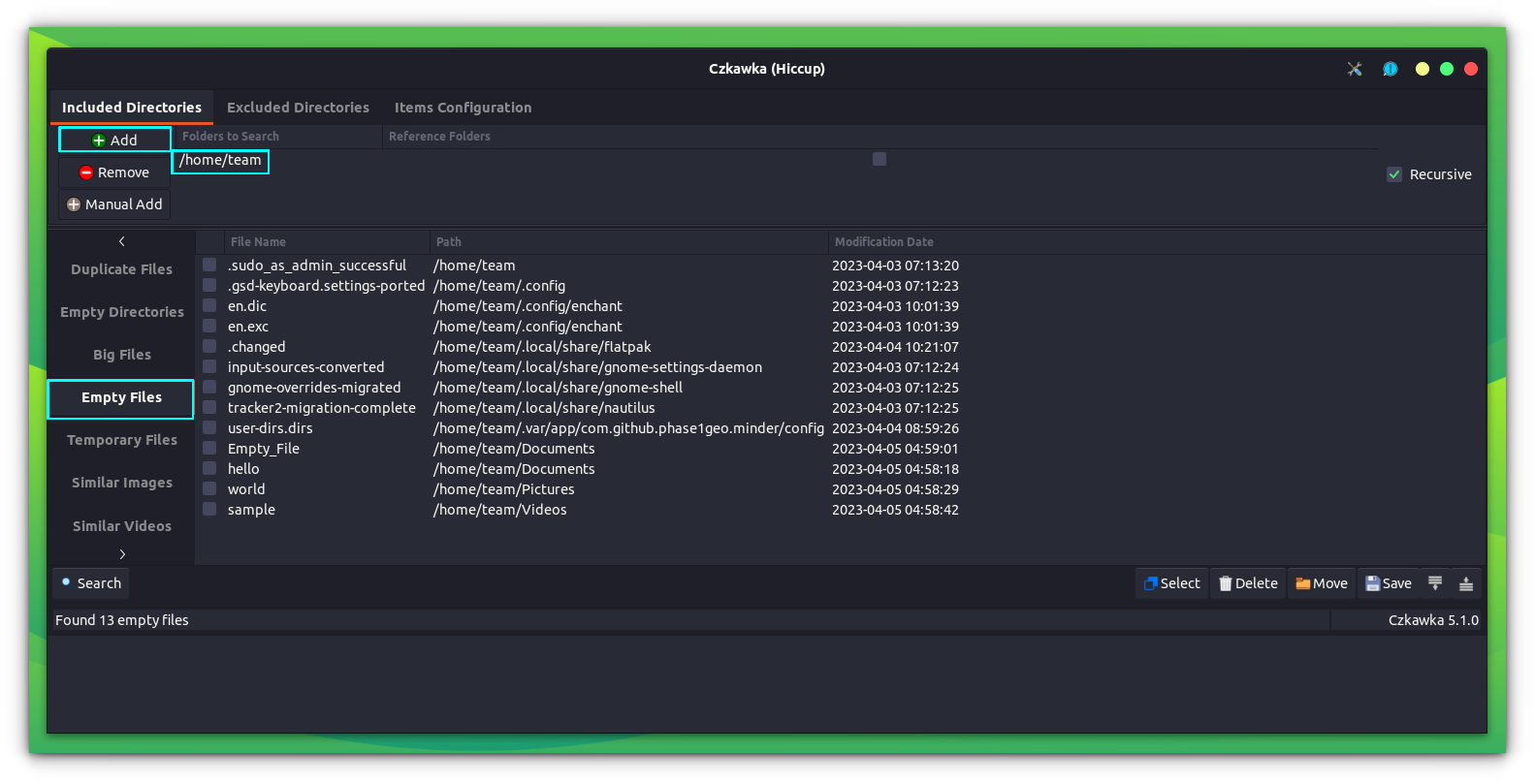
Similarly, you can use the other options to perform various other functions. The below screenshot shows Czkawka detecting empty files.
Other GUI Tools
dupeGuru is another GUI tool, that offers duplicate file detection and removal. It is more simple and minimal compared to Czkawka.
Installing dupeGuru
For Debian/Fedora based distributions, there are .deb/.rpm files available on their downloads page. Check out our article on how to install .deb files on Ubuntu for any help.
Or, you can use the official PPA from dupeGuru team. But the PPA is currently maintained only up to Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. If you have it, then run the following commands to install:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:dupeguru/ppa
sudo apt update
sudo apt install dupeguruUsing DupeGuru
Open dupeGuru from overview, and you can find the necessary option on the home screen itself.
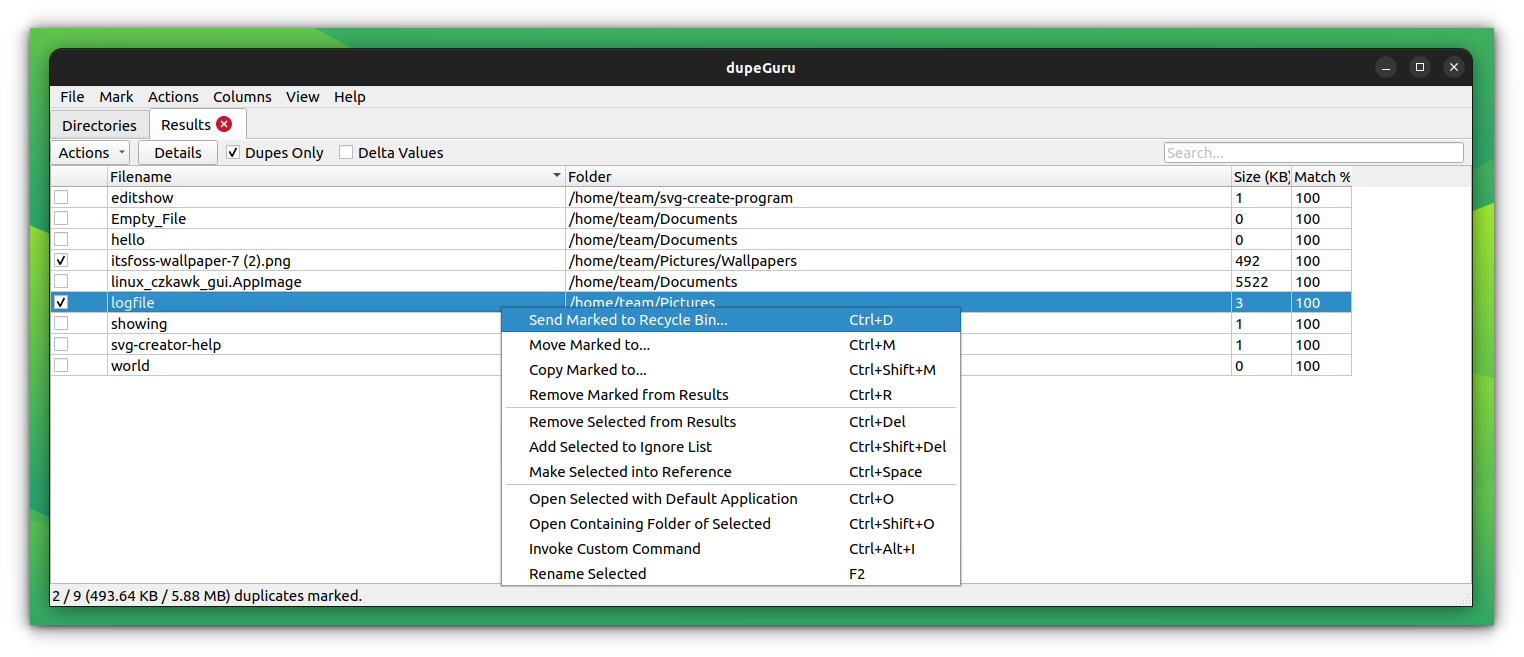
This will give the duplicate file list. We can take several measures like remove, move, copy, rename etc.
Rdfind: CLI tool to find and remove duplicate files
Rdfind or redundant data find, is a command line utility to find and remove duplicate files on Linux. The tool is available to install on Ubuntu through the official repositories. Open a terminal and run:
sudo apt install rdfindUsing Rdfind
There are numerous functions available with rdfind, like search for duplicates, search and remove duplicates etc. In order to search a particular directory to find duplicate files, use the following command:
rdfind <path-to-the -directory>The above command will search the specified path for duplicates and save the list of duplicate files along with location details to a text file, named results.txt.
You can use cat command to view the list of duplicate files so found.

rdfindSimilarly, rdfind offers -deleteduplicates option to remove the duplicate files found. By default, this option is set to false. If you are sure, you want to delete the duplicate files found, use:
rdfind -deleteduplicates true <path-to-required-directory>Upon executing this command, the tool will create a results.txt file, that list the duplicate files in the specified directory, and then deletes the duplicate files.

rdfindYou can cat the results.txt file later to view the duplicate files that were present.
| Important Options available in rdfind | Use |
|---|---|
| -deleteduplicates true|false | Delete duplicate files. Default value is false |
| -outputname name | Specify a different name to the results file |
| -ignoreempty true|false | Ignore empty files. Default value is True |
| -n, -dryrun true|false | Displays what should have been done, don't actually delete or link anything. Default value is false. |
| -minsize N | Ignores files with less than N bytes |
| -maxsize N | Ignores files with N bytes or more. By default, disabled. |
Other CLI Tools
There are a few more tools that let you detect and delete duplicate files.
1. FDUPES
FDUPES is a command line utility to find and remove duplicate files on Linux. It can list out the duplicate files in a particular folder or recursively within a folder. It asks which file to preserve before deletion, and the noprompt option lets you delete all the duplicate files, keeping the first one without asking you.
Installation on Debian / Ubuntu
sudo apt install fdupesOnce installed, you can search duplicate files using the command below:
fdupes /path/to/folderFor recursively searching within a folder, use -r option
fdupes -r /homeThis will only list the duplicate files and do not delete them by itself. You can manually delete the duplicate files or use -d option to delete them interactively.
fdupes -d /path/to/folder
Here, you can mark the files that can be removed. Once you have done marking, enter prune on the prompt. This will delete the selected duplicates. Now, you can exit the prompt by entering exit.
2. Rmlint
Rmlint is an extremely fast tool to remove duplicates and other lint from your filesystem. With this tool, you can find duplicate files & directories, empty files, recursive empty directories, broken symlinks etc.
To Install rmlint on Ubuntu, open a terminal and run:
sudo apt install rmlintYou can use this by running rmlint in any directory. It will list the possibilities, like files that can be removed in that particular directory. Rmlint itself will not delete any files. Also, by default, rmlint will ignore hidden files and will not follow symlinks.
Once the tool is executed, it will save a shell script to the directory where it was used. You can execute this shell script to remove the duplicate files.

For more information about this tool, refer to their official documentation.
Final Words
There are many other ways and tools to find and delete duplicate files on Linux. Personally, I prefer the FDUPES command line tool; it’s simple and does not take much resources.
On a similar topic, I have written about removing duplicate photos in Linux.

How do you deal with the finding and removing duplicate files in your Linux system? Do tell us in the comment section.


